

Defining generated columns with PostgreSQL and TypeORM
source link: https://wanago.io/2021/11/29/generated-columns-postgresql-typeorm/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.


On this blog, we’ve covered a variety of different column types. So far, we’ve performed various operations on said columns such as INSERT and UPDATE to modify the data directly. In this article, we cover generated columns that work differently.
Generated columns in PostgreSQL
We call the above columns generated because PostgreSQL automatically computes their data based on predefined expressions. However, the crucial thing is that we can’t insert any data into them directly.
Generated columns became available in PostgreSQL 12 in 2019
The SQL standard consists of two types of generated columns:
- virtual,
- stored.
Virtual generated columns
The idea behind virtual generated columns is that it occupies no disk storage. Therefore, it is computed on the fly when requested. A good example is returning the value with the SELECT statement. Unfortunately, PostgreSQL currently doesn’t implement virtual generated columns.
Stored generated columns
The stored generated columns occupy storage in the same way as a regular column. However, instead of computing the value every time it is requested, PostgreSQL does so only when the row is modified.
To define a stored generated column, we need to use the GENERATED ALWAYS AS followed by expression and the keyword STORED:
Above, we’ve defined the full_name column to be a combination of the first_name and last_name. It is common to refer to other columns while defining a generated column. That being said, a generated column can’t refer to another generated column.
Let’s test the above table by inserting a row:
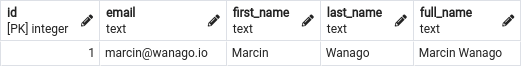
As we can see in the above table, PostgreSQL automatically figured out the value for the full_name column.
Types of expressions we can use
There are a few different types of expressions we can use when defining a generated column. For example, besides operating on text as in the previous example, we can also do so with numbers.
Besides simple operations, we can also use functions. The crucial thing is that they have to be immutable. An immutable function can’t modify the database and must return the same result given the same arguments.
An interesting example of a function that is not immutable is concat. Let’s try to use it instead of the || operator:
ERROR: generation expression is not immutable
Surprisingly, concat can yield different results based on the database configuration. Unfortunately, it makes it not immutable.
If you want to know more about timezones, check out Managing date and time with PostgreSQL and TypeORM
Generated columns with TypeORM
Fortunately, TypeORM started supporting generated columns for PostgreSQL a few days ago.
Please remember that we need to use the ' sign with the column names 'firstName' and 'lastName' above. Otherwise, PostgreSQL would transform them to firstname and lastname.
An issue with updating entities
There is an important catch when using generated columns. Consider the following example:
There is a good chance that our application allows us to update posts with the PUT method. With it, we expect the users of our API to send all of the properties of the entity. Unfortunately, appending the paragraphsNumber in the body of the request will cause an error.
We can quickly solve the above issue with the class-transformer library and the @Exclude() decorator:
With it, the class-transformer excludes the paragraphsNumber field from the body of the request.
If you want to know more about the class-transformer library, check out API with NestJS #5. Serializing the response with interceptors
Simulating virtual generated columns with getters
While PostgreSQL does not support virtual generated columns, there is a simple way of simulating them when using TypeORM and classes. To do that, we can use a getter.
There is a good chance you are using the class-transformer library along with TypeORM. If you want to return the value along with the rest of the data, you need to use the @Expose() decorator:
When doing the above, the database does not store the fullName value in a column. Instead, it is computed every time on the fly when accessed. The crucial thing to keep in mind is that PostgreSQL won’t know anything about the fullName value, so we can’t use it in any SQL queries.
Summary
The generated columns can come in handy when we often do a set of operations with our data. Instead of retrieving the data and performing the calculations, we can optimize this process by operating on the data beforehand. We need to keep in mind that we do the above optimization at the cost of our INSERT and UPDATE operations.
Another considerable use case for generated columns is when we want to refactor our database. For example, we can define generated columns if we’re going to change some of our columns but keep the backward compatibility.
All of the above make the generated columns a feature that is worth knowing. Especially since TypeORM just recently started supporting it for PostgreSQL.
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK