

scaffold-eth 挑战2:创建ERC20代币及买卖合约(part2)
source link: https://learnblockchain.cn/article/3245
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

接上一篇:我们创建了一个 ERC20 及使用 ETH 购买Token 的功能。现在我们进一步完善它。
练习3:允许Vendor回购
这是练习的最后一部分,也是最难的一部分,不是从技术的角度,而是从概念和用户体验的角度。
我们希望允许用户将他们的代币卖给Vendor合约。如你所知,当合约的功能被声明为 payable时,它可以接受ETH,但它只允许接受ETH。
我们现在需要实现:让Vendor直接从用户Token余额中提取Token,并回馈等值的ETH,这就是使用 授权机制。
将发生的流程是这样:
- 用户调用Token 的
approve授权Vendor合约可将代币从用户钱包转移到Vendor(这是用户直接 调用Token合约)。当你调用approve函数时,需要指定你想让被授权者能够转移的代币数量 ,(这里可设置为最大值)。 - 用户将在Vendor的合约上调用
sellTokens函数,将用户的余额转移到Vendor的余额上。 - 买卖的合约将向用户的钱包转账同等数量的ETH。
要掌握的重要概念
- ERC20 approve 函数 -
amount为spender可使用调用者的代币上的数量。函数返回一个布尔值,表示操作是否成功。函数触发Approval事件。 - ERC20 transferFrom 函数 - 将
amount代币从sender移动到recipient。amount随后从调用者的授权的数量中扣除。返回一个布尔值,表示操作是否成功。发出一个transfer事件。
一个重要的说明,我想解释一下:用户体验及安全
这个授权机制并不是什么新东西,如果你曾经使用过像Uniswap这样的DEX,你已经做了这个。
approve函数允许其他钱包/合约最大限度地转移你在函数参数中指定的代币数量。这是什么意思?如果我想交易200个代币,我应该授权Vendor合约只能转移自己的200个代币。如果我想再次卖出100个,我则需要再次授权。这是一个好的用户体验吗?也许不是,但这是最安全的一个。
DEX使用另一种方法。为了避免每次把代币A换成代币B时都要求用户授权,DEX直接要求授权最大可能的代币数量。这意味着什么呢?每个DEX合约都有可能在你不知道的情况下偷走你所有的代币。你应该时刻注意幕后发生的事情!
Vendor.sol
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.4;
import "hardhat/console.sol";
import "./YourToken.sol";
// Learn more about the ERC20 implementation
// on OpenZeppelin docs: https://docs.openzeppelin.com/contracts/4.x/api/access#Ownable
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/access/Ownable.sol";
contract Vendor is Ownable {
// Our Token Contract
YourToken yourToken;
// token price for ETH
uint256 public tokensPerEth = 100;
// Event that log buy operation
event BuyTokens(address buyer, uint256 amountOfETH, uint256 amountOfTokens);
event SellTokens(address seller, uint256 amountOfTokens, uint256 amountOfETH);
constructor(address tokenAddress) {
yourToken = YourToken(tokenAddress);
}
/**
* @notice Allow users to buy tokens for ETH
*/
function buyTokens() public payable returns (uint256 tokenAmount) {
require(msg.value > 0, "Send ETH to buy some tokens");
uint256 amountToBuy = msg.value * tokensPerEth;
// check if the Vendor Contract has enough amount of tokens for the transaction
uint256 vendorBalance = yourToken.balanceOf(address(this));
require(vendorBalance >= amountToBuy, "Vendor contract has not enough tokens in its balance");
// Transfer token to the msg.sender
(bool sent) = yourToken.transfer(msg.sender, amountToBuy);
require(sent, "Failed to transfer token to user");
// emit the event
emit BuyTokens(msg.sender, msg.value, amountToBuy);
return amountToBuy;
}
/**
* @notice Allow users to sell tokens for ETH
*/
function sellTokens(uint256 tokenAmountToSell) public {
// Check that the requested amount of tokens to sell is more than 0
require(tokenAmountToSell > 0, "Specify an amount of token greater than zero");
// Check that the user's token balance is enough to do the swap
uint256 userBalance = yourToken.balanceOf(msg.sender);
require(userBalance >= tokenAmountToSell, "Your balance is lower than the amount of tokens you want to sell");
// Check that the Vendor's balance is enough to do the swap
uint256 amountOfETHToTransfer = tokenAmountToSell / tokensPerEth;
uint256 ownerETHBalance = address(this).balance;
require(ownerETHBalance >= amountOfETHToTransfer, "Vendor has not enough funds to accept the sell request");
(bool sent) = yourToken.transferFrom(msg.sender, address(this), tokenAmountToSell);
require(sent, "Failed to transfer tokens from user to vendor");
(sent,) = msg.sender.call{value: amountOfETHToTransfer}("");
require(sent, "Failed to send ETH to the user");
}
/**
* @notice Allow the owner of the contract to withdraw ETH
*/
function withdraw() public onlyOwner {
uint256 ownerBalance = address(this).balance;
require(ownerBalance > 0, "Owner has not balance to withdraw");
(bool sent,) = msg.sender.call{value: address(this).balance}("");
require(sent, "Failed to send user balance back to the owner");
}
}
让我们回顾一下sellTokens:
首先,检查tokenAmountToSell是否大于0,否则,我们回退交易。你需要至少卖出1代币!
然后我们检查用户的代币余额至少大于他试图出售的代币数量,你不能超额出售你不拥有的东西!
之后,我们计算卖出操作后给用户的ETH数量 AmountOfETHToTransfer。我们需要确定Vendor能够支付这个金额,所以我们要检查Vendor的余额(以ETH为单位)是否大于要转账给用户的金额。
如果一切正常,我们就进行(bool sent) = yourToken.transferFrom(msg.sender, address(this), tokenAmountToSell);操作。我们告诉YourToken合约将tokenAmountToSell从用户msg.sender的余额转移到Vendor地址 address(this)。
最后要做的是将ETH金额转回用户的地址。然后我们就完成了!
更新你的App.jsx
为了在React应用程序中进行测试,你可以更新App.jsx,添加两个Card进行Approve和Sell代币(见文章末尾的GitHub代码库),或者你可以直接从调试合约标签中进行所有操作,它提供了所有需要的功能。
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G1Wcb6Q3mYI
练习4:创建测试用例
从之前文章中你已经知道,测试是应用程序的安全和优化的一个重要基础。你不应该跳过它们,Solidity 环境下的测试利用了四个库:
测试sellTokens()函数
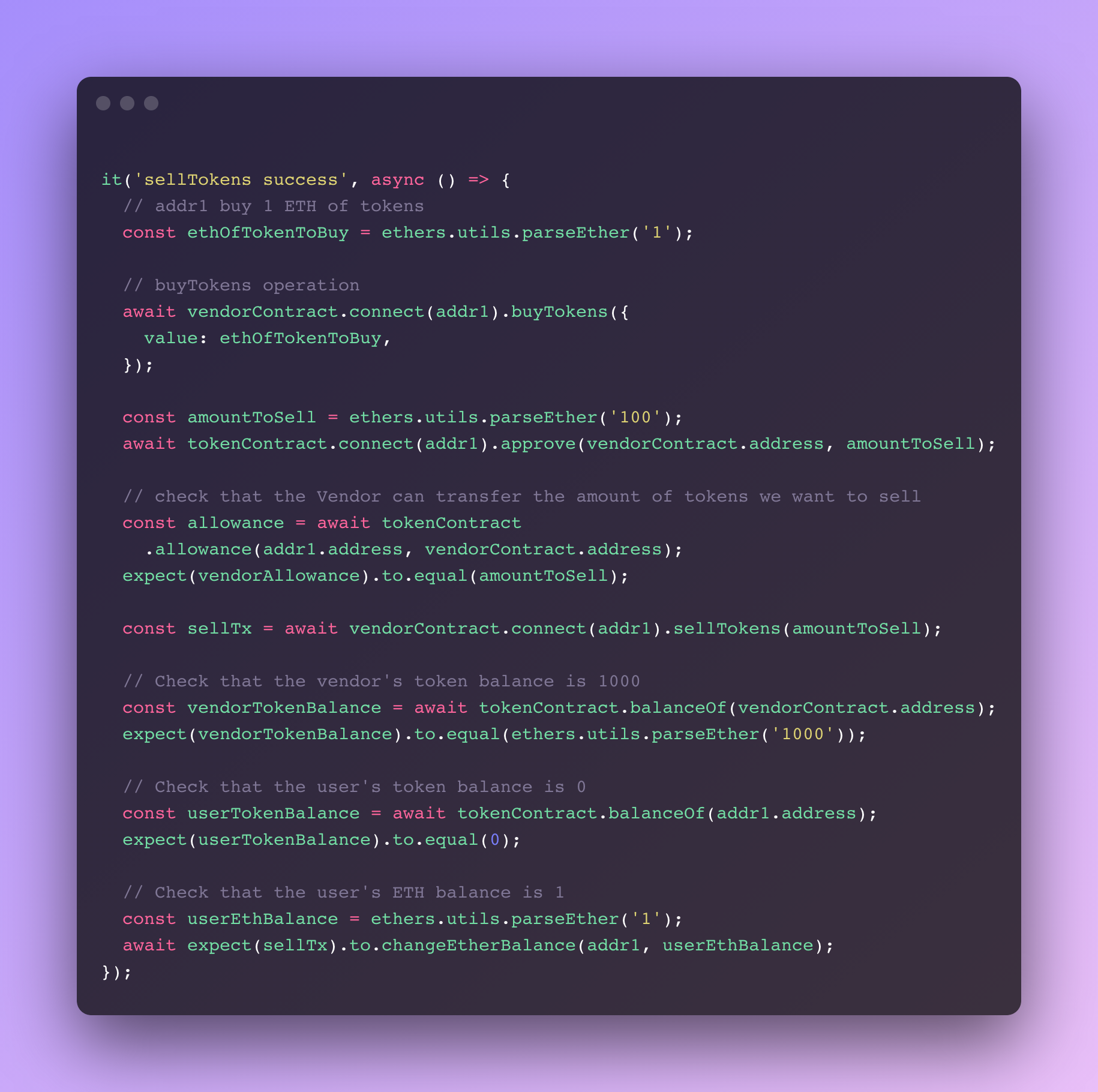
这个测试将验证我们的 sellTokens 函数是否按预期工作。
让我们回顾一下逻辑:
- 首先,
addr1从Vendor合约中购买一些代币。 - 在出售之前,正如我们之前所说,我们需要授权 Vendor合约,以便能够将我们想要出售的代币数量转移给Vender。
- 在授权之后,检查Vendor的代币allowance数量 等于 授权转移给Vendor的数量。这个检查可以跳过,因为我们知道OpenZeppeling已经对他们的代码进行了实战测试,但我只是想把它加进去,以便学习。
- 我们准备使用Vendor合约的
sellTokens函数来出售刚刚买到的代币数量。
在这一点上,我们需要检查三件事:
- 用户的代币余额为0(卖出了所有的代币)
- 用户的钱包通过该交易增加了1个ETH
- 买卖的代币余额为1000(用户转入了100个代币)
Waffle提供了一些很酷的工具来检查以太坊余额的变化和代币余额的变化,但不幸的是,后者似乎有一个问题(请查看我刚刚创建的GitHub问题)。
测试覆盖完整代码
const {ethers} = require('hardhat');
const {use, expect} = require('chai');
const {solidity} = require('ethereum-waffle');
use(solidity);
describe('Staker dApp', () => {
let owner;
let addr1;
let addr2;
let addrs;
let vendorContract;
let tokenContract;
let YourTokenFactory;
let vendorTokensSupply;
let tokensPerEt...
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK