

30个类手写Spring核心原理之MVC映射功能(4)
source link: https://my.oschina.net/gupaoedutom/blog/5359516
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
本文节选自《Spring 5核心原理》
接下来我们来完成MVC模块的功能,应该不需要再做说明。Spring MVC的入口就是从DispatcherServlet开始的,而前面的章节中已完成了web.xml的基础配置。下面就从DispatcherServlet开始添砖加瓦。
1 MVC顶层设计
1.1 GPDispatcherServlet
我们已经了解到Servlet的生命周期由init()到service()再到destory()组成,destory()方法我们不做实现。前面我们讲过,这是J2EE中模板模式的典型应用。下面先定义好全局变量:
package com.tom.spring.formework.webmvc.servlet;
import com.tom.spring.formework.annotation.GPController;
import com.tom.spring.formework.annotation.GPRequestMapping;
import com.tom.spring.formework.context.GPApplicationContext;
import com.tom.spring.formework.webmvc.*;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
//Servlet只是作为一个MVC的启动入口
@Slf4j
public class GPDispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
private final String LOCATION = "contextConfigLocation";
//读者可以思考一下这样设计的经典之处
//GPHandlerMapping最核心的设计,也是最经典的
//它直接干掉了Struts、Webwork等MVC框架
private List<GPHandlerMapping> handlerMappings = new ArrayList<GPHandlerMapping>();
private Map<GPHandlerMapping,GPHandlerAdapter> handlerAdapters = new HashMap<GPHandlerMapping, GPHandlerAdapter>();
private List<GPViewResolver> viewResolvers = new ArrayList<GPViewResolver>();
private GPApplicationContext context;
}
下面实现init()方法,我们主要完成IoC容器的初始化和Spring MVC九大组件的初始化。
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
//相当于把IoC容器初始化了
context = new GPApplicationContext(config.getInitParameter(LOCATION));
initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(GPApplicationContext context) {
//有九种策略
//针对每个用户请求,都会经过一些处理策略处理,最终才能有结果输出
//每种策略可以自定义干预,但是最终的结果都一致
// ============= 这里说的就是传说中的九大组件 ================
initMultipartResolver(context);//文件上传解析,如果请求类型是multipart,将通过MultipartResolver进行文件上传解析
initLocaleResolver(context);//本地化解析
initThemeResolver(context);//主题解析
/** 我们自己会实现 */
//GPHandlerMapping 用来保存Controller中配置的RequestMapping和Method的对应关系
initHandlerMappings(context);//通过HandlerMapping将请求映射到处理器
/** 我们自己会实现 */
//HandlerAdapters 用来动态匹配Method参数,包括类转换、动态赋值
initHandlerAdapters(context);//通过HandlerAdapter进行多类型的参数动态匹配
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);//如果执行过程中遇到异常,将交给HandlerExceptionResolver来解析
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);//直接将请求解析到视图名
/** 我们自己会实现 */
//通过ViewResolvers实现动态模板的解析
//自己解析一套模板语言
initViewResolvers(context);//通过viewResolver将逻辑视图解析到具体视图实现
initFlashMapManager(context);//Flash映射管理器
}
private void initFlashMapManager(GPApplicationContext context) {}
private void initRequestToViewNameTranslator(GPApplicationContext context) {}
private void initHandlerExceptionResolvers(GPApplicationContext context) {}
private void initThemeResolver(GPApplicationContext context) {}
private void initLocaleResolver(GPApplicationContext context) {}
private void initMultipartResolver(GPApplicationContext context) {}
//将Controller中配置的RequestMapping和Method进行一一对应
private void initHandlerMappings(GPApplicationContext context) {
//按照我们通常的理解应该是一个Map
//Map<String,Method> map;
//map.put(url,Method)
//首先从容器中获取所有的实例
String [] beanNames = context.getBeanDefinitionNames();
try {
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
//到了MVC层,对外提供的方法只有一个getBean()方法
//返回的对象不是BeanWrapper,怎么办?
Object controller = context.getBean(beanName);
//Object controller = GPAopUtils.getTargetObject(proxy);
Class<?> clazz = controller.getClass();
if (!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(GPController.class)) {
continue;
}
String baseUrl = "";
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(GPRequestMapping.class)) {
GPRequestMapping requestMapping = clazz.getAnnotation(GPRequestMapping.class);
baseUrl = requestMapping.value();
}
//扫描所有的public类型的方法
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (!method.isAnnotationPresent(GPRequestMapping.class)) {
continue;
}
GPRequestMapping requestMapping = method.getAnnotation(GPRequestMapping.class);
String regex = ("/" + baseUrl + requestMapping.value().replaceAll("\\*", ".*")).replaceAll("/+", "/");
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
this.handlerMappings.add(new GPHandlerMapping(pattern, controller, method));
log.info("Mapping: " + regex + " , " + method);
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void initHandlerAdapters(GPApplicationContext context) {
//在初始化阶段,我们能做的就是,将这些参数的名字或者类型按一定的顺序保存下来
//因为后面用反射调用的时候,传的形参是一个数组
//可以通过记录这些参数的位置index,逐个从数组中取值,这样就和参数的顺序无关了
for (GPHandlerMapping handlerMapping : this.handlerMappings){
//每个方法有一个参数列表,这里保存的是形参列表
this.handlerAdapters.put(handlerMapping,new GPHandlerAdapter());
}
}
private void initViewResolvers(GPApplicationContext context) {
//在页面中输入http://localhost/first.html
//解决页面名字和模板文件关联的问题
String templateRoot = context.getConfig().getProperty("templateRoot");
String templateRootPath = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource (templateRoot).getFile();
File templateRootDir = new File(templateRootPath);
for (File template : templateRootDir.listFiles()) {
this.viewResolvers.add(new GPViewResolver(templateRoot));
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们只实现了九大组件中的三大核心组件的基本功能,分别是HandlerMapping、HandlerAdapter、ViewResolver,完成MVC最核心的调度功能。其中HandlerMapping就是策略模式的应用,用输入URL间接调用不同的Method已达到获取结果的目的。顾名思义,HandlerAdapter应用的是适配器模式,将Request的字符型参数自动适配为Method的Java实参,主要实现参数列表自动适配和类型转换功能。ViewResolver也算一种策略,根据不同的请求选择不同的模板引擎来进行页面的渲染。 接下来看service()方法,它主要负责接收请求,得到Request和Response对象。在Servlet子类中service()方法被拆分成doGet()方法和doPost()方法。我们在doGet()方法中直接调用doPost()方法,在doPost()方法中调用doDispatch()方法,真正的调用逻辑由doDispatch()来执行。
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req,resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
doDispatch(req, resp);
}catch (Exception e){
resp.getWriter().write("<font size='25' color='blue'>500 Exception</font><br/>Details: <br/>" + Arrays.toString(e.getStackTrace()).replaceAll("\\[|\\]","")
.replaceAll("\\s","\r\n") + "<font color='green'><i>Copyright@GupaoEDU </i></font>");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws Exception{
//根据用户请求的URL来获得一个Handler
GPHandlerMapping handler = getHandler(req);
if(handler == null){
processDispatchResult(req,resp,new GPModelAndView("404"));
return;
}
GPHandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(handler);
//这一步只是调用方法,得到返回值
GPModelAndView mv = ha.handle(req, resp, handler);
//这一步才是真的输出
processDispatchResult(req,resp, mv);
}
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response, GPModelAndView mv) throws Exception {
//调用viewResolver的resolveViewName()方法
if(null == mv){ return;}
if(this.viewResolvers.isEmpty()){ return;}
if (this.viewResolvers != null) {
for (GPViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) {
GPView view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(mv.getViewName(), null);
if (view != null) {
view.render(mv.getModel(),request,response);
return;
}
}
}
}
private GPHandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(GPHandlerMapping handler) {
if(this.handlerAdapters.isEmpty()){return null;}
GPHandlerAdapter ha = this.handlerAdapters.get(handler);
if (ha.supports(handler)) {
return ha;
}
return null;
}
private GPHandlerMapping getHandler(HttpServletRequest req) {
if(this.handlerMappings.isEmpty()){ return null;}
String url = req.getRequestURI();
String contextPath = req.getContextPath();
url = url.replace(contextPath,"").replaceAll("/+","/");
for (GPHandlerMapping handler : this.handlerMappings) {
Matcher matcher = handler.getPattern().matcher(url);
if(!matcher.matches()){ continue;}
return handler;
}
return null;
}
GPDisptcherServlet的完整代码请关注微信公众号回复“Spring”。下面补充实现上面的代码中缺失的依赖类。
1.2 GPHandlerMapping
我们已经知道HandlerMapping主要用来保存URL和Method的对应关系,这里其实使用的是策略模式。
package com.tom.spring.formework.webmvc;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class GPHandlerMapping {
private Object controller; //目标方法所在的contrller对象
private Method method; //URL对应的目标方法
private Pattern pattern; //URL的封装
public GPHandlerMapping(Pattern pattern,Object controller, Method method) {
this.controller = controller;
this.method = method;
this.pattern = pattern;
}
public Object getController() {
return controller;
}
public void setController(Object controller) {
this.controller = controller;
}
public Method getMethod() {
return method;
}
public void setMethod(Method method) {
this.method = method;
}
public Pattern getPattern() {
return pattern;
}
public void setPattern(Pattern pattern) {
this.pattern = pattern;
}
}
1.3 GPHandlerAdapter
原生Spring的HandlerAdapter主要完成请求传递到服务端的参数列表与Method实参列表的对应关系,完成参数值的类型转换工作。核心方法是handle(),在handle()方法中用反射来调用被适配的目标方法,并将转换包装好的参数列表传递过去。
package com.tom.spring.formework.webmvc;
import com.tom.spring.formework.annotation.GPRequestParam;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
//专人干专事
public class GPHandlerAdapter {
public boolean supports(Object handler){
return (handler instanceof GPHandlerMapping);
}
public GPModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp, Object handler) throws Exception{
GPHandlerMapping handlerMapping = (GPHandlerMapping)handler;
//每个方法有一个参数列表,这里保存的是形参列表
Map<String,Integer> paramMapping = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
//这里只是给出命名参数
Annotation[][] pa = handlerMapping.getMethod().getParameterAnnotations();
for (int i = 0; i < pa.length ; i ++) {
for (Annotation a : pa[i]) {
if(a instanceof GPRequestParam){
String paramName = ((GPRequestParam) a).value();
if(!"".equals(paramName.trim())){
paramMapping.put(paramName,i);
}
}
}
}
//根据用户请求的参数信息,跟Method中的参数信息进行动态匹配
//resp 传进来的目的只有一个:将其赋值给方法参数,仅此而已
//只有当用户传过来的ModelAndView为空的时候,才会新建一个默认的
//1. 要准备好这个方法的形参列表
//方法重载时形参的决定因素:参数的个数、参数的类型、参数顺序、方法的名字
//只处理Request和Response
Class<?>[] paramTypes = handlerMapping.getMethod().getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0;i < paramTypes.length; i ++) {
Class<?> type = paramTypes[i];
if(type == HttpServletRequest.class ||
type == HttpServletResponse.class){
paramMapping.put(type.getName(),i);
}
}
//2. 得到自定义命名参数所在的位置
//用户通过URL传过来的参数列表
Map<String,String[]> reqParameterMap = req.getParameterMap();
//3. 构造实参列表
Object [] paramValues = new Object[paramTypes.length];
for (Map.Entry<String,String[]> param : reqParameterMap.entrySet()) {
String value = Arrays.toString(param.getValue()).replaceAll("\\[|\\]",""). replaceAll("\\s","");
if(!paramMapping.containsKey(param.getKey())){continue;}
int index = paramMapping.get(param.getKey());
//因为页面传过来的值都是String类型的,而在方法中定义的类型是千变万化的
//所以要针对我们传过来的参数进行类型转换
paramValues[index] = caseStringValue(value,paramTypes[index]);
}
if(paramMapping.containsKey(HttpServletRequest.class.getName())) {
int reqIndex = paramMapping.get(HttpServletRequest.class.getName());
paramValues[reqIndex] = req;
}
if(paramMapping.containsKey(HttpServletResponse.class.getName())) {
int respIndex = paramMapping.get(HttpServletResponse.class.getName());
paramValues[respIndex] = resp;
}
//4. 从handler中取出Controller、Method,然后利用反射机制进行调用
Object result = handlerMapping.getMethod().invoke(handlerMapping.getController(), paramValues);
if(result == null){ return null; }
boolean isModelAndView = handlerMapping.getMethod().getReturnType() == GPModelAndView.class;
if(isModelAndView){
return (GPModelAndView)result;
}else{
return null;
}
}
private Object caseStringValue(String value,Class<?> clazz){
if(clazz == String.class){
return value;
}else if(clazz == Integer.class){
return Integer.valueOf(value);
}else if(clazz == int.class){
return Integer.valueOf(value).intValue();
}else {
return null;
}
}
}
1.4 GPModelAndView
原生Spring中ModelAndView类主要用于封装页面模板和要往页面传送的参数的对应关系。
package com.tom.spring.formework.webmvc;
import java.util.Map;
public class GPModelAndView {
private String viewName; //页面模板的名称
private Map<String,?> model; //往页面传送的参数
public GPModelAndView(String viewName) {
this(viewName,null);
}
public GPModelAndView(String viewName, Map<String, ?> model) {
this.viewName = viewName;
this.model = model;
}
public String getViewName() {
return viewName;
}
public void setViewName(String viewName) {
this.viewName = viewName;
}
public Map<String, ?> getModel() {
return model;
}
public void setModel(Map<String, ?> model) {
this.model = model;
}
}
1.5 GPViewResolver
原生Spring中的ViewResolver主要完成模板名称和模板解析引擎的匹配。通过在Serlvet中调用resolveViewName()方法来获得模板所对应的View。在这个Mini版本中简化了实现,只实现了一套默认的模板引擎,语法也是完全自定义的。
package com.tom.spring.formework.webmvc;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Locale;
//设计这个类的主要目的是:
//1. 将一个静态文件变为一个动态文件
//2. 根据用户传送不同的参数,产生不同的结果
//最终输出字符串,交给Response输出
public class GPViewResolver {
private final String DEFAULT_TEMPLATE_SUFFIX = ".html";
private File templateRootDir;
private String viewName;
public GPViewResolver(String templateRoot){
String templateRootPath = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(templateRoot). getFile();
this.templateRootDir = new File(templateRootPath);
}
public GPView resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
this.viewName = viewName;
if(null == viewName || "".equals(viewName.trim())){ return null;}
viewName = viewName.endsWith(DEFAULT_TEMPLATE_SUFFIX) ? viewName : (viewName + DEFAULT_TEMPLATE_SUFFIX);
File templateFile = new File((templateRootDir.getPath() + "/" + viewName).replaceAll ("/+", "/"));
return new GPView(templateFile);
}
public String getViewName() {
return viewName;
}
}
1.6 GPView
这里的GPView就是前面所说的自定义模板解析引擎,其核心方法是render()。在render()方法中完成对模板的渲染,最终返回浏览器能识别的字符串,通过Response输出。
package com.tom.spring.formework.webmvc;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.util.Map;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class GPView {
public static final String DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE = "text/html;charset=utf-8";
private File viewFile;
public GPView(File viewFile){
this.viewFile = viewFile;
}
public String getContentType(){
return DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE;
}
public void render(Map<String, ?> model,HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception{
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
RandomAccessFile ra = new RandomAccessFile(this.viewFile,"r");
try {
String line = null;
while (null != (line = ra.readLine())) {
line = new String(line.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"),"utf-8");
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("¥\\{[^\\}]+\\}",Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(line);
while (matcher.find()) {
String paramName = matcher.group();
paramName = paramName.replaceAll("¥\\{|\\}","");
Object paramValue = model.get(paramName);
if (null == paramValue) { continue; }
//要把¥{}中间的这个字符串取出来
line = matcher.replaceFirst(makeStringForRegExp(paramValue.toString()));
matcher = pattern.matcher(line);
}
sb.append(line);
}
}finally {
ra.close();
}
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//response.setContentType(DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE);
response.getWriter().write(sb.toString());
}
//处理特殊字符
public static String makeStringForRegExp(String str) {
return str.replace("\\", "\\\\").replace("*", "\\*")
.replace("+", "\\+").replace("|", "\\|")
.replace("{", "\\{").replace("}", "\\}")
.replace("(", "\\(").replace(")", "\\)")
.replace("^", "\\^").replace("$", "\\$")
.replace("[", "\\[").replace("]", "\\]")
.replace("?", "\\?").replace(",", "\\,")
.replace(".", "\\.").replace("&", "\\&");
}
}
从上面的代码可以看出,GPView是基于HTML文件来对页面进行渲染的。但是加入了一些自定义语法,例如在模板页面中扫描到¥{name}这样的表达式,就会从ModelAndView的Model中找到name所对应的值,并且用正则表达式将其替换(外国人喜欢用美元符号$,我们的模板引擎就用人民币符号¥)。
2 业务代码实现
2.1 IQueryService
定义一个负责查询业务的顶层接口IQueryService,提供一个query()方法:
package com.tom.spring.demo.service;
/**
* 查询业务
*
*/
public interface IQueryService {
/**
* 查询
*/
public String query(String name);
}
2.2 QueryService
查询业务的实现QueryService也非常简单,就是打印一下调用时间和传入的参数,并封装为JSON格式返回:
package com.tom.spring.demo.service.impl;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import com.tom.spring.demo.service.IQueryService;
import com.tom.spring.formework.annotation.GPService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* 查询业务
*
*/
@GPService
@Slf4j
public class QueryService implements IQueryService {
/**
* 查询
*/
public String query(String name) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String time = sdf.format(new Date());
String json = "{name:\"" + name + "\",time:\"" + time + "\"}";
log.info("这是在业务方法中打印的:" + json);
return json;
}
}
2.3 IModifyService
定义一个增、删、改业务的顶层接口IModifyService:
package com.tom.spring.demo.service;
/**
* 增、删、改业务
*/
public interface IModifyService {
/**
* 增加
*/
public String add(String name, String addr) ;
/**
* 修改
*/
public String edit(Integer id, String name);
/**
* 删除
*/
public String remove(Integer id);
}
2.4 ModifyService
增、删、改业务的实现ModifyService也非常简单,主要是打印传过来的参数:
package com.tom.spring.demo.service.impl;
import com.tom.spring.demo.service.IModifyService;
import com.tom.spring.formework.annotation.GPService;
/**
* 增、删、改业务
*/
@GPService
public class ModifyService implements IModifyService {
/**
* 增加
*/
public String add(String name,String addr) {
return "modifyService add,name=" + name + ",addr=" + addr;
}
/**
* 修改
*/
public String edit(Integer id,String name) {
return "modifyService edit,id=" + id + ",name=" + name;
}
/**
* 删除
*/
public String remove(Integer id) {
return "modifyService id=" + id;
}
}
2.5 MyAction
Controller的主要功能是负责调度,不做业务实现。业务实现方法全部在Service层,一般我们会将Service实例注入Controller。MyAction中主要实现对IQueryService和IModifyService的调度,统一返回结果:
package com.tom.spring.demo.action;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.tom.spring.demo.service.IModifyService;
import com.tom.spring.demo.service.IQueryService;
import com.tom.spring.formework.annotation.GPAutowired;
import com.tom.spring.formework.annotation.GPController;
import com.tom.spring.formework.annotation.GPRequestMapping;
import com.tom.spring.formework.annotation.GPRequestParam;
import com.tom.spring.formework.webmvc.GPModelAndView;
/**
* 公布接口URL
*/
@GPController
@GPRequestMapping("/web")
public class MyAction {
@GPAutowired IQueryService queryService;
@GPAutowired IModifyService modifyService;
@GPRequestMapping("/query.json")
public GPModelAndView query(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@GPRequestParam("name") String name){
String result = queryService.query(name);
return out(response,result);
}
@GPRequestMapping("/add*.json")
public GPModelAndView add(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,
@GPRequestParam("name") String name,@GPRequestParam("addr") String addr){
String result = modifyService.add(name,addr);
return out(response,result);
}
@GPRequestMapping("/remove.json")
public GPModelAndView remove(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,
@GPRequestParam("id") Integer id){
String result = modifyService.remove(id);
return out(response,result);
}
@GPRequestMapping("/edit.json")
public GPModelAndView edit(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,
@GPRequestParam("id") Integer id,
@GPRequestParam("name") String name){
String result = modifyService.edit(id,name);
return out(response,result);
}
private GPModelAndView out(HttpServletResponse resp,String str){
try {
resp.getWriter().write(str);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
2.6 PageAction
专门设计PageAction是为了演示Mini版Spring对模板引擎的支持,实现从Controller层到View层的传参,以及对模板的渲染进行最终输出:
package com.tom.spring.demo.action;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import com.tom.spring.demo.service.IQueryService;
import com.tom.spring.formework.annotation.GPAutowired;
import com.tom.spring.formework.annotation.GPController;
import com.tom.spring.formework.annotation.GPRequestMapping;
import com.tom.spring.formework.annotation.GPRequestParam;
import com.tom.spring.formework.webmvc.GPModelAndView;
/**
* 公布接口URL
*/
@GPController
@GPRequestMapping("/")
public class PageAction {
@GPAutowired IQueryService queryService;
@GPRequestMapping("/first.html")
public GPModelAndView query(@GPRequestParam("teacher") String teacher){
String result = queryService.query(teacher);
Map<String,Object> model = new HashMap<String,Object>();
model.put("teacher", teacher);
model.put("data", result);
model.put("token", "123456");
return new GPModelAndView("first.html",model);
}
}
3 定制模板页面
为了更全面地演示页面渲染效果,分别定义了first.html对应PageAction中的first.html请求、404.html默认页和500.html异常默认页。
3.1 first.html
first.html定义如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-cn">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>SpringMVC模板引擎演示</title>
</head>
<center>
<h1>大家好,我是¥{teacher}老师<br/>欢迎大家一起来探索Spring的世界</h1>
<h3>Hello,My name is ¥{teacher}</h3>
<div>¥{data}</div>
Token值:¥{token}
</center>
</html>
3.2 404.html
404.html定义如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-cn">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>页面去火星了</title>
</head>
<body>
<font size='25' color='red'>404 Not Found</font><br/><font color='green'><i>Copyright @GupaoEDU</i></font>
</body>
</html>
3.3 500.html
500.html定义如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-cn">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>服务器好像累了</title>
</head>
<body>
<font size='25' color='blue'>500 服务器好像有点累了,需要休息一下</font><br/>
<b>Message:¥{detail}</b><br/>
<b>StackTrace:¥{stackTrace}</b><br/>
<font color='green'><i>Copyright@GupaoEDU</i></font>
</body>
</html>
4 运行效果演示
在浏览器中输入 http://localhost/web/query.json?name=Tom ,就会映射到MyAction中的@GPRequestMapping(“query.json”)对应的query()方法,得到如下图所示结果。
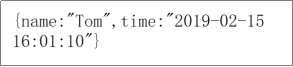
在浏览器中输入 http://localhost/web/addTom.json?name=tom&addr=HunanChangsha ,就会映射到MyAction中的@GPRequestMapping(“add*.json”)对应的add()方法,得到如下图所示结果。
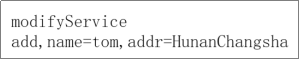
在浏览器中输入 http://localhost/web/remove.json?id=66 ,就会映射到MyAction中的@GPRequestMapping(“remove.json”)对应的remove()方法,并将id自动转换为int类型,得到如下图所示结果。

在浏览器中输入 http://localhost/web/edit.json?id=666&name=Tom ,就会映射到MyAction中的@GPRequestMapping(“edit.json”)对应的edit()方法,并将id自动转换为int类型,得到如下图所示结果。

在浏览器中输入 http://localhost/first.html?teacher=Tom ,就会映射到PageAction中的@GPRequestMapping(“first.html”)对应的query()方法,得到如下图所示结果。

到这里,已经实现了Spring从IoC、ID到MVC的完整功能。虽然忽略了一些细节,但是我们已经了解到,Spring的核心设计思想其实并没有我们想象得那么神秘。我们已经巧妙地用到了工厂模式、静态代理模式、适配器模式、模板模式、策略模式、委派模式等,使得代码变得非常优雅。 关注微信公众号『 Tom弹架构 』回复“Spring”可获取完整源码。

本文为“Tom弹架构”原创,转载请注明出处。技术在于分享,我分享我快乐!
如果本文对您有帮助,欢迎关注和点赞;如果您有任何建议也可留言评论或私信,您的支持是我坚持创作的动力。关注微信公众号『 Tom弹架构 』可获取更多技术干货!
原创不易,坚持很酷,都看到这里了,小伙伴记得点赞、收藏、在看,一键三连加关注!如果你觉得内容太干,可以分享转发给朋友滋润滋润!
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK