

彻底搞懂 Kubernetes 中的 Events
source link: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/451177868
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

彻底搞懂 Kubernetes 中的 Events
大家好,我是张晋涛。
之前我写了一篇《更优雅的 Kubernetes 集群事件度量方案》,利用 Jaeger 利用 tracing 的方式来采集 Kubernetes 集群中的 events 并进行展示。最终效果如下:
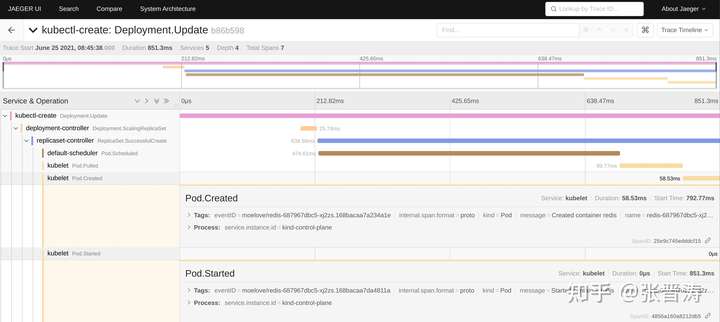
写那篇文章的时候,立了个 flag 要详细介绍下其中的原理,鸽了很久,现在年底了,也该发出来了。
Eents 概览
我们先来做个简单的示例,来看看 Kubernetes 集群中的 events 是什么。
创建一个新的名叫 moelove 的 namespace ,然后在其中创建一个叫做 redis 的 deployment。接下来查看这个 namespace 中的所有 events。
(MoeLove) ➜ kubectl create ns moelove
namespace/moelove created
(MoeLove) ➜ kubectl -n moelove create deployment redis --image=ghcr.io/moelove/redis:alpine
deployment.apps/redis created
(MoeLove) ➜ kubectl -n moelove get deploy
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
redis 1/1 1 1 11s
(MoeLove) ➜ kubectl -n moelove get events
LAST SEEN TYPE REASON OBJECT MESSAGE
21s Normal Scheduled pod/redis-687967dbc5-27vmr Successfully assigned moelove/redis-687967dbc5-27vmr to kind-worker3
21s Normal Pulling pod/redis-687967dbc5-27vmr Pulling image "ghcr.io/moelove/redis:alpine"
15s Normal Pulled pod/redis-687967dbc5-27vmr Successfully pulled image "ghcr.io/moelove/redis:alpine" in 6.814310968s
14s Normal Created pod/redis-687967dbc5-27vmr Created container redis
14s Normal Started pod/redis-687967dbc5-27vmr Started container redis
22s Normal SuccessfulCreate replicaset/redis-687967dbc5 Created pod: redis-687967dbc5-27vmr
22s Normal ScalingReplicaSet deployment/redis Scaled up replica set redis-687967dbc5 to 1
但是我们会发现默认情况下 kubectl get events 并没有按照 events 发生的顺序进行排列,所以我们往往需要为其增加 --sort-by='{.metadata.creationTimestamp}' 参数来让其输出可以按时间进行排列。
这也是为何 Kubernetes v1.23 版本中会新增 kubectl alpha events 命令的原因。我在之前的文章《K8S 生态周报| Kubernetes v1.23.0 正式发布,新特性一览》中已进行了详细的介绍,这里就不展开了。
按时间排序后可以看到如下结果:
(MoeLove) ➜ kubectl -n moelove get events --sort-by='{.metadata.creationTimestamp}'
LAST SEEN TYPE REASON OBJECT MESSAGE
2m12s Normal Scheduled pod/redis-687967dbc5-27vmr Successfully assigned moelove/redis-687967dbc5-27vmr to kind-worker3
2m13s Normal SuccessfulCreate replicaset/redis-687967dbc5 Created pod: redis-687967dbc5-27vmr
2m13s Normal ScalingReplicaSet deployment/redis Scaled up replica set redis-687967dbc5 to 1
2m12s Normal Pulling pod/redis-687967dbc5-27vmr Pulling image "ghcr.io/moelove/redis:alpine"
2m6s Normal Pulled pod/redis-687967dbc5-27vmr Successfully pulled image "ghcr.io/moelove/redis:alpine" in 6.814310968s
2m5s Normal Created pod/redis-687967dbc5-27vmr Created container redis
2m5s Normal Started pod/redis-687967dbc5-27vmr Started container redis
通过以上的操作,我们可以发现 events 实际上是 Kubernetes 集群中的一种资源。当 Kubernetes 集群中资源状态发生变化时,可以产生新的 events。
深入 Events
单个 Event 对象
既然 events 是 Kubernetes 集群中的一种资源,正常情况下它的 metadata.name 中应该包含其名称,用于进行单独操作。所以我们可以使用如下命令输出其 name :
(MoeLove) ➜ kubectl -n moelove get events --sort-by='{.metadata.creationTimestamp}' -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{"\n"}{end}'
redis-687967dbc5-27vmr.16c4fb7bde8c69d2
redis-687967dbc5.16c4fb7bde6b54c4
redis.16c4fb7bde1bf769
redis-687967dbc5-27vmr.16c4fb7bf8a0ab35
redis-687967dbc5-27vmr.16c4fb7d8ecaeff8
redis-687967dbc5-27vmr.16c4fb7d99709da9
redis-687967dbc5-27vmr.16c4fb7d9be30c06
选择其中的任意一条 event 记录,将其输出为 YAML 格式进行查看:
(MoeLove) ➜ kubectl -n moelove get events redis-687967dbc5-27vmr.16c4fb7bde8c69d2 -o yaml
action: Binding
apiVersion: v1
eventTime: "2021-12-28T19:31:13.702987Z"
firstTimestamp: null
involvedObject:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
name: redis-687967dbc5-27vmr
namespace: moelove
resourceVersion: "330230"
uid: 71b97182-5593-47b2-88cc-b3f59618c7aa
kind: Event
lastTimestamp: null
message: Successfully assigned moelove/redis-687967dbc5-27vmr to kind-worker3
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2021-12-28T19:31:13Z"
name: redis-687967dbc5-27vmr.16c4fb7bde8c69d2
namespace: moelove
resourceVersion: "330235"
uid: e5c03126-33b9-4559-9585-5e82adcd96b0
reason: Scheduled
reportingComponent: default-scheduler
reportingInstance: default-scheduler-kind-control-plane
source: {}
type: Normal
可以看到其中包含了很多信息, 这里我们先不展开。我们看另一个例子。
kubectl describe 中的 Events
我们可以分别对 Deployment 对象和 Pod 对象执行 describe 的操作,可以得到如下结果(省略掉了中间输出):
- 对 Deployment 操作
(MoeLove) ➜ kubectl -n moelove describe deploy/redis
Name: redis
Namespace: moelove
...
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 15m deployment-controller Scaled up replica set redis-687967dbc5 to 1
- 对 Pod 操作
(MoeLove) ➜ kubectl -n moelove describe pods redis-687967dbc5-27vmr
Name: redis-687967dbc5-27vmr
Namespace: moelove
Priority: 0
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 18m default-scheduler Successfully assigned moelove/redis-687967dbc5-27vmr to kind-worker3
Normal Pulling 18m kubelet Pulling image "ghcr.io/moelove/redis:alpine"
Normal Pulled 17m kubelet Successfully pulled image "ghcr.io/moelove/redis:alpine" in 6.814310968s
Normal Created 17m kubelet Created container redis
Normal Started 17m kubelet Started container redis
我们可以发现 对不同的资源对象进行 describe 的时候,能看到的 events 内容都是与自己有直接关联的。在 describe Deployment 的时候,看不到 Pod 相关的 Events 。
这说明, Event 对象中是包含它所描述的资源对象的信息的,它们是有直接联系的。
结合前面我们看到的单个 Event 对象,我们发现 involvedObject 字段中内容就是与该 Event 相关联的资源对象的信息。
更进一步了解 Events
我们来看看如下的示例,创建一个 Deployment ,但是使用一个不存在的镜像:
(MoeLove) ➜ kubectl -n moelove create deployment non-exist --image=ghcr.io/moelove/non-exist
deployment.apps/non-exist created
(MoeLove) ➜ kubectl -n moelove get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
non-exist-d9ddbdd84-tnrhd 0/1 ErrImagePull 0 11s
redis-687967dbc5-27vmr 1/1 Running 0 26m
我们可以看到当前的 Pod 处于一个 ErrImagePull 的状态。查看当前 namespace 中的 events (我省略掉了之前 deploy/redis 的记录)
(MoeLove) ➜ kubectl -n moelove get events --sort-by='{.metadata.creationTimestamp}'
LAST SEEN TYPE REASON OBJECT MESSAGE
35s Normal SuccessfulCreate replicaset/non-exist-d9ddbdd84 Created pod: non-exist-d9ddbdd84-tnrhd
35s Normal ScalingReplicaSet deployment/non-exist Scaled up replica set non-exist-d9ddbdd84 to 1
35s Normal Scheduled pod/non-exist-d9ddbdd84-tnrhd Successfully assigned moelove/non-exist-d9ddbdd84-tnrhd to kind-worker3
17s Warning Failed pod/non-exist-d9ddbdd84-tnrhd Error: ErrImagePull
17s Warning Failed pod/non-exist-d9ddbdd84-tnrhd Failed to pull image "ghcr.io/moelove/non-exist": rpc error: code = Unknown desc = failed to pull and unpack image "ghcr.io/moelove/non-exist:latest": failed to resolve reference "ghcr.io/moelove/non-exist:latest": failed to authorize: failed to fetch anonymous token: unexpected status: 403 Forbidden
18s Normal Pulling pod/non-exist-d9ddbdd84-tnrhd Pulling image "ghcr.io/moelove/non-exist"
4s Warning Failed pod/non-exist-d9ddbdd84-tnrhd Error: ImagePullBackOff
4s Normal BackOff pod/non-exist-d9ddbdd84-tnrhd Back-off pulling image "ghcr.io/moelove/non-exist"
对这个 Pod 执行 describe 操作:
(MoeLove) ➜ kubectl -n moelove describe pods non-exist-d9ddbdd84-tnrhd
...
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 4m default-scheduler Successfully assigned moelove/non-exist-d9ddbdd84-tnrhd to kind-worker3
Normal Pulling 2m22s (x4 over 3m59s) kubelet Pulling image "ghcr.io/moelove/non-exist"
Warning Failed 2m21s (x4 over 3m59s) kubelet Failed to pull image "ghcr.io/moelove/non-exist": rpc error: code = Unknown desc = failed to pull and unpack image "ghcr.io/moelove/non-exist:latest": failed to resolve reference "ghcr.io/moelove/non-exist:latest": failed to authorize: failed to fetch anonymous token: unexpected status: 403 Forbidden
Warning Failed 2m21s (x4 over 3m59s) kubelet Error: ErrImagePull
Warning Failed 2m9s (x6 over 3m58s) kubelet Error: ImagePullBackOff
Normal BackOff 115s (x7 over 3m58s) kubelet Back-off pulling image "ghcr.io/moelove/non-exist"
我们可以发现,这里的输出和之前正确运行 Pod 的不一样。最主要的区别在与 Age 列。这里我们看到了类似 115s (x7 over 3m58s) 这样的输出。
它的含义表示: 该类型的 event 在 3m58s 中已经发生了 7 次,最近的一次发生在 115s 之前
但是当我们去直接 kubectl get events 的时候,我们并没有看到有 7 次重复的 event 。这说明 Kubernetes 会自动将重复的 events 进行合并。
选择最后一条 Events (方法前面内容已经讲了) 并将其内容使用 YAML 格式进行输出:
(MoeLove) ➜ kubectl -n moelove get events non-exist-d9ddbdd84-tnrhd.16c4fce570cfba46 -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
count: 43
eventTime: null
firstTimestamp: "2021-12-28T19:57:06Z"
involvedObject:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: spec.containers{non-exist}
kind: Pod
name: non-exist-d9ddbdd84-tnrhd
namespace: moelove
resourceVersion: "333366"
uid: 33045163-146e-4282-b559-fec19a189a10
kind: Event
lastTimestamp: "2021-12-28T18:07:14Z"
message: Back-off pulling image "ghcr.io/moelove/non-exist"
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2021-12-28T19:57:06Z"
name: non-exist-d9ddbdd84-tnrhd.16c4fce570cfba46
namespace: moelove
resourceVersion: "334638"
uid: 60708be0-23b9-481b-a290-dd208fed6d47
reason: BackOff
reportingComponent: ""
reportingInstance: ""
source:
component: kubelet
host: kind-worker3
type: Normal
这里我们可以看到其字段中包括一个 count 字段,表示同类 event 发生了多少次。以及 firstTimestamp 和 lastTimestamp 分别表示了这个 event 首次出现了最近一次出现的时间。这样也就解释了前面的输出中 events 持续的周期了。
彻底搞懂 Events
以下内容是从 Events 中随便选择的一条,我们可以看到它包含的一些字段信息:
apiVersion: v1
count: 1
eventTime: null
firstTimestamp: "2021-12-28T19:31:13Z"
involvedObject:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: ReplicaSet
name: redis-687967dbc5
namespace: moelove
resourceVersion: "330227"
uid: 11e98a9d-9062-4ccb-92cb-f51cc74d4c1d
kind: Event
lastTimestamp: "2021-12-28T19:31:13Z"
message: 'Created pod: redis-687967dbc5-27vmr'
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2021-12-28T19:31:13Z"
name: redis-687967dbc5.16c4fb7bde6b54c4
namespace: moelove
resourceVersion: "330231"
uid: 8e37ec1e-b3a1-420c-96d4-3b3b2995c300
reason: SuccessfulCreate
reportingComponent: ""
reportingInstance: ""
source:
component: replicaset-controller
type: Normal
其中主要字段的含义如下:
- count: 表示当前同类的事件发生了多少次 (前面已经介绍)
- involvedObject: 与此 event 有直接关联的资源对象 (前面已经介绍) , 结构如下:
type ObjectReference struct {
Kind string
Namespace string
Name string
UID types.UID
APIVersion string
ResourceVersion string
FieldPath string
}
- source: 直接关联的组件, 结构如下:
type EventSource struct {
Component string
Host string
}
- reason: 简单的总结(或者一个固定的代码),比较适合用于做筛选条件,主要是为了让机器可读,当前有超过 50 种这样的代码;
- message: 给一个更易让人读懂的详细说明
- type: 当前只有
Normal和Warning两种类型, 源码中也分别写了其含义:
// staging/src/k8s.io/api/core/v1/types.go
const (
// Information only and will not cause any problems
EventTypeNormal string = "Normal"
// These events are to warn that something might go wrong
EventTypeWarning string = "Warning"
)
所以,当我们将这些 Events 都作为 tracing 的 span 采集回来后,就可以按照其 source 进行分类,按 involvedObject 进行关联,按时间进行排序了。
总结
在这篇文章中,我主要通过两个示例,一个正确部署的 Deploy,以及一个使用不存在镜像部署的 Deploy,深入的介绍了 Events 对象的实际的作用及其各个字段的含义。
对于 Kubernetes 而言,Events 中包含了很多有用的信息,但是这些信息却并不会对 Kubernetes 造成什么影响,它们也并不是实际的 Kubernetes 的日志。默认情况下 Kubernetes 中的日志在 1 小时后就会被清理掉,以便释放对 etcd 的资源占用。
所以为了能更好的让集群管理员知道发生了什么,在生产环境中,我们通常会把 Kubernetes 集群的 events 也给采集回来。我个人比较推荐的工具是: https://github.com/opsgenie/kubernetes-event-exporter
当然你也可以按照我之前的文章 《更优雅的 Kubernetes 集群事件度量方案》,利用 Jaeger 利用 tracing 的方式来采集 Kubernetes 集群中的 events 并进行展示。
欢迎订阅我的文章公众号【MoeLove】
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK