

Custom health probes with Application Gateway Ingress Controller
source link: https://www.thorsten-hans.com/custom-health-probes-with-application-gateway-ingress-controller/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Custom health probes with Application Gateway Ingress Controller
Published Wed, Feb 16, 2022 / by Thorsten Hans / Estimated reading time: 3 min
With Azure Application Gateway Ingress Controller (AGIC), we can integrate an existing Azure Application Gateway instance with Kubernetes. In Kubernetes, an ingress controller is responsible for routing inbound requests to applications running inside the cluster. AGIC automatically watches Ingress resources inside your cluster and automatically updates the linked instance of Azure Application Gateway upon reconciliation.
Azure Application Gateway uses health probes to determine if the desired backend target can serve requests. Azure Application Gateway won’t send incoming requests to the backend target if a configured health probe fails. Instead, it will respond to the request with an HTTP 502. If the health probe is successful, incoming requests will be forwarded to the desired backend target, responsible for handling the requests and generating proper responses.
Although the Application Gateway is configured automatically, we can customize the health probe configured on Azure Application Gateway from Kubernetes. Currently, AGIC supports three different ways for configuring those health probes:
- Reuse of the pod’s
livenessProbeandreadinessProbe - Explicit health probe configuration by leveraging
Ingressannotations - Relying on the AGIC fallback health probe
Let’s take a look at each of them now.
Reuse of container livenessProbe and readinessProbe
The best way to control health probes in Azure Application Gateway is to define livenessProbe and readinessProbe on the actual Deployment, ReplicaSet, or Pod. During reconciliation, AGIC reads them and uses their values to create the corresponding health probe in your Application Gateway instance. For demonstration purposes, consider having the following Deployment, Service, and Ingress:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: api
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: api
spec:
containers:
- name: api
image: thorstenhans/healthz-api:0.0.1
resources:
limits:
memory: "64Mi"
cpu: "50m"
requests:
memory: "64Mi"
cpu: "50m"
livenessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 20
timeoutSeconds: 5
httpGet:
port: 5000
path: /healthz/liveness
readinessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 5
httpGet:
port: 5000
path: /healthz/readiness
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: api
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: api
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 5000
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: api
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: azure/application-gateway
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: acme-cluster-issuer
labels:
name: api
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- api-sample.thorsten-hans.com
secretName: "api-sample-tls"
rules:
- host: api-sample.thorsten-hans.com
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
path: "/"
backend:
service:
name: api
port:
number: 80
With livenessProbe and readinessProbe in, applying these resources would result in the following Azure Application Gateway health probe:
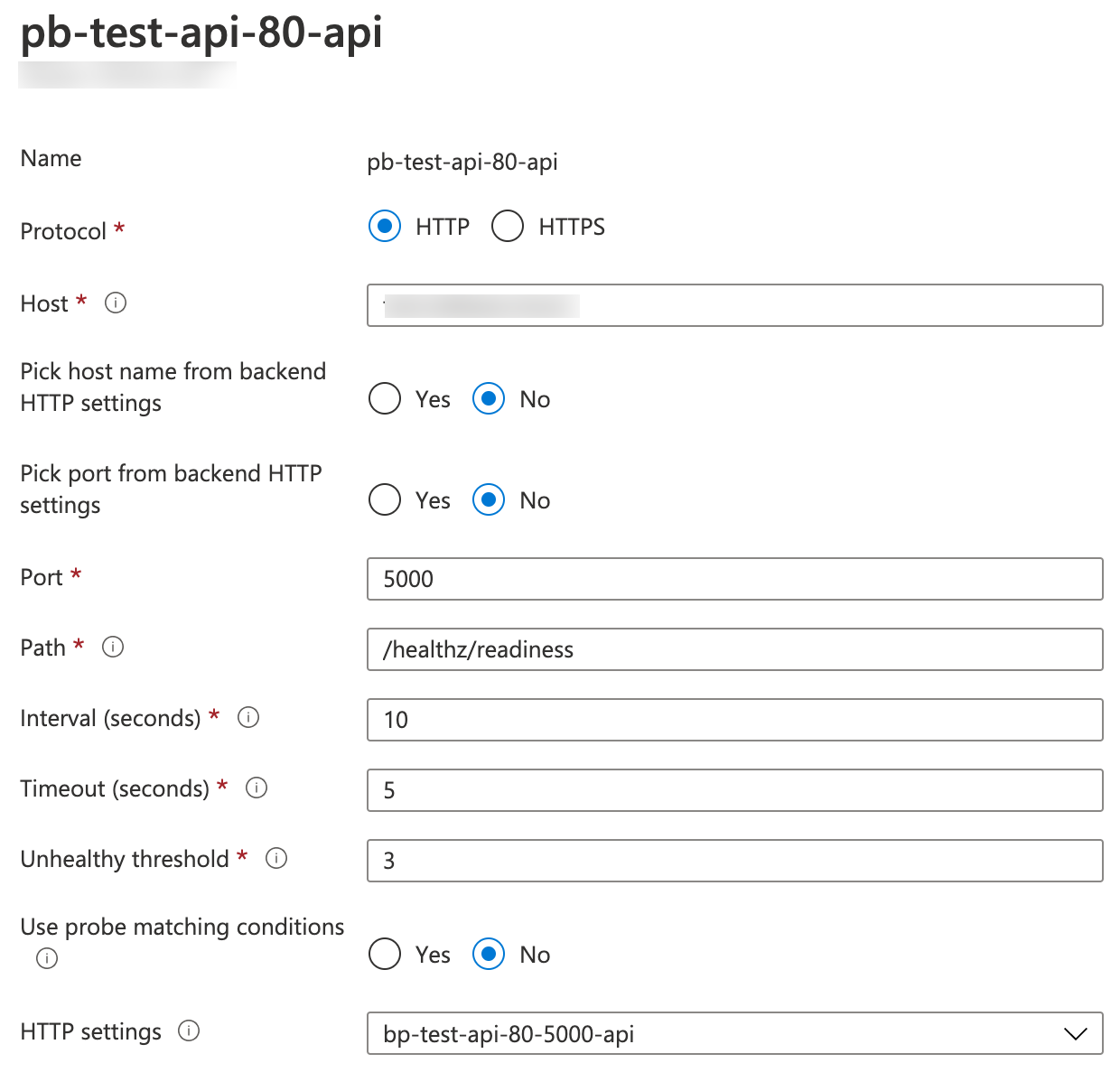
Reuse of readinessProbe as health probe in Azure Application Gateway
If both readinessProbe and livenessProbe are specified, AGIC will use readinessProbe to configure the health probe in Application Gateway.
Explicit health probe configuration by leveraging Ingress annotations
AGIC watches Ingress resources in your Kubernetes cluster that are annotated with kubernetes.io/ingress.class: azure/application-gateway. We can extend the Ingress resource and provide additional annotations to control the health probe that AGIC will configure in Azure Application Gateway. The following snippet shows how to instruct Azure Application Gateway to send an HTTP GET request to /healthz/configured-with-annotations every 45 seconds.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: api
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: azure/application-gateway
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: acme-cluster-issuer
appgw.ingress.kubernetes.io/health-probe-path: /healthz/liveness
appgw.ingress.kubernetes.io/health-probe-interval: "45"
labels:
name: api
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- api-sample.thorsten-hans.com
secretName: "api-sample-tls"
rules:
- host: api-sample.thorsten-hans.com
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
path: "/"
backend:
service:
name: api
port:
number: 80
AGIC supports a bunch of annotations on Ingress resources. See the list of all annotations in ingress_annotations.go here. Once you have applied the Ingress modifications with kubectl apply -f your-ingress-file.yml and AGIC reconciliation has finished, you should see the modified health probe in Azure Application Gateway:
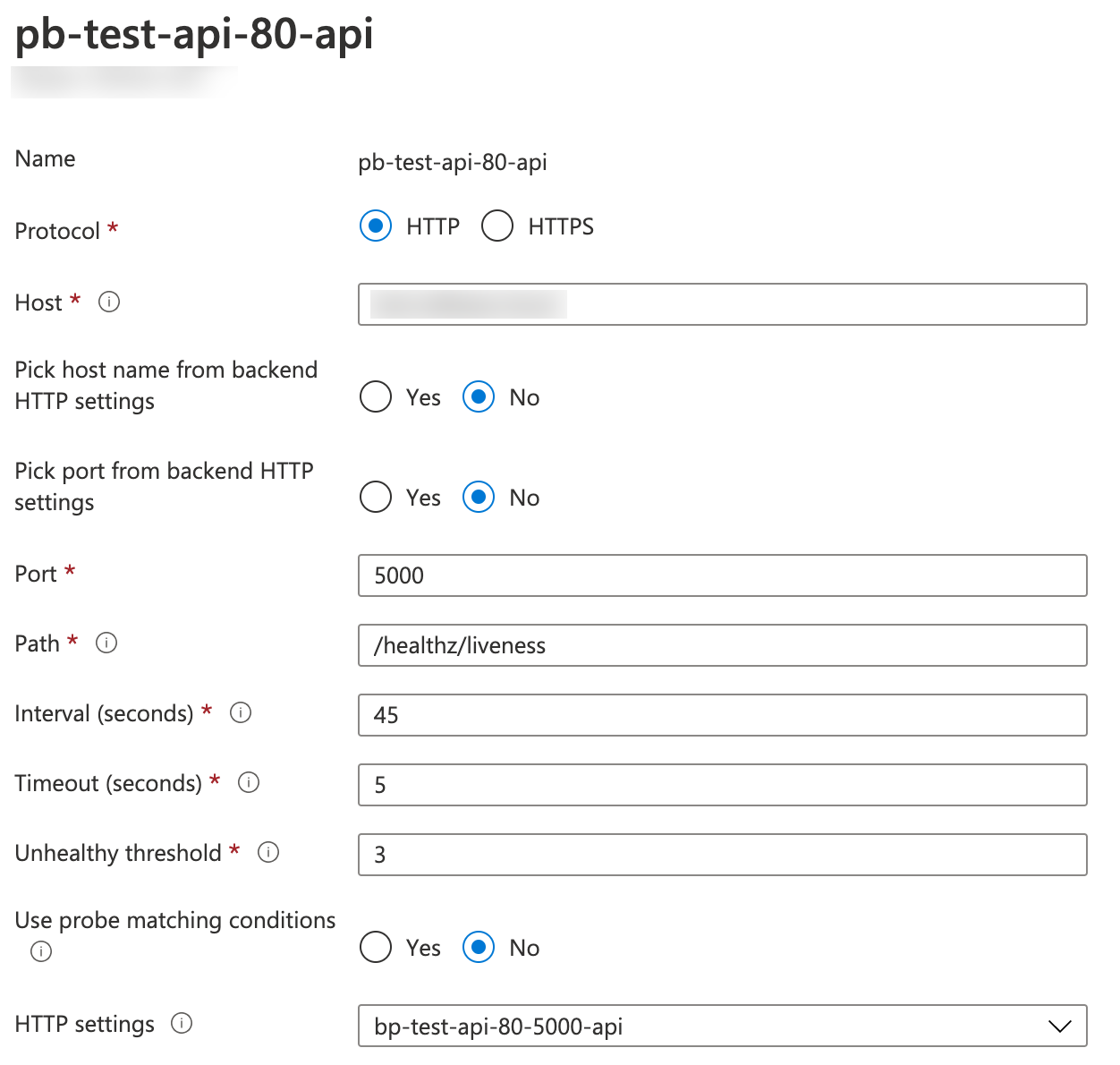
The annotation based health probe in Azure Application Gateway
Relying on the AGIC fallback health probe
If we neither specify custom probes (readinessProbe or livenessProbe) nor provide a custom configuration using Ingress annotations, AGIC instructs Azure Application Gateway to send an HTTP GET request to the root route (/) every 30 seconds for determining the health of the particular backend. Again let’s take a look at a small sample:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: api
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: api
spec:
containers:
- name: api
image: thorstenhans/healthz-api:0.0.1
resources:
limits:
memory: "64Mi"
cpu: "50m"
requests:
memory: "64Mi"
cpu: "50m"
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: api
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: api
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 5000
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: api
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: azure/application-gateway
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: acme-cluster-issuer
labels:
name: api
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- api-sample.thorsten-hans.com
secretName: "api-sample-tls"
rules:
- host: api-sample.thorsten-hans.com
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
path: "/"
backend:
service:
name: api
port:
number: 80
Once deployed, you should see Azure Application Gateway using the fallback health probe as shown in the following figure:
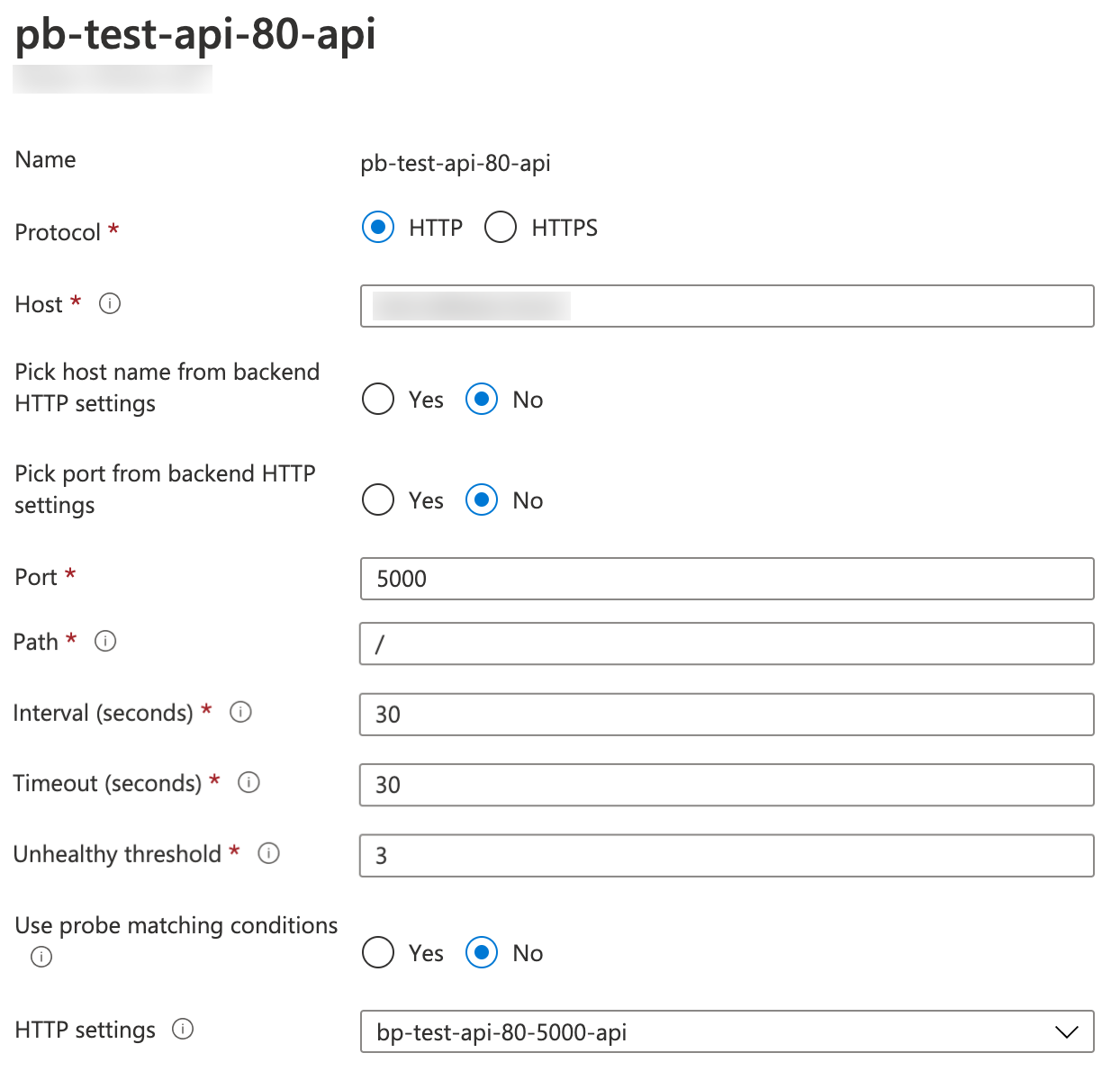
The fallback health probe in Azure Application Gateway
Azure Application Gateway health probe determination order
If you’re using AGIC to get your Azure Application Gateway configured automatically, keep the determination order for health probes in mind.
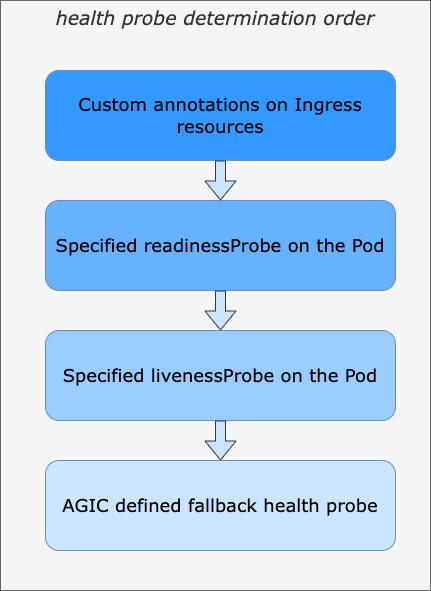
Application Gateway health probe determination order
Recap
Suppose you’re running Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) and want to integrate your applications running within AKS seamlessly with your virtual network infrastructure. In that case, you may want to use Azure Application Gateway Ingress Controller (AGIC) in favor of other (even more popular) ingress controllers.
Being able to fine-tune Application Gateway health probes while still having AGIC managing the entire Application Gateway configuration automatically is the key to preventing your HTTP requests from resulting in responses with an HTTP 502 status code.
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK