

《Chrome V8原理讲解》第十四篇 看V8如何表示JS的动态类型
source link: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/431618062
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

《Chrome V8原理讲解》第十四篇 看V8如何表示JS的动态类型
JavaScript是动态类型语言,数据类型具有不确定性。V8是用C++编写的,C++是强类型语言,要求类型确定。类型确定的C++是如何表达类型不确定的JS呢?解决方法是:操作JS数据前先查询类型,再操作。这又产生了新问题——性能损耗,因为类型查询是极为耗时的操作,频繁使用严重影响程序运行速度。为此,V8采用了Map机制,也称为隐藏类(Hidden Class)。注意: Map机制与JS中的map()没有关系,只是同名。Map机制可以很好地表达JS的不确定性,但它的主要作用是降低性能损耗。本文通过形象化的比喻和深入的源码分析,使大家从宏观和微观角度全面认识Map机制,本文组织结构:Map原理,它如何表达Javascript的动态类型(章节2);V8初始化阶段对Map的处理过程(章节3)。
2 Map原理
由于Javascript类型的不确定性,V8操作Javascript对象(例如:调用方法、访问对对象成员)前要先查询其类型。因此,V8引入了Map机制,它是一种用于描述类型的数据结构,可以形象地把它叫作“地图”,它的使用特点是固定的位置存储指定的内容,如图1所示。
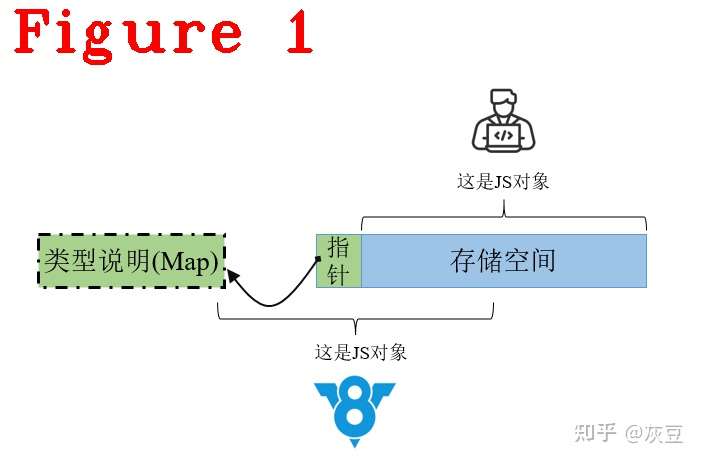
借助图1,我们对Map机制进行概要描述:
(1) JS开发者角度,仅能看到存储空间,这段存储空间保存了开发者定义的JS对象,但V8不知道对象类型;
(2) 指针,它是存储空间的第一个位置,类型是指针,大小8byte(64位系统中),由V8维护,开发者看不到,所以叫隐藏类。它的作用是指向Map;
(3) V8角度,查询存储空间的第一个位置,就可以找到Map。这个Map大小是80byte,存储信息的格式与位置也是固定的,存储信息包括:JS对象的存储空间有哪些成员,成员类型,成员偏移地址等。所以说,Map就是地图。
V8通过查询Map,可以知道存储空间内存放了什么,怎么存放的,进而正确操作JS对象。一句话总结:V8利用类型确定的Map类(c++实现的class对象)管理JS的动态对象。其实,在V8角度看,Map类型是确定的,所以整体数据类型就是确定的。最重要是Map提高了效率,因为它代替了耗时的JS对象类型检索操作。
下面来看Map的布局:
1. Map layout:
2. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+
3. // | _ Type _ | _ Description _ |
4. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+
5. // | TaggedPointer | map - Always a pointer to the MetaMap root |
6. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+
7. // | Int | The first int field |
8. // `---+----------+---------------------------------------------+
9. // | Byte | [instance_size] |
10. // +----------+---------------------------------------------+
11. // | Byte | If Map for a primitive type: |
12. // | | native context index for constructor fn |
13. // | | If Map for an Object type: |
14. // | | inobject properties start offset in words |
15. // +----------+---------------------------------------------+
16. // | Byte | [used_or_unused_instance_size_in_words] |
17. // | | For JSObject in fast mode this byte encodes |
18. // | | the size of the object that includes only |
19. // | | the used property fields or the slack size |
20. // | | in properties backing store. |
21. // +----------+---------------------------------------------+
22. // | Byte | [visitor_id] |
23. // +----+----------+---------------------------------------------+
24. // | Int | The second int field |
25. // `---+----------+---------------------------------------------+
26. // | Short | [instance_type] |
27. // +----------+---------------------------------------------+
28. // | Byte | [bit_field] |
29. // | | - has_non_instance_prototype (bit 0) |
30. // | | - is_callable (bit 1) |
31. // | | - has_named_interceptor (bit 2) |
32. // | | - has_indexed_interceptor (bit 3) |
33. // | | - is_undetectable (bit 4) |
34. // | | - is_access_check_needed (bit 5) |
35. // | | - is_constructor (bit 6) |
36. // | | - has_prototype_slot (bit 7) |
37. // +----------+---------------------------------------------+
38. // | Byte | [bit_field2] |
39. // | | - new_target_is_base (bit 0) |
40. // | | - is_immutable_proto (bit 1) |
41. // | | - unused bit (bit 2) |
42. // | | - elements_kind (bits 3..7) |
43. // +----+----------+---------------------------------------------+
44. // | Int | [bit_field3] |
45. // | | - enum_length (bit 0..9) |
46. // | | - number_of_own_descriptors (bit 10..19) |
47. // | | - is_prototype_map (bit 20) |
48. // | | - is_dictionary_map (bit 21) |
49. // | | - owns_descriptors (bit 22) |
50. // | | - is_in_retained_map_list (bit 23) |
51. // | | - is_deprecated (bit 24) |
52. // | | - is_unstable (bit 25) |
53. // | | - is_migration_target (bit 26) |
54. // | | - is_extensible (bit 28) |
55. // | | - may_have_interesting_symbols (bit 28) |
56. // | | - construction_counter (bit 29..31) |
57. // | | |
58. // +*************************************************************+
59. // | Int | On systems with 64bit pointer types, there |
60. // | | is an unused 32bits after bit_field3 |
61. // +*************************************************************+
62. // | TaggedPointer | [prototype] |
63. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+
64. // | TaggedPointer | [constructor_or_backpointer] |
65. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+
66. // | TaggedPointer | [instance_descriptors] |
67. // +*************************************************************+
68. // ! TaggedPointer ! [layout_descriptors] !
69. // ! ! Field is only present if compile-time flag !
70. // ! ! FLAG_unbox_double_fields is enabled !
71. // ! ! (basically on 64 bit architectures) !
72. // +*************************************************************+
73. // | TaggedPointer | [dependent_code] |
74. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+
75. // | TaggedPointer | [prototype_validity_cell] |
76. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+
77. // | TaggedPointer | If Map is a prototype map: |
78. // | | [prototype_info] |
79. // | | Else: |
80. // | | [raw_transitions] |
81. // +---------------+---------------------------------------------+前面提到Map是格式统一、大小固定的数据结构,即规定的位置代表指定的含义。上面代码是它的格式,它大小是80个字节,代码9行,instance_size代表图1中的存储空间的大小;代码24行,instance_type代表图1中的存储空间内的JS数据类型,例如:JS数组、JSFunction等。代码66行,instance_descriptors对JS数据的详细描述,例如:每个成员都是什么,存在哪里等。
注意:每一个JavaScript对象的存储空间的第一个位置都是一个Map指针,也就是每个js对象都有Map,Map大小不因js对象不同而改变,始终是80字节,存储内容也如上所示,保持不变。它用来描述JS对象的形状,相同形状的不同js对象共同一个Map。“形状相同”是类型一样,内部成员存储布局也一样,如下面代码:
function Point(x,y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
var fun1 = new Point(1,2);
var fun2 = new Point(3,4);fun1和fun2共用一个Map,因为他们的形状一样。执行fun2.z=80;之后,fun2的形状发生了变,随之会有新的Map产生,叫Map迁移,后续文章会讲解。
下面来看是Map类的核心代码:
1. class Map : public HeapObject {
2. public:
3. //...............省略很多..................
4. DECL_PRIMITIVE_ACCESSORS(bit_field, byte)
5. DECL_PRIMITIVE_ACCESSORS(relaxed_bit_field, byte)
6. // Bit positions for |bit_field|.
7. #define MAP_BIT_FIELD_FIELDS(V, _) \
8. V(HasNonInstancePrototypeBit, bool, 1, _) \
9. V(IsCallableBit, bool, 1, _) \
10. V(HasNamedInterceptorBit, bool, 1, _) \
11. V(HasIndexedInterceptorBit, bool, 1, _) \
12. V(IsUndetectableBit, bool, 1, _) \
13. V(IsAccessCheckNeededBit, bool, 1, _) \
14. V(IsConstructorBit, bool, 1, _) \
15. V(HasPrototypeSlotBit, bool, 1, _)
16. DEFINE_BIT_FIELDS(MAP_BIT_FIELD_FIELDS)
17. #undef MAP_BIT_FIELD_FIELDS
18. // Bit field 2.
19. DECL_PRIMITIVE_ACCESSORS(bit_field2, byte)
20. // Bit positions for |bit_field2|.
21. #define MAP_BIT_FIELD2_FIELDS(V, _) \
22. V(NewTargetIsBaseBit, bool, 1, _) \
23. V(IsImmutablePrototypeBit, bool, 1, _) \
24. V(UnusedBit, bool, 1, _) \
25. V(ElementsKindBits, ElementsKind, 5, _)
26. DEFINE_BIT_FIELDS(MAP_BIT_FIELD2_FIELDS)
27. #undef MAP_BIT_FIELD2_FIELDS
28. DECL_PRIMITIVE_ACCESSORS(bit_field3, uint32_t)
29. V8_INLINE void clear_padding();
30. // Bit positions for |bit_field3|.
31. #define MAP_BIT_FIELD3_FIELDS(V, _) \
32. V(EnumLengthBits, int, kDescriptorIndexBitCount, _) \
33. V(NumberOfOwnDescriptorsBits, int, kDescriptorIndexBitCount, _) \
34. V(IsPrototypeMapBit, bool, 1, _) \
35. V(IsDictionaryMapBit, bool, 1, _) \
36. V(OwnsDescriptorsBit, bool, 1, _) \
37. V(IsInRetainedMapListBit, bool, 1, _) \
38. V(IsDeprecatedBit, bool, 1, _) \
39. V(IsUnstableBit, bool, 1, _) \
40. V(IsMigrationTargetBit, bool, 1, _) \
41. V(IsExtensibleBit, bool, 1, _) \
42. V(MayHaveInterestingSymbolsBit, bool, 1, _) \
43. V(ConstructionCounterBits, int, 3, _)
44. DEFINE_BIT_FIELDS(MAP_BIT_FIELD3_FIELDS)
45. #undef MAP_BIT_FIELD3_FIELDS
46. DEFINE_FIELD_OFFSET_CONSTANTS(HeapObject::kHeaderSize,
47. TORQUE_GENERATED_MAP_FIELDS)
48. //...............省略很多..................
49. OBJECT_CONSTRUCTORS(Map, HeapObject);
50. };上述代码中,只保留了MAP格式的定义,我们对DEFINE_FIELD_OFFSET_CONSTANTS做展开,如下:
1. enum {
2. TORQUE_GENERATED_MAP_FIELDS_StartOffset= 7,
3. kInstanceSizeInWordsOffset=8, kInstanceSizeInWordsOffsetEnd = 8,
4. kInObjectPropertiesStartOrConstructorFunctionIndexOffset=9, kInObjectPropertiesStartOrConstructorFunctionIndexOffsetEnd = 9,
5. kUsedOrUnusedInstanceSizeInWordsOffset=10, kUsedOrUnusedInstanceSizeInWordsOffsetEnd = 10,
6. kVisitorIdOffset=11, kVisitorIdOffsetEnd = 11,
7. kInstanceTypeOffset=12, kInstanceTypeOffsetEnd = 13,
8. kBitFieldOffset=14, kBitFieldOffsetEnd = 14,
9. kBitField2Offset=15, kBitField2OffsetEnd = 15,
10. kBitField3Offset=16, kBitField3OffsetEnd = 19,
11. kOptionalPaddingOffset=20, kOptionalPaddingOffsetEnd = 23,
12. kStartOfStrongFieldsOffset=24, kStartOfStrongFieldsOffsetEnd = 23,
13. kPrototypeOffset=24, kPrototypeOffsetEnd = 31,
14. kConstructorOrBackPointerOffset=32, kConstructorOrBackPointerOffsetEnd = 39,
15. kInstanceDescriptorsOffset=40, kInstanceDescriptorsOffsetEnd = 47,
16. kLayoutDescriptorOffset=48, kLayoutDescriptorOffsetEnd = 55,
17. kDependentCodeOffset=56, kDependentCodeOffsetEnd = 63,
18. kPrototypeValidityCellOffset=64, kPrototypeValidityCellOffsetEnd = 71,
19. kEndOfStrongFieldsOffset=72, kEndOfStrongFieldsOffsetEnd = 71,
20. kStartOfWeakFieldsOffset=72, kStartOfWeakFieldsOffsetEnd = 71,
21. kTransitionsOrPrototypeInfoOffset=72, kTransitionsOrPrototypeInfoOffsetEnd = 79,
22. kEndOfWeakFieldsOffset=80, kEndOfWeakFieldsOffsetEnd = 79,
23. kSize=80, kSizeEnd = 79,
24. }代码2行TORQUE_GENERATED_MAP_FIELDS_StartOffset说明了Map的起始偏移是7(从0算起),也就是第8个字节,前面提到一个Map的大小是80个字节,由于Map继承Heap对象,这80个字节中的前8个字节是Heap对象,所以它的实际可用的字节是72个,每个成员的偏移和大小与前述第一段代码(Map Layout)对应。Map的创建和回收由V8的Heap负责管理,下面是创建Map的源码位置:
1. AllocationResult Heap::AllocateRaw(int size_in_bytes, AllocationType type,
2. AllocationOrigin origin,
3. AllocationAlignment alignment) {
4. //.....省略很多.......
5. if (AllocationType::kYoung == type) {
6. //.....省略很多.......
7. } else if (AllocationType::kOld == type) {
8. //.....省略很多.......
9. } else if (AllocationType::kCode == type) {
10. if (size_in_bytes <= code_space()->AreaSize() && !large_object) {
11. allocation = code_space_->AllocateRawUnaligned(size_in_bytes);
12. } else {
13. allocation = code_lo_space_->AllocateRaw(size_in_bytes);
14. }
15. } else if (AllocationType::kMap == type) {
16. allocation = map_space_->AllocateRawUnaligned(size_in_bytes);
17. } else if (AllocationType::kReadOnly == type) {
18. #ifdef V8_USE_SNAPSHOT
19. DCHECK(isolate_->serializer_enabled());
20. #endif
21. DCHECK(!large_object);
22. DCHECK(CanAllocateInReadOnlySpace());
23. DCHECK_EQ(AllocationOrigin::kRuntime, origin);
24. allocation =
25. read_only_space_->AllocateRaw(size_in_bytes, alignment, origin);
26. } else {
27. UNREACHABLE();
28. }
29. return allocation;
30. }代码15行,type=KMap时size_in_bytes是80,进入代码16行分配内存,图2给出了执行代码16的调用堆栈。
AllocateRaw()分配内存后返回到AllocateMap(),对内存进行初始化,代码如下:
1. Map Factory::InitializeMap(Map map, InstanceType type, int instance_size,
2. ElementsKind elements_kind,
3. int inobject_properties) {
4. map.set_instance_type(type);
5. map.set_prototype(*null_value(), SKIP_WRITE_BARRIER);
6. map.set_constructor_or_backpointer(*null_value(), SKIP_WRITE_BARRIER);
7. map.set_instance_size(instance_size);
8. if (map.IsJSObjectMap()) {
9. DCHECK(!ReadOnlyHeap::Contains(map));
10. map.SetInObjectPropertiesStartInWords(instance_size / kTaggedSize -
11. inobject_properties);
12. DCHECK_EQ(map.GetInObjectProperties(), inobject_properties);
13. map.set_prototype_validity_cell(*invalid_prototype_validity_cell());
14. } else {
15. DCHECK_EQ(inobject_properties, 0);
16. map.set_inobject_properties_start_or_constructor_function_index(0);
17. map.set_prototype_validity_cell(Smi::FromInt(Map::kPrototypeChainValid));
18. }
19. map.set_dependent_code(DependentCode::cast(*empty_weak_fixed_array()),
20. SKIP_WRITE_BARRIER);
21. map.set_raw_transitions(MaybeObject::FromSmi(Smi::zero()));
22. map.SetInObjectUnusedPropertyFields(inobject_properties);
23. map.SetInstanceDescriptors(isolate(), *empty_descriptor_array(), 0);
24. if (FLAG_unbox_double_fields) {
25. map.set_layout_descriptor(LayoutDescriptor::FastPointerLayout());
26. }
27. //.................省略很多...............
28. return map;
29. }上面代码是对Map的初始化,按最开始给出的May layout对每个字段(bit位、byte位、short位等)进行初始化。代码8,9,10,13行对JSObject对象中的InObject数据进行初始化,“InObject”是存储在JSObject对象内部的数据,访问这些数据更快。代码28返回Map,至此Map生成完毕,后续会通过这个Map访问图1中的存储空间,请读者自行跟踪代码,不再赘述。
3 Map初始化
在V8的启动阶段,CreateInitialMaps()对所有Javascript类型分别建立对应的空Map,“空Map”说明了创建某个JS类型数据所需的最小内存空间。这样,开发者创建javascript对象时,V8先用对应的空Map申请一段最小空间,随时开发者对JS对象添加成员,Map也会发生改变。下面给出Map初始化的源码:
1. bool Heap::CreateInitialMaps() {//....代码太长,中间省略很多........
2. HeapObject obj;
3. {
4. AllocationResult allocation = AllocatePartialMap(MAP_TYPE, Map::kSize);
5. if (!allocation.To(&obj)) return false;
6. }
7. Map new_meta_map = Map::unchecked_cast(obj);
8. set_meta_map(new_meta_map);
9. new_meta_map.set_map_after_allocation(new_meta_map);
10. //...................分隔线....................
11. ReadOnlyRoots roots(this);
12. { // Partial map allocation
13. #define ALLOCATE_PARTIAL_MAP(instance_type, size, field_name) \
14. { \
15. Map map; \
16. if (!AllocatePartialMap((instance_type), (size)).To(&map)) return false; \
17. set_##field_name##_map(map); \
18. }
19. ALLOCATE_PARTIAL_MAP(FIXED_ARRAY_TYPE, kVariableSizeSentinel, fixed_array);
20. ALLOCATE_PARTIAL_MAP(WEAK_FIXED_ARRAY_TYPE, kVariableSizeSentinel,
21. weak_fixed_array);
22. ALLOCATE_PARTIAL_MAP(WEAK_ARRAY_LIST_TYPE, kVariableSizeSentinel,
23. //...................分隔线....................
24. #undef ALLOCATE_PARTIAL_MAP
25. }
26. // Allocate the empty array.
27. {
28. AllocationResult alloc =
29. AllocateRaw(FixedArray::SizeFor(0), AllocationType::kReadOnly);
30. if (!alloc.To(&obj)) return false;
31. obj.set_map_after_allocation(roots.fixed_array_map(), SKIP_WRITE_BARRIER);
32. FixedArray::cast(obj).set_length(0);
33. }
34. set_empty_fixed_array(FixedArray::cast(obj));
35. //...................分隔线....................
36. FinalizePartialMap(roots.meta_map());
37. FinalizePartialMap(roots.fixed_array_map());
38. FinalizePartialMap(roots.weak_fixed_array_map());
39. {
40. if (!AllocateRaw(FixedArray::SizeFor(0), AllocationType::kReadOnly)
41. .To(&obj)) {
42. return false;
43. }
44. obj.set_map_after_allocation(roots.closure_feedback_cell_array_map(),
45. SKIP_WRITE_BARRIER);
46. FixedArray::cast(obj).set_length(0);
47. set_empty_closure_feedback_cell_array(ClosureFeedbackCellArray::cast(obj));
48. }
49. DCHECK(!InYoungGeneration(roots.empty_fixed_array()));
50. roots.bigint_map().SetConstructorFunctionIndex(
51. Context::BIGINT_FUNCTION_INDEX);
52. return true;
53. }分隔线把代码分成了四部分,代码4,5,6,7,8行创建meta_data,这是所有Map都要用的元信息;代码13~22行,结合宏模板ALLOCATE_PARTIAL_MAP创建ARRAY和ARRAY_LIST类型的Map;代码27~34行创建其类型Map;分三批创建是因为后者的创建要依赖前者。最后,36开始,是完成所有Map创建的最终工作,并存储到root_table中,图3给出部分Map在root_table中的存储位置。
root_table是由下面的一系列宏板定义实现的指针类型数组,通过debug跟踪代码,可以看到meta_data在root_table中的位置下标是10,其它的下标请读者自行计算。
#define READ_ONLY_ROOT_LIST(V) \
STRONG_READ_ONLY_ROOT_LIST(V) \
INTERNALIZED_STRING_ROOT_LIST(V) \
PRIVATE_SYMBOL_ROOT_LIST(V) \
PUBLIC_SYMBOL_ROOT_LIST(V) \
WELL_KNOWN_SYMBOL_ROOT_LIST(V) \
STRUCT_MAPS_LIST(V) \
ALLOCATION_SITE_MAPS_LIST(V) \
DATA_HANDLER_MAPS_LIST(V)
#define MUTABLE_ROOT_LIST(V) \
STRONG_MUTABLE_IMMOVABLE_ROOT_LIST(V) \
STRONG_MUTABLE_MOVABLE_ROOT_LIST(V) \
V(StringTable, string_table, StringTable) \
SMI_ROOT_LIST(V)
#define ROOT_LIST(V) \
READ_ONLY_ROOT_LIST(V) \
MUTABLE_ROOT_LIST(V)上述定义了root_table,通过宏模板的参数,可猜想出每个元素的大体功能和作用,配合debug跟踪来验证猜想是否确。
好了,今天到这里,下次见。
恳请读者批评指正、提出宝贵意见
微信:qq9123013 备注:v8交流 邮箱:[email protected]
本文由灰豆原创发布
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK