

POJ 3414 - Pots
source link: https://exp-blog.com/algorithm/poj/poj3414-pots/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

POJ 3414
- POJ 3414 - Pots
- Time: 1000MS
- Memory: 65536K
- 难度: 初级
- 分类: BFS
给出了两个瓶子的容量A,B, 以及一个目标水量C,
对A、B可以有如下操作:
- FILL(i): fill the pot i (1 ≤ i ≤ 2) from the tap;
- DROP(i): empty the pot i to the drain;
- POUR(i,j): pour from pot i to pot j; after this operation either the pot j is full (and there may be some water left in the pot i), or the pot i is empty (and all its contents have been moved to the pot j).
问经过哪几个操作后能使得任意一个瓶子的残余水量为C。
若不可能得到则输出impossible
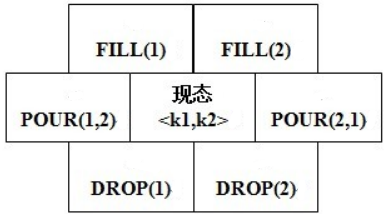
6入口的BFS
把两个两个桶的某个同一时间的状态看做一个整体,视为初态
可对初态进行六种操作,即 FILL(1), FILL(2), DROP(1), DROP(2), POUR(1,2), POUR(2,1)
这6种操作在我的程序中分别用一个整数进行记录:
- 1z0: 清空z瓶子
- 2z0: 装满z瓶子
- 3xy: 从x瓶倒向y瓶
x,y,z∈{1,2}
这样在输出操作时就能根据数字的特点 进行选择性输出 了
这题有两个难点
第一就是要输出得到容量C的过程:
对于BFS的题而言这种要求是非常刁钻的,回溯每一步时很容易就混淆了下标。
解决方法:对于每一步的操作,我们都得对它设置一个pos指针,使它指向前一步操作在 queue[] 队列的下标,即对下标进行回溯,再顺序输出每一步操作。
第二就是状态记录:
怎样记录两个瓶子在同一时间点的状态,又能使得搜索标记时为O(1)的复杂度?
瓶子某时刻的残余水量就是该瓶子的状态,设残余水量为k1 k2
开始时我想对k1 k2进行各种运算组合,但都无法保证k1 k2的运算组合是独一无二的。
最后我决定用 ostringstream 在k1 k2 两个数字之间加上一个逗号,把他们变为字符串string,再利用map进行标记,相当成功。
最后我简单说说各种操作的数学表达式:
设1瓶的容量为v1,残余水量为k1, 2瓶的容量为v2,残余水量为 k2 , 那么:
fill(1)相当于k1=v1fill(2)相当于k2=v2drop(1)相当于k1=0drop(2)相当于k2=0- 对于
Pour(1,2):
若k1+k2<=v2,则k2=k1+k2,k1=0(有先后顺序)
否则k1=k1+k2-v2,k2=v2(有先后顺序) Pour(2,1)亦同理
//Memory Time
//232K 32MS
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int v1,v2; //两个瓶子的容量
int c; //目标残余水量
int k1,k2; //在某状态时两个瓶子的剩余水量,temporary
typedef class
{
public:
int x,y; //当前状态(两个瓶子中的水量)
int pos; //记录前一状态在队列queue中的下标
int step; //当前步数
}process;
//把整数a、b整合为 "a,b" 的字符串形式(不包括引号),用于标记状态
string combAB(int a,int b)
{
string s;
ostringstream oss;
oss<<a;
oss<<',';
oss<<b;
s=oss.str();
oss.str(""); //清空oss对象内所存储的流
return s;
}
void fill(int i)
{
switch(i)
{
case 1: {k1=v1; return;}
case 2: {k2=v2; return;}
}
}
void drop(int i)
{
switch(i)
{
case 1: {k1=0; return;}
case 2: {k2=0; return;}
}
}
void pour(int i,int j)
{
switch(i)
{
case 1: // v1 to v2
{
if(k1+k2<=v2)
{
k2=k1+k2;
k1=0;
}
else
{
k1=k1+k2-v2;
k2=v2;
}
return;
}
case 2: // v2 to v1
{
if(k1+k2<=v1)
{
k1=k1+k2;
k2=0;
}
else
{
k2=k1+k2-v1;
k1=v1;
}
return;
}
}
}
void BFS(void)
{
int operation[1000]={0}; //当前步的操作: 1z0:清空z瓶子 2z0:装满z瓶子 3xy:从x瓶倒向y瓶
map<string,bool>vist;
vist["0,0"]=true;
process queue[1000]; //状态队列
int head,tail;
queue[head=0].x=0;
queue[tail=0].y=0;
queue[tail++].step=0;
string ts; //temporary
while(head<tail)
{
process p=queue[head];
if(p.x==c || p.y==c) //得到要求的剩余水量c
{
cout<<p.step<<endl;
/*下标回溯,输出操作过程*/
int ps=p.step;
int* steps=new int[ps+1]; //从1到p.step顺序记录各步操作的下标,不使用steps[0]
steps[ps--]=tail-1;
while(ps)
{
steps[ps]=queue[ steps[ps+1] ].pos;
ps--;
}
for(int i=1;i<=p.step;i++)
{
int temp=operation[ steps[i]-1 ]; //注意各个数组间的下标关系
switch(temp/100)
{
case 1:
{
cout<<"DROP("<<(temp/10)%10<<')'<<endl;
break;
}
case 2:
{
cout<<"FILL("<<(temp/10)%10<<')'<<endl;
break;
}
case 3:
{
cout<<"POUR("<<(temp/10)%10<<','<<temp%10<<')'<<endl;
break;
}
}
}
delete steps;
return;
}
/*装满v1*/
k1=p.x;
k2=p.y;
fill(1);
ts=combAB(k1,k2);
if(!vist[ts])
{
vist[ts]=true;
queue[tail].x=k1;
queue[tail].y=k2;
queue[tail].step=p.step+1; //当前的操作步数
queue[tail].pos=head; //前一步操作在queue[]中的下标
operation[tail++]=210; //当前的操作
}
/*装满v2*/
k1=p.x;
k2=p.y;
fill(2);
ts=combAB(k1,k2);
if(!vist[ts])
{
vist[ts]=true;
queue[tail].x=k1;
queue[tail].y=k2;
queue[tail].step=p.step+1;
queue[tail].pos=head;
operation[tail++]=220;
}
/*清空v1*/
k1=p.x;
k2=p.y;
drop(1);
ts=combAB(k1,k2);
if(!vist[ts])
{
vist[ts]=true;
queue[tail].x=k1;
queue[tail].y=k2;
queue[tail].step=p.step+1;
queue[tail].pos=head;
operation[tail++]=110;
}
/*清空v2*/
k1=p.x;
k2=p.y;
drop(2);
ts=combAB(k1,k2);
if(!vist[ts])
{
vist[ts]=true;
queue[tail].x=k1;
queue[tail].y=k2;
queue[tail].step=p.step+1;
queue[tail].pos=head;
operation[tail++]=120;
}
/*v1倒向v2*/
k1=p.x;
k2=p.y;
pour(1,2);
ts=combAB(k1,k2);
if(!vist[ts])
{
vist[ts]=true;
queue[tail].x=k1;
queue[tail].y=k2;
queue[tail].step=p.step+1;
queue[tail].pos=head;
operation[tail++]=312;
}
/*v2倒向v1*/
k1=p.x;
k2=p.y;
pour(2,1);
ts=combAB(k1,k2);
if(!vist[ts])
{
vist[ts]=true;
queue[tail].x=k1;
queue[tail].y=k2;
queue[tail].step=p.step+1;
queue[tail].pos=head;
operation[tail++]=321;
}
head++;
}
cout<<"impossible"<<endl;
return;
}
int main(void)
{
while(cin>>v1>>v2>>c)
BFS();
return 0;
}Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK