

字典树之旅02.Trie 的标准实现
source link: https://my.oschina.net/xcafe/blog/5348849
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

上一篇文章简单介绍了 Trie,让大家对其有一些感性认知。
这篇文章会先介绍 Trie 的标准实现,然后给出完整代码和测试用例,然后再结合代码实现来分析其优缺点。
论文中通常称这种简单实现为 standard trie,有些文章译为标准实现,还有些译为朴素实现,《算法.第4版》中则译为单词查找树,这些说的都是同一种数据结构。
2. 基本介绍
假如有六个单词:ab, abc, abcd, abd, bcd, cda
如果想查找某个单词,我们可以用散列表来保存。但:
-
输入"ab",输出前缀为 "ab" 的所有单词;
-
输入一段文本,输出文本中存在这六个单词的哪几个,以及单词出现的起止位置……
那么,散列表处理起来就有些困难了。这时,我们可以建立下图所示的树形结构。
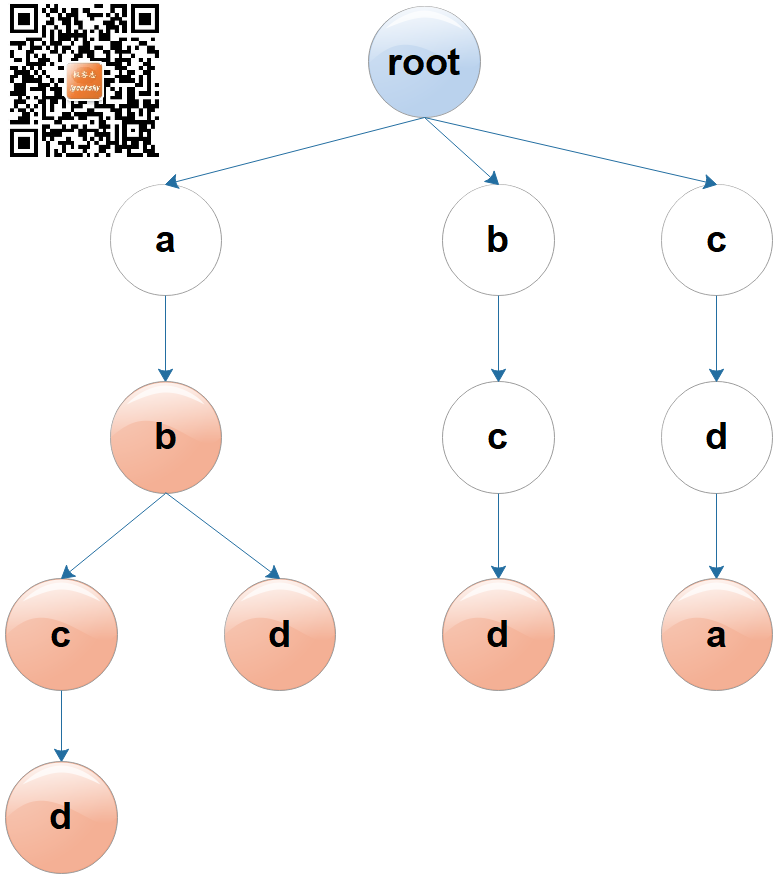
图1:字典树
注:图中蓝色(根节点)、白色(无值节点)和红色(有值节点)仅仅是为了便于理解作出的标识,字典树并没有颜色概念。
每个键是一个字符序列,每个字符是一个节点,节点之间用边相连。
基本性质:
- 根节点不包含字符,非根节点包含一个字符;
- 一个节点的所有子节点包含的字符均不相同;
- 非根节点有且仅有一个指向它的父节点;
- 值保存在键的最后一个字符所在的节点。
根据以上性质,我们可以得到一些有意思的推论:
- 一个节点的所有子节点都具有相同前缀;
- 从根节点到任意节点所经过的路径构成一个字符串,且该字符串在这棵树中是唯一的;
- 值可以存在于叶子节点,也可以存在于非叶节点。
查找键
只要从根节点开始顺着序列路径递归查找子节点,就能命中(未命中)键。
譬如查找 abcd,root --> a --> b --> c --> d,命中,返回abcd;譬如查找 cab,root --> c --> 空,未命中,停止查找,返回空。
查找以输入字符串为前缀的键
先找到前缀节点,然后遍历其子节点。
譬如查找 ab 的后缀:1. 先找到 ab 对应的节点,root --> a --> b,找到 b 节点;2. 遍历 b 节点的所有子节点。
3. 树的实现
3.1. 节点定义
package com.igeeksky.perfect.nlp.trie;
private static class StandardNode<V> {
// 因为数组容量R与字符集大小一致,可以省略此字符
// char c;
// 值(支持泛型,可以是非字符串)
V val;
// 子节点
StandardNode<V>[] table;
public StandardNode() {
}
// R为数组容量
public StandardNode(int R) {
this.table = new StandardNode[r];
}
}
-
StandardTrie 中所有节点的数组容量相同,其大小与字符表的大小相等。
如使用 UTF-16 字符集,其字符数是65536,那么数组容量 R 为65536,则正好可以不重复地映射到数组的位置区间 [0, 65535]。
-
StandardTrie 中的节点定义可以省略字符,通过位置隐式转换得到字符。
譬如,小写字符 'a',转换成 int 值是97, 因此 table[97] 就是 'a' 字符节点。
如仅使用英文小写字母表,可将 R 设为26。转换 :((int)c) - 97 将字符转换为索引位置;(char)(index+97) 将索引位置转换为字符。
-
每个数组的容量均为 R,因此可以将字典树看作是 R 路树。图2中我省略了数组,这里把数组补充上去,见下图:
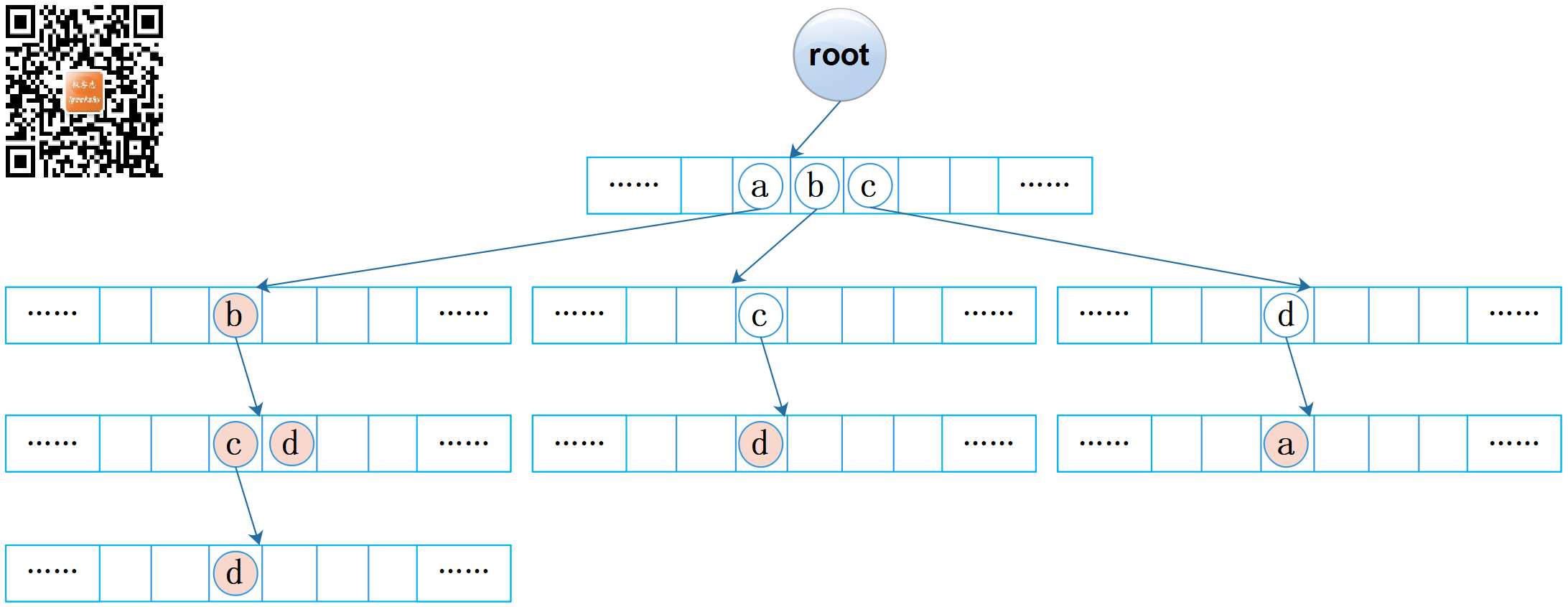
图2:字典树(数组)
观察图 2,我们发现可能会有大量空链接存在,这意味着可能会有大量的空间被浪费!!!
这里我们暂且不管空链接问题,先定义接口,然后实现代码,最后再结合代码来总结分析其优缺点。
3.2. 接口定义
package com.igeeksky.perfect.api;
/**
* 字典树接口
*
* @author Patrick.Lau
* @since 1.0.0 2021-11-30
*/
public interface Trie<V> extends BaseMap<String, V> {
/**
* 前缀匹配:查找给定字符串 word 的最长前缀
* <pre>
* Trie中已有键:ab, abc, abcd, abd, bcd, cda
* trie.prefixMatch("abcdef")
* 返回结果:[abcd, abcd]
* </pre>
*/
Tuple2<String, V> prefixMatch(String word);
/**
* 前缀搜索:查找以给定字符串prefix为前缀的所有键值对(字典序)
*
* <pre>
* Trie中已有键:ab, abc, abcd, abd, bcd, cda
* trie.keysWithPrefix("ab")
* 返回结果:[[ab, ab], [abc, abc], [abcd, abcd], [abd, abd]]
* </pre>
*/
List<Tuple2<String, V>> keysWithPrefix(String prefix);
/**
* 包含匹配:查找给定文本text中包含的键(及关联的值和键在文本中的起止位置)
* <pre>
* Trie中已有键:ab, abc, abcd, abd, bcd, cda
* trie.matchAll("xxbcdexx")
* 返回结果:[{"start":2, "end":4, "key":"bcd", "value":"bcd"}]
* </pre>
*/
List<Found<V>> matchAll(String text);
}
- Trie 接口继承自 BaseMap,除了这3个特有方法,还有 BaseMap 接口的 put 、get、remove……等方法。
- Tuple2 是二元组,值1为 key,值2为 value,值1和值2均不可变且不能为空。
3.3. 代码实现
Map同名方法
public class StandardTrie<V> implements Trie<V> {
private int size;
private static final int R = 65536;
private final BasicNode<V> root = new BasicNode<>(R);
/**
* 添加键值对
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
*/
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void put(String key, V value) {
int len = key.length();
if (len == 0) {
return;
}
StandardNode<V> node = root;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (node.table == null) {
// 小优化:只有添加子节点时才创建数组,即叶子节点无数组
node.table = new StandardNode[R];
}
char c = key.charAt(i);
StandardNode<V> child = node.table[c];
if (child == null) {
node.table[c] = (child = new StandardNode<>());
}
node = child;
}
if(node.val == null){
++size;
}
node.val = value;
}
/**
* 通过key获取值
*
* @param key 键
* @return 值
*/
@Override
public V get(String key) {
StandardNode<V> node = find(key);
return (node == null) ? null : node.val;
}
/**
* 移除键值对
*/
@Override
public V remove(String key) {
StandardNode<V> node = find(key);
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
V oldVal = node.val;
if (oldVal != null) {
// 使用惰性删除:仅把关联的值置空,没有真正删除节点
node.val = null;
--size;
}
return oldVal;
}
/**
* 通过key查找节点
*
* @param key 键
* @return key对应的节点
*/
private StandardNode<V> find(String key) {
int len = key.length();
if (len == 0) {
return null;
}
StandardNode<V> node = root;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (node.table == null) {
return null;
}
char c = key.charAt(i);
node = node.table[c];
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
}
return node;
}
}
代码实现是非常非常简单,就是循环查找(添加)子节点而已。
Trie特有方法
查找给定字符串的最长前缀
public Tuple2<String, V> prefixMatch(String word) {
int len = word.length();
if (len == 0) {
return null;
}
StandardNode<V> node = root;
Tuple2<String, V> tuple2 = null;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (node.table == null) {
return tuple2;
}
char c = word.charAt(i);
node = node.table[c];
if (node == null) {
return tuple2;
}
if (node.val != null) {
tuple2 = Tuples.of(word.substring(0, i + 1), node.val);
}
}
return tuple2;
}
查找以给定字符串为前缀的所有键
@Override
public List<Tuple2<String, V>> keysWithPrefix(String prefix) {
List<Tuple2<String, V>> list = new LinkedList<>();
StandardNode<V> parent = find(prefix);
traversal(parent, prefix, list);
return list;
}
// 遍历所有后缀节点(深度优先)
private void traversal(StandardNode<V> parent, String prefix, List<Tuple2<String, V>> list) {
if (parent != null) {
if (parent.val != null) {
list.add(Tuples.of(prefix, parent.val));
}
if (parent.table != null) {
for (int c = 0; c < R; c++) {
// 由于数组中可能存在大量空链接,因此遍历时可能会有很多无意义操作
String key = prefix + (char) c;
StandardNode<V> node = parent.table[c];
traversal(node, key, list);
}
}
}
}
查找给定文本中包含的键
譬如树中现在有键值对:"abcd : abcd" 和 "bcdef : bcdef",输入 "abcdefg" ,此方法返回该文本中中包含的键及关联的值和键在文本中的起止位置。
观察代码,我们发现此方法是将输入文本的每一个字符都作为起始字符进行比较,但我们也可以看到 "abcd" 和 "bcdef" 有共同的字符串"bcd",那么是否可以跳过已经比较的 "bcd",然后直接比较后面的 "ef" 呢?
当然是可以的,大名鼎鼎的单模式匹配算法 KMP 就是这么做的,所以这是一个可以优化的点。
@Override
public List<Found<V>> matchAll(String text) {
List<Found<V>> list = new LinkedList<>();
int len = text.length();
// 每一个字符都作为起始字符进行比较
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
matchAll(list, text, i, len);
}
return list;
}
private void matchAll(List<Found<V>> list, String text, int start, int end) {
StandardNode<V> node = root;
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (node.table == null) {
return;
}
char c = text.charAt(i);
node = node.table[c];
if (node == null) {
return;
}
if (node.val != null) {
list.add(new Found<>(start, i, text.substring(start, i + 1), node.val));
}
}
}
以上就是 Trie 标准实现的全部代码,连同节点定义不超过200行。接下来,我们测试代码逻辑。
public class StandardTrieTest {
// 测试前缀匹配
@Test
public void prefixMatch() {
StandardTrie<String> trie = new StandardTrie<>();
trie.put("abc", "abc");
trie.put("abd", "abd");
Tuple2<String, String> tuple2 = trie.prefixMatch("abcd");
Assert.assertEquals("abc", tuple2.getT2());
}
// 查找所有以给定字符串为前缀的key
@Test
public void keysWithPrefix() {
StandardTrie<String> trie = new StandardTrie<>();
trie.put("ab", "ab");
trie.put("abc", "abc");
trie.put("abcd", "abcd");
trie.put("abd", "abd");
trie.put("bcd", "bcd");
trie.put("cda", "cda");
List<Tuple2<String, String>> keysWithPrefix = trie.keysWithPrefix("ab");
Assert.assertEquals("[[ab, ab], [abc, abc], [abcd, abcd], [abd, abd]]", keysWithPrefix.toString());
}
// 查找输入文本中包含的键值对
@Test
public void matchAll() {
StandTrie<String> trie = new StandTrie<>();
trie.put("abcd", "abcd");
trie.put("bcdef", "bcdef");
trie.put("abe", "abe");
List<Found<String>> matchAll = trie.matchAll("abcdefg");
String expected = "[{\"start\":0, \"end\":3, \"key\":\"abcd\", \"value\":\"abcd\"}, {\"start\":1, \"end\":5, \"key\":\"bcdef\", \"value\":\"bcdef\"}]";
Assert.assertEquals(expected, matchAll.toString());
}
}
4. 性能分析
4.1. 时间与空间
通过代码我们可以发现 StandardTrie 有三个非常明显的特点:
- 支持动态更新:StandardTrie 是动态查找树,支持在查找期间更新数据元素。
- 时间性能非常好:增删查都只跟字符串的长度 m 相关,且其时间复杂度最好和最坏的情况都是 O(m)。非常非常棒的性质!!!
- 空间性能非常差:随着树的高度增加,其空间消耗是平方级增长。如数组容量为 RR,则第一层可能有 R 个 空链接+节点,第二层可能有 R^2 个 空链接+节点,第三层可能有 R^3 个 空链接+节点……而且很多数组可能只含1个有效节点,却有 R-1 个空链接。更准确的空间估算如下:
命题
一棵标准字典树的链接数量在 R 至 RN(w-1)+R 之间,其中 R 为数组的固定容量,N 为键的数量,w 为键的平均长度。
证明:
由代码实现可知,叶子节点无链接,每个非叶节点都有 R 条链接,每个键都需有一个节点来保存其关联的值。
当 w < 1 时,w 仅有一个取值:0(空树),此时仅有根节点的链接,因此链接数量最小,为R;
当 w >= 1 时,所有键的首字符不同时节点数最多,此时链接数量最大,其计算方式为:R乘以节点总数 - R乘以叶子节点数 + 根节点链接数,即 RNw - RN + R,化简得 RN(w - 1) + R。
- 注1:根据公式,减去节点总数 Nw ,即可得到最大空链接数量公式(当w<1时,R-Nw;当w>=1时,RN(w-1)+R- Nw)。
- 注2:这里的命题与证明与《Algorithms.4th》一书的 命题 I 略有不同,是因为这里的代码做了小小的优化:叶子节点无链接。
综上,减小 R 可以有效地降低空间浪费。
4.2. 对比 HashMap
如果使用字符串作为键,StandardTrie 在某些应用场景可以替代 HashMap。
- HashMap 需要计算键的 Hashcode,StandardTrie 无需计算;
- StandardTrie 的时间复杂度最好和最坏都是O(m);HashMap 最好是O(m),最坏是O(mlogk),m 为字符串长度,k 为键的数量。
- StandardTrie 可以利用公共前缀来避免保存重复字符。
注:通常说 HashMap 的时间复杂度是 O(1),是将字符串的比较看作是常数时间,事实上 HashMap 也需要逐字符比较。这里为让对比双方的计量标准保持一致,所以 HashMap 的时间复杂度也应该乘以 m,为O(m)。
- String 的字符数组分配的是连续内存空间,字符比对快;StandardTrie 的字符节点是非连续空间,节点查找慢。
- HashMap 的键比对过程可能仅需要访问一次主存,StandardTrie 的节点比对过程可能需要多次访问主存。
- HashMap 的节点保存的是完整的字符串,内存开销较小;StandardTrie 中每个字符都需要一个 StandardNode 对象,每个 StandardNode 在 Java 中至少需要 24 byte内存,是一个字符的12倍。
使用长度为10的固定字符串,循环调用 get 方法2亿次,对比 HashMap 与 StandardTrie 的时间消耗。
public class StandardTrieTest {
@Test
public void performance() {
StandardTrie<String> trie = new StandardTrie<>();
String finalKey = "abcdefghij";
trie.put(finalKey, finalKey);
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(finalKey, finalKey);
// 2亿次
int size = 200000000;
String[] array = new String[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
// 避免 String 缓存hashcode,使得hashmap省略计算hashcode的开销,因此重新生成相同的key
array[i] = new String(finalKey.toCharArray());
}
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (String key : array) {
trie.get(key);
}
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("trie-get:\t" + (t2 - t1));
for (String key : array) {
map.get(key);
}
long t3 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(" map-get:\t" + (t3 - t2));
}
}
我的电脑上的测试结果:
# 测试平台
# CPU:Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-7900X CPU @ 3.30GHz
# RAM:64G DDR4(3000 MHz)
# OS:Win10(21H1)
# JDK:11.0.5
trie-get: 5609
map-get: 4436
这是一个非常简单的测试,但也验证了两个结果判断:
- StandardTrie 的性能非常好;
- StandardTrie 的节点查找慢,即使无需额外计算 Hashcode,依然还是比 HashMap 略慢。
如果字符表较小,键普遍不长,能接受大量的内存消耗(浪费),可以考虑使用 StandardTrie。
根据以上代码和分析,我们可以总结出三个可以优化的点:
- 提升空间性能;
- 提升 CPU 缓存友好度;
- 单模式匹配算法推广到多模式匹配。
这三点是其它优化算法和变体结构的主要方向,在后续章节中,我再结合具体的代码实现来描述。
实验性代码:https://github.com/patricklaux/perfect-code
生产级代码:https://github.com/patricklaux/xtool
[1]: R. Sedgewick and K. Wayne. "Algorithms, fourth edition." Addison-Wesley(2011):730-753
[2]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trie
[3]:http://web.stanford.edu/class/cs166/lectures/16/Slides16.pdf
[4]:https://cglab.ca/~morin/teaching/5408/notes/strings.pdf
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK