

Compound 合约部署
source link: https://learnblockchain.cn/article/2915
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Compound 合约部署
最近一直再研究Compound的代码,compound能够经历牛熊成长为借贷龙头,它的合约逻辑代码上面有非常多值得学习的地方。鉴于此前一直只是再看代码,缺少了一步实际跑代码的过程,感觉学习Compound时,始终有点缺憾。故今天就详细记录下Compound合约的部署步骤,以飨读者。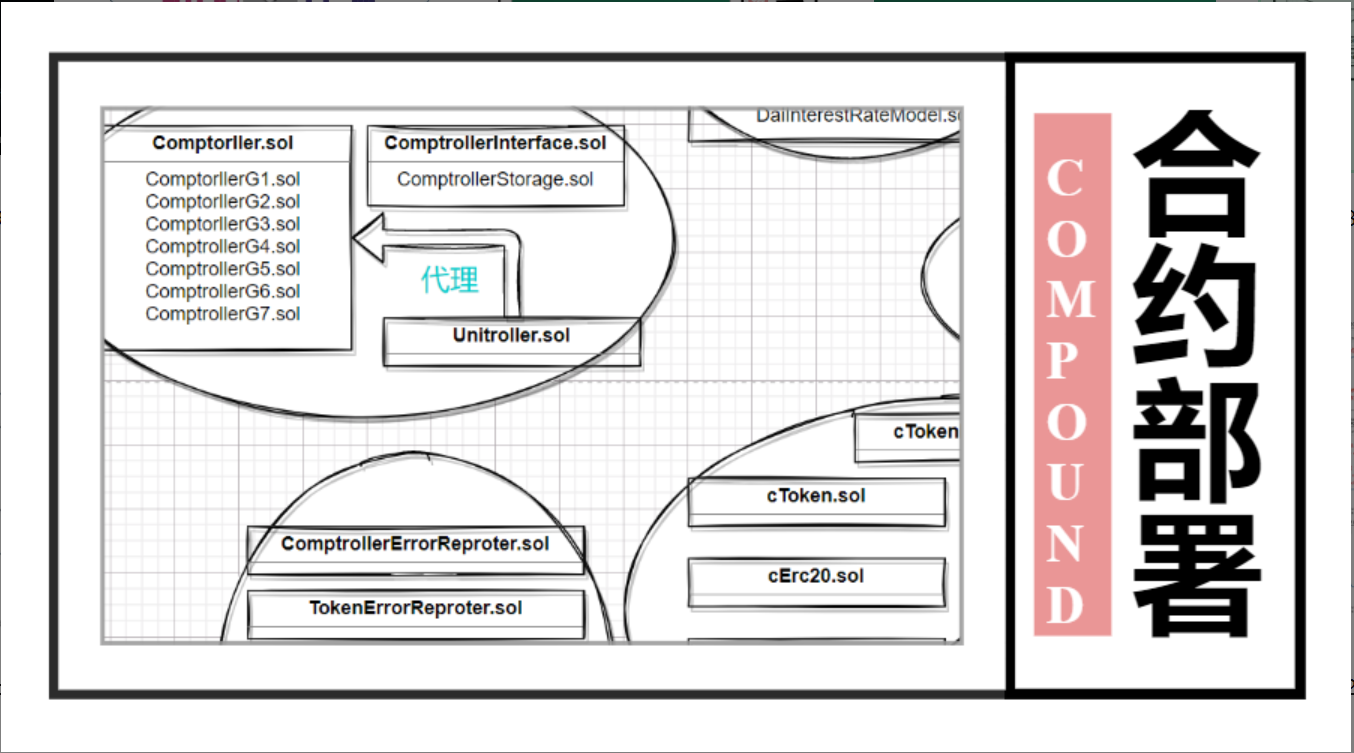
可以点击链接查看原文:https://t.1yb.co/A8CX
也顺便关注我一下:微信号woodward1993, 我的公众号:bug合约写手,涨粉涨粉:)
Compound合约结构
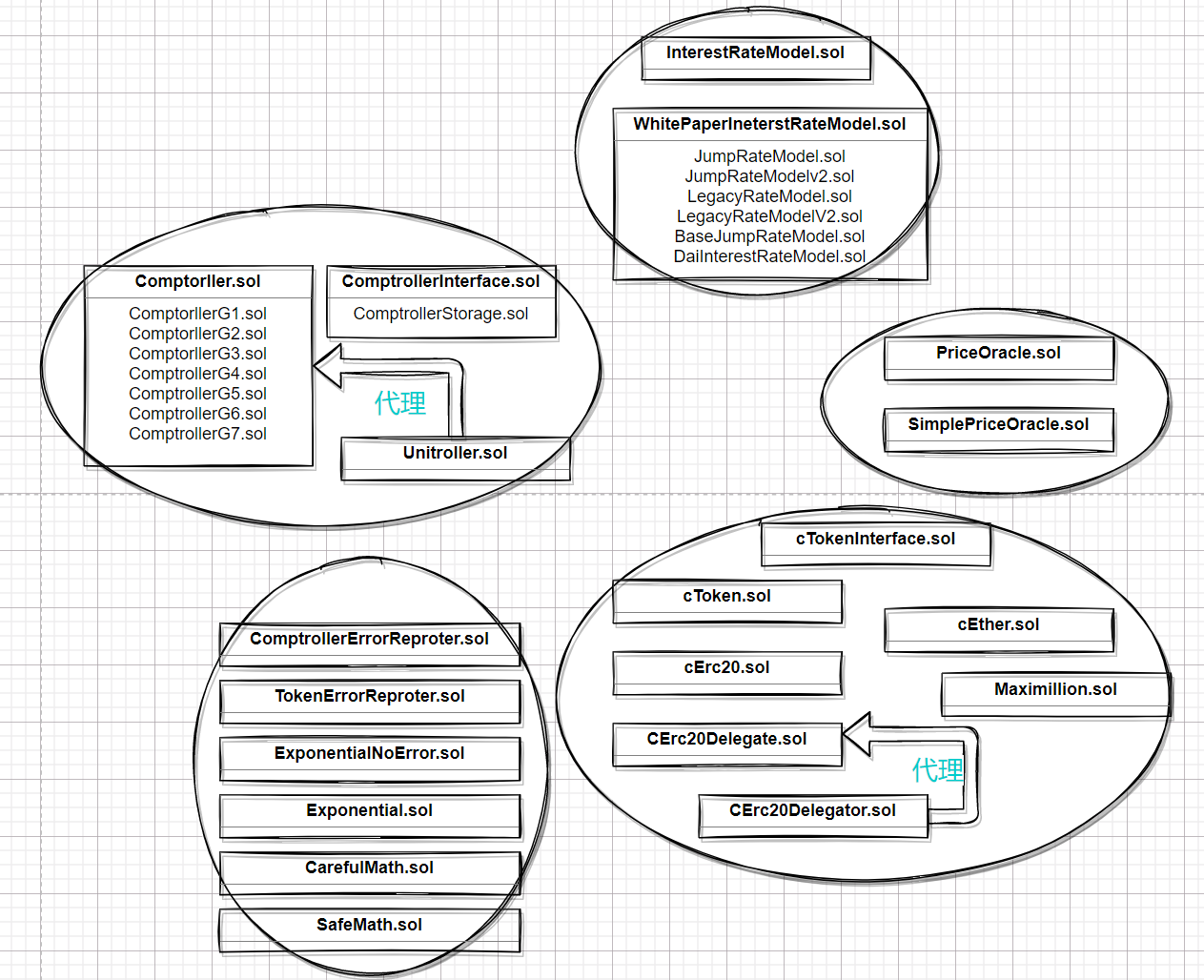
从上面的图片可以看到,Compound中含有的合约代码量还是很大的,文件数量30+。故再部署前,我们需要先梳理清楚各个合约之间的关系,并将其分组,梳理出各个模块,及初始化参数。
为简单起见,我们采取渐进式部署法 😆, 即每一步都只把主要逻辑代码跑起来,不相关的合约就不部署。
小目标:最小可运行
分析如上图,最小可运行的合约至少应该包括:comptorller模块,ctoken模块,InterestRate模块,PriceOracle模块以及辅组合约模块。
comptroller模块
在comptorller模块部署中,我们选择ComptorllerG1, 因为G1是Comptorller的第一个版本,参数最少
模块
文件
初始化参数
初始化步骤
comptroller模块
Unitroller.sol
NA
_setPendingImplementation(comptrollerG1)
ComptrollerG1.sol
NA
_become()
注意:再comptorller模块中,需要终端用户调用的函数为enterMarkets,故上述调用完成后还需要手动调用enterMarkets函数.
在初始化过程中,最重要的一点是想清楚comptroller._become应该是谁来调用?一种误解是使用unitroller,即代理合约来调用该become方法,因为所有的数据都保存在代理合约中。但实际上在compound设计中,unitroller是代理合约,comptroller是逻辑实现合约,通过delegatecall来实现远程合约调用。
最简单的一种方式是在Proxy代理合约中,增加一个管理函数,让管理员来设置逻辑实现合约的地址。compound中也使用了这一模式,在unicontroller合约中,它添加了 转移Proxy所有权的函数,其impl合约需要接受转移,以防止意外地升级到无效的合同。
unitroller = new Unitroller();
comptroller = new ComptrollerG1();
unitrollerProxy = ComptrollerG1(address(unitroller));
unitroller._setPendingImplementation(address(comptroller));
unitrollerProxy._setPriceOracle(priceOracle);
unitrollerProxy._setCloseFactor(500000000000000000);
unitrollerProxy._setMaxAssets(20);
unitrollerProxy._setLiquidationIncentive(1080000000000000000);
unitrollerProxy._supportMarket(CToken(address(cUni)));
Comptroller模块部署完成后,系统的存储变化:
Unitroller {
address public admin => alice;
address public pendingAdmin => address(0);
address public comptrollerImplementation => address(ComptrollerG1);
address public pendingComptrollerImplementation => address(0);
PriceOracle public oracle => address(SimplePriceOracle);
uint public closeFactorMantissa => 500000000000000000;
uint public liquidationIncentiveMantissa => 1080000000000000000;
uint public maxAssets => 20;
// msg.sender => [cUni]
mapping(address => CToken[]) public accountAssets;
struct Market {
bool isListed;
uint collateralFactorMantissa;
mapping(address => bool) accountMembership;
}
//cUni => (true, 600000000000000000, {msg.sender:true})
mapping(address => Market) public markets;
}
priceOracle模块
此处只需要部署测试用的simplePriceOracle部分,compound中关于pricefeed的合约留在后续部署:
模块 文件 初始化参数 初始化步骤 priceOracle模块 SimplePriceOracle.sol NA NASimplePriceOracle priceOracle = new SimplePriceOracle();
priceOracle.setUnderlyingPrice(cUni, 1e18);
interestRate模块,
此处只需要部署最简单的WhitePaperInterestRateModel部分,其他的利率模型留待下次部署
模块 文件 初始化参数 初始化步骤 InterestRate模块 WhitePaperInterestRateModel.solbaseRate=50000000000000000 multiplier=120000000000000000
constructor(baseRate,multiplier)
WhitePaperInterestRateModel whitePaper = new WhitePaperInterestRateModel(50000000000000000,120000000000000000);
cToken模块
这里我们选择cUni来部署,涉及到的合约有:cUniDelegate,cUNI,Uni(测试用的ERC20token)
模块 文件 初始化参数 初始化步骤 cToken模块 token.sol
部署一个测试代币:Uni
cERC20Delegate.sol
NA
_becomeImplementation()
CErc20Delegator.sol(cUni)
如下图所示
constructor(),_setImplementation()
cToken模块部署完成后,系统存储的变化:
cUni=>{
//cTokenStorage
bool internal _notEntered = true;
string public name = Compound Uniswap;
string public symbol = cUNI;
uint8 public decimals = 8;
address payable public admin = alice;
address payable public pendingAdmin = address(0);
ComptrollerInterface public comptroller = address(unitroller);
InterestRateModel public interestRateModel = address(whitepaper);
uint internal initialExchangeRateMantissa ;
uint public reserveFactorMantissa = 250000000000000000;
uint public accrualBlockNumber = 12927103;
uint public borrowIndex = 1067279966577335160;
uint public totalBorrows = 818650076167450321877884;
uint public totalReserves = 38954225225705070309036;
uint public totalSupply = 63681038419777549;
mapping (address => uint) internal accountTokens;
mapping (address => mapping (address => uint)) internal transferAllowances;
struct BorrowSnapshot {
uint principal;
uint interestIndex;
}
mapping(address => BorrowSnapshot) internal accountBorrows;
//cErc20storage
address public underlying = address(Uni);
//cDelegationStorage
address public implementation = address(cDeleagator);
}
对cUni的构造函数中传入数据进行分析如下:
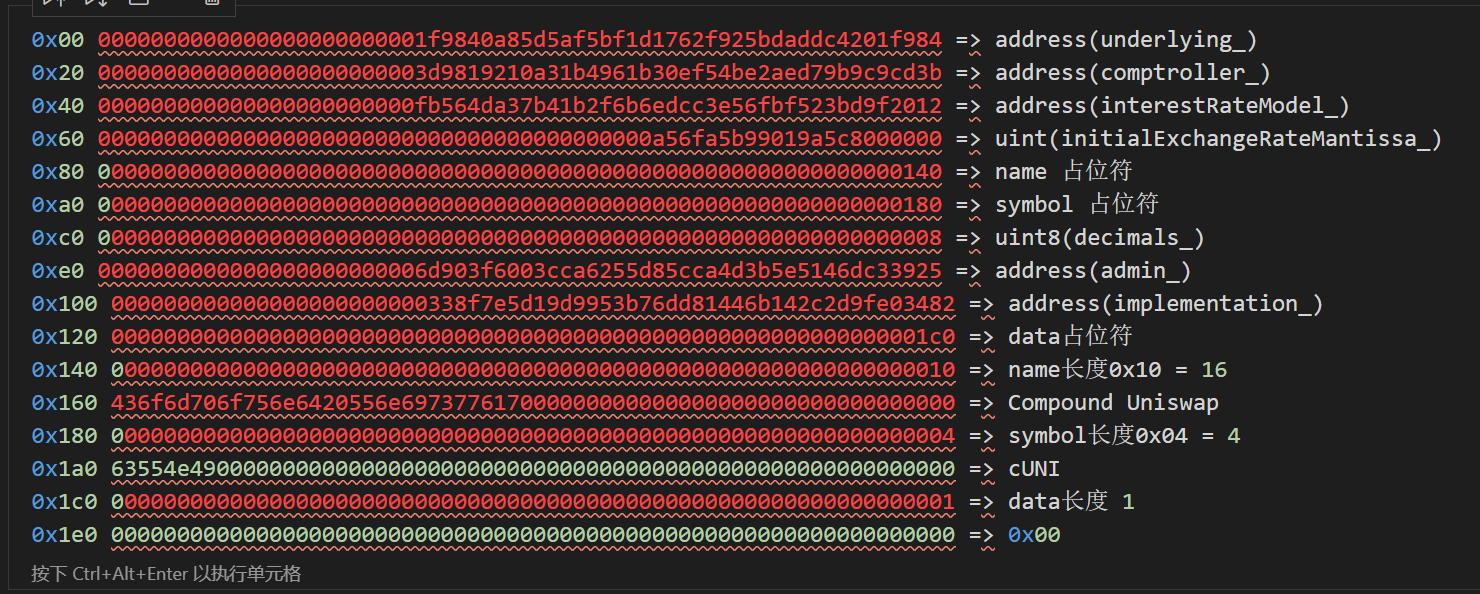
故我们的初始化代码为:
Token uni = new Token("Uniswap Test","Uni",18,uint(-1));
cERC20Delegate cUniDelegate = new cERC20Delegate();
bytes memory data = 0x00;
CErc20Delegator cUni = new CErc20Delegator(address(uni),
address(unitroller),
address(whitepaper),
200000000000000000000000000,
"Compound Uniswap",
"cUNI",
alice,
address(cUniDelegate),
data
);
cUni._setImplementation(address(cUniDelegate), false, data);
cUni._setReserveFactor(250000000000000000);
整理setup
将上述4个模块的初始化代码整理如下:
pragma solidity ^0.5.16;
//cToken
import "./CErc20Delegator.sol";
import "./CErc20Delegate.sol";
import "./Token.sol";
//comptroller
import "./Unitroller.sol";
import "./ComptrollerG1.sol";
//interestModel
import "./WhitePaperInterestRateModel.sol";
//priceOracle
import "./SimplePriceOracle.sol";
contract Setup {
Token public uni;
CErc20Delegator public cUni;
CErc20Delegate public cUniDelegate;
Unitroller public unitroller;
ComptrollerG1 public comptroller;
ComptrollerG1 public unitrollerProxy;
WhitePaperInterestRateModel public whitePaper;
SimplePriceOracle public priceOracle;
constructor() public payable{
//先初始化priceOracle
priceOracle = new SimplePriceOracle();
//再初始化whitepaper
whitePaper = new WhitePaperInterestRateModel(50000000000000000,
120000000000000000);
//再初始化comptroller
unitroller = new Unitroller();
comptroller = new ComptrollerG1();
unitrollerProxy = ComptrollerG1(address(unitroller));
unitroller._setPendingImplementation(address(comptroller));
comptroller._become(unitroller, priceOracle, 500000000000000000, 20, true);
unitrollerProxy._setPriceOracle(priceOracle);
unitrollerProxy._setCloseFactor(500000000000000000);
unitrollerProxy._setMaxAssets(20);
unitrollerProxy._setLiquidationIncentive(1080000000000000000);
//最后初始化cToken
uni = new Standard_Token(uint(-1),"Uniswap Test",18,"Uni");
cUniDelegate = new CErc20Delegate();
bytes memory data = new bytes(0x00);
cUni = new CErc20Delegator(
address(uni),
ComptrollerInterface(address(unitroller)),
InterestRateModel(address(whitePaper)),
200000000000000000000000000,
"Compound Uniswap",
"cUNI",
8,
address(uint160(address(this))),
address(cUniDelegate),
data
);
cUni._setImplementation(address(cUniDelegate), false, data);
cUni._setReserveFactor(250000000000000000);
//设置uni的价格
priceOracle.setUnderlyingPrice(CToken(address(cUni)), 1e18);
//支持的markets
unitrollerProxy._supportMarket(CToken(address(cUni)));
unitrollerProxy._setCollateralFactor(CToken(address(CUni)),
600000000000000000);
//将uni的代币全部转移给msg.sender,方便后续测试
uni.transfer(msg.sender, uni.balanceOf(address(this)));
}
}
前面我们部署了comptroller合约,现在我们需要写一部分测试,看具体的合约逻辑执行。在最小可运行的compound合约中,我们部署了抵押token:uni,以及compound铸造出来的token:cUni. 并部署了cUni实际调用的逻辑cUniDelegate, 然后cUni的借贷模型中采用的是WhitepaperInterestRateModel,对应的审计合约是comptrollerG1.
下面我们分别就compound中,最核心的用户交互逻辑来编写5个测试,简单验证逻辑可行性。
测试1:存 mint
用户向compound中存款的逻辑是:用户向compound中存入Uni代币, compound根据当前的汇率算出铸造的cUni代币数量,将对应的cUni代币转账给用户。
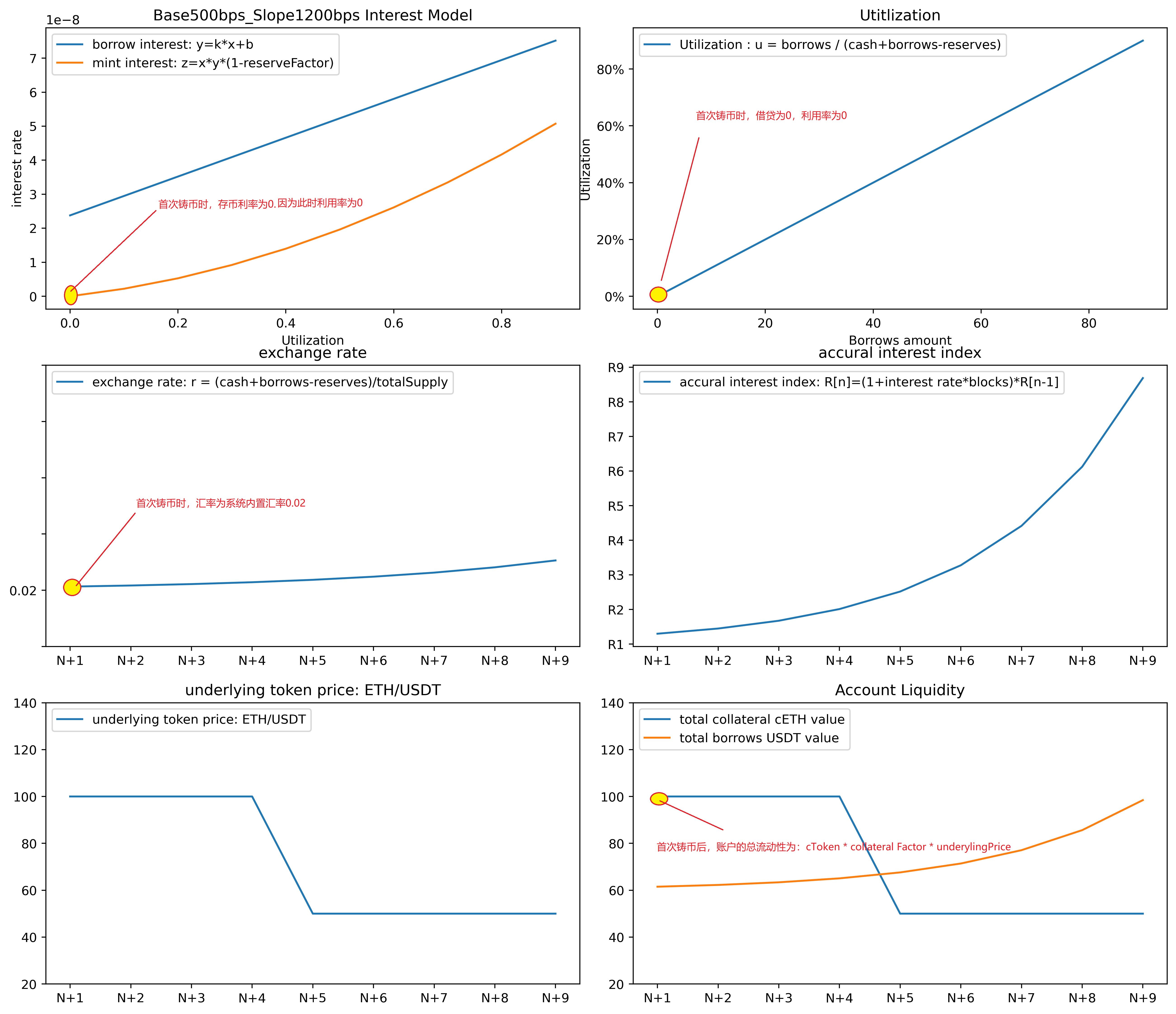
从上图可以分析得到:
对于第一笔mint交易,即一个空的market中首笔铸币交易,其汇率exchange rate为初始的0.02, 再没有任何贷款的情况下,利用率u = 0, 存款利率也为0, 此时该账户的总流动性为:cToken*collateral factor * price
则具体的测试流程如下:
//alice 有所有的Uni代币
uni.balanceOf(alice) = uint(-1)
//alice 调用unitroller的enterMarkets方法, 因为在mintAllowed函数中,存在一个检查:require(markets[cToken].isListed), 故即使在mint中也需要先调用enterMarkets
address[] memory addr = new address[](1);
addr[0] = cUni;
ComptrollerG1(address(unitroller)).enterMarkets(addr);
//此时alice调用enterMarkets后,全局变量accountAssets[alice] = cToken[cUni], markets[cUni]={true, 60%,{alice:true},false}
//alice 调用cUni的mint方法
uni.approve(address(cUni),uint(-1));
cUni.mint(7584007913129639935);
7584007913129639935/200000000
cUni.balanceOf(alice) = 37920039565;
cUni.totalSupply() = 37920039565
cUni.getCash() = 7584007913129639935
cUni.supplyRatePerBlock() = 0 //此时没有借款,利用率为0
ComptrollerG1(address(unitroller)).getAccountLiquidity(alice) = 4550404747877783960 = 7584007913129639935 * 0.6 //用户流动性:为UnderlyingToken * 0.6 * price
用户函数:enterMarkets
用户的地址中对应用户的所有资产列表,当计算一个用户的所有流动性时。在借贷一种资产前,一个或者多种资产必须被提供给compound以用作抵押。在借贷发生前,任何借贷出的资产必须通过这种方式添加进入compound中。该函数的返回值是一个列表,即该用户的所有资产列表。
function enterMarkets(address[] memory cTokens) public returns (uint[] memory) {
//对于每一种cToken
uint len = cTokens.length;
uint[] memory result = new uint[](len);
for (uint i=0; i < len; i++) {
//首先检查用户是否已经添加过该种cTOken,如果已经添加过,则返回true,否则继续
CToken cToken = CToken(cTokens[i]);
Markets storage market = markets[address(cToken)];
if (!market.isListed) {
result[i] = uint(Error.MARKET_NOT_LISTED);
continue;
}
//其次检查用户是否达到了最大种类的资产,如果达到了最大种类资产,则返回false,否则继续
if(accountAssets[msg.sender].length >= maxAssets) {
result[i] = uint(Error.TOO_MANY_ASSETS);
continue;
}
//检查该种cToken是否已经被列入,如果没有,则返回false,否则继续
if (market.accountMembership[msg.sender] == true) {
result[i] = uint(Error.NO_ERROR);
continue;
}
//检查预言机的价格不等于0
//将资产添加进入accountAssts中,并将用户的memberships[cToken][user]=true
market.accountMembership[msg.sender] = true;
accountAssets[msg.sender].push(cToken);
//继续下一种资产,注意列表的大小会随着for循环而增加,故比较maxAssets时,必须用storage的数值来比较
result[i] = uint(Error.NO_ERROR);
}
return result;
//返回累计的结果
}
测试2:借 borrow
借币逻辑是:用户在compound中有多种cToken资产,记录在accountAssets中。 然后用户向compound借出一定量的uni资产,同时增加用户的负债额度。compound在接受用户的借款请求时,首先会检查cToken有没有上市,再检查用户是否enterMarket,然后根据现在的预言机报价检查用户的账户流动性。
整个borrow流程分为三步:
第一步:accuralInterest
如图4所示。在accuralInterest步骤中,如Accural Interest Index图4, 从A4点移动到B4点,即:
同时计算截至该block前的借贷额度所产生的利息,即
然后将产生的利息的一部分存入总的reserves中,即
此时系统中的totalBorrows并不包括即将借贷的部分,且market中的资金利用率也不变,借贷利率不变维持在A点
第二步:borrowAllowed
如图6所示。在borrowAllowed步骤中,Comptroller除开验证cToken的合法性外,以及用户是否enterMarket,还会计算虚拟的账户流动性。首先计算该账户中所有的cToken对应的价值。计算方法是cToken的数量按照B点对应的汇率换算成对应的Underlying Token,然后乘以market中设置的collateral factor,然后乘以该underlying token的实时价格, 即
此处的exchangeRate计算中,cash和totalBorrows仅为B点前结息部分,不包含即将借出的borrowAmount部分。
对于借贷部分,它首先拿到已经结息的借贷总额accountBorrows[B],然后加上此次要借出的borrowAmount,然后乘以underlying token的实时价格, 即。
用资产的价值减去债务的价值得到流动性,如果流动性为正,则允许借出。如果流动性为负,则不允许借出。
第三步:borrowFresh
在borrowFresh这一步,主要是拿到截至此刻的accountBorrows[msg.sender]对应的已贷款(含利息)以及对用此刻的InterestRate[A],
然后将新的贷款额和最新的InterestRate[B]更新到accountBalance中。并更新整个market的totalBorrows,即移动market的利用率从A点到B点,以及该利用率对应的借贷和存储利率。
注意:在这一步中,要理解汇率exchange Rate的变化。简单讲,汇率会缓慢增加,增加的原因是每一个ΔBlocks所对应产生的利息(不是利率)的一部分(1-reserveFactor)存入了market中,即totalBorrows⋅borrowRatePrev⋅ΔBlocks⋅(1−reserveFactor), 导致了underlyingToken的单调递增。如果单纯看汇率的公式:
很难以看出其为何单调递增。原因就在于totalBorrows在每一次调用accuralInterest后,都会复利计算,即将产生的利息加回到债务作为新的债务中。而产生的一部分利息会存入资金池的reserve中,剩余的一部分利息则会存入资金池里,用于给cToken持有人.
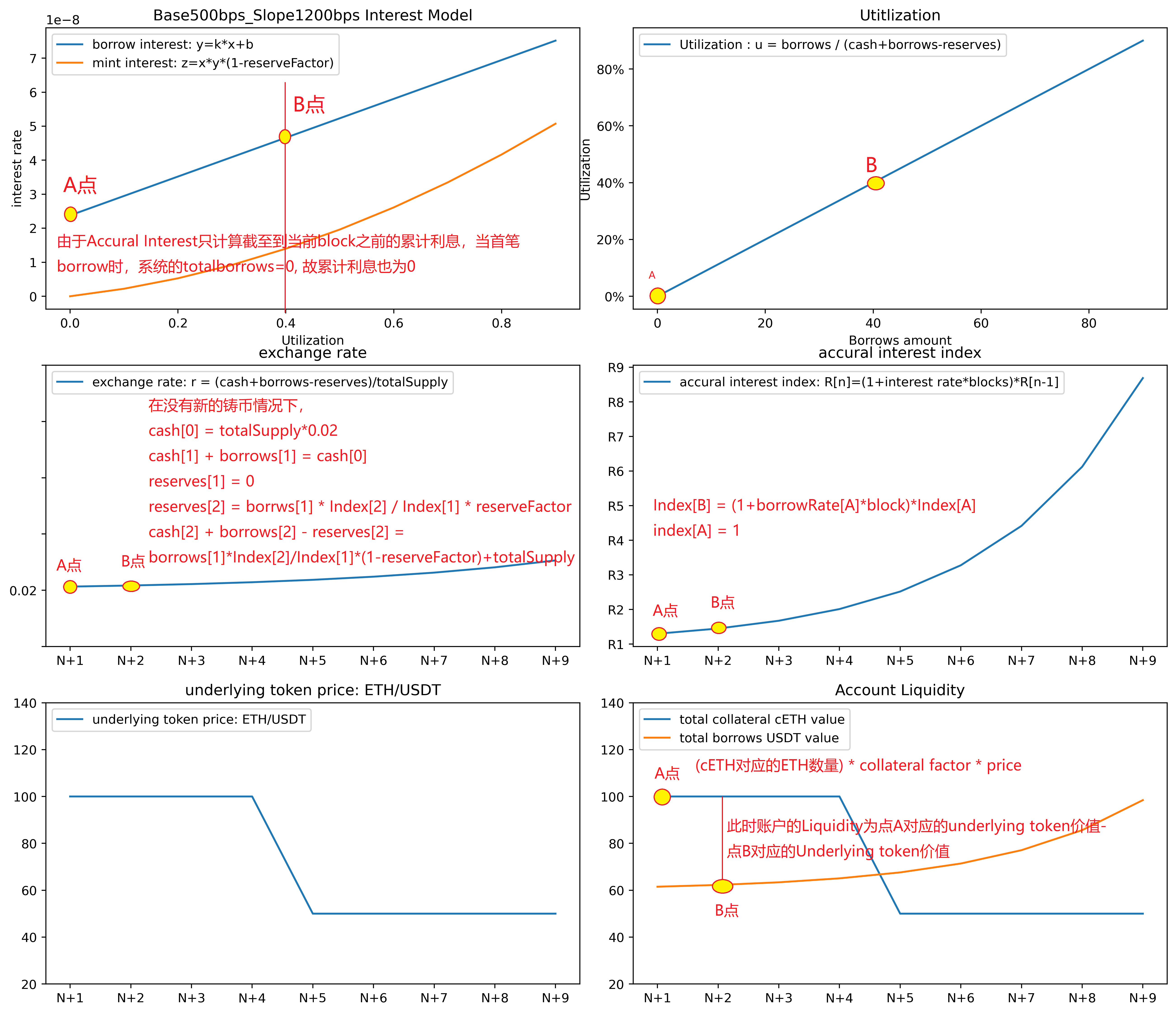
当借出一定数量的underlying tokens时,compound会首先计算下截止到当前block为止,此前的借贷额度所产生的利息,并将该利息的一部分存入reserve中,剩余的利息用于给cToken增值
function borrowAllowed(address cToken, address borrower, uint borrowAmount)
external
returns (uint)
{
//检查cToken是否上架
Market memory market = markets[cToken];
require(market.isListed,"ComptrollerG1/borrowAllowed no listed");
//检查用户是否enterMarkets,通过cToken与用户的membership来检查
require(market.membership[borrower], "ComptrollerG1/borrowAllowed no membership");
//检查underlying Token的实时价格
require(priceOracle.getUnderlyingPrice(cToken) != 0, "Comptroller/borrowAllowed underlying price should not be 0");
//计算用户总资产的流动性
(Error err, uint liquidity, uint shortfall) = getHypotheticalAccountLiquidityInternal(borrower, CToken(cToken),0,borrowAmount);
require(err == Error.NO_ERROR, "Comptroller/borrowAllowed getHyp falied");
//返回
require(shortfall == 0, "Comptroller/borrowAllowed insufficient liquidity");
return liquidity;
}
测试流程:
//alice 在compound中存入了7584007913129639935的uni代币,获得了37920039565的cUni代币
//alice 向compound提出借款4584007913129639935的uni代币
cUni.borrow(2584007913129639935);
cUni.totalBorrows() = 2584007913129639935;
cUni.getCash() == 5000000000000000000 = 7584007913129639935 - 2584007913129639935
cUni.supplyRatePerBlock = 11046856810
cUni.exchangeRateStored() = 200000000003418771090092875
cUni.borrowRatePerBlock() = 43229717700
利用率:utilization = cUni.supplyRatePerBlock / cUni.borrowRatePerBlock * (1- 0.25) =
cUni.borrowIndex() = 1000000095129377644
cUni.accrualBlockNumber() = 4
测试3:还 repay
repay操作是borrow的逆操作,可以通过repayBorrow偿还自己的贷款,repayBorrowBehalf代为偿还他人贷款,其具体逻辑是用户批准cToken合约使用其underlying token,先调用accuralInterest计算目前利率指数和对全部借贷额计息,然后调用comptroller.repayBorrowAllowed函数检查是否可以偿还,最后调用repayBorrowFresh偿还。
accuralInterest
在偿还贷款前,用户会首先调用accuralIntrest函数,其作用是计算最新的利率指数,并对全部借贷额计息。如图所示,利率指数会从B点移动到C点。注意利率指数与accountBorrows无关,且其总是呈现指数增加的形式。因为在利率指数的定义中,其只与borrowRatePrev, 即图中的borrowRate[B]点相关,即上一时刻的借贷利率相关,与当前账户的借贷数目无关。
repayBorrowAllowed
在comptroller的repayBorrowAllowed函数中只检查了cToken的合法性
repayBorrowFresh
即先拿到已结息的accountBorrows[msg.sender]参数,包含上一时刻的贷款本金及利率指数,并利用当前时刻的Index对其结息后减去repayBorrowAmount,即:
然后从已结息的totalBorrows中扣除repayBorrowAmount。
最后从msg.sender中转账对应的repayBorrowAmount Token到cToken中,此时的资金利用率从B点回落到C点,对应的贷款利率也从B点回落到C点。
测试流程如下:
uni.approve(cToken, repayBorrowAmount);
cUni.repayBorrow(repayBorrowAmount);
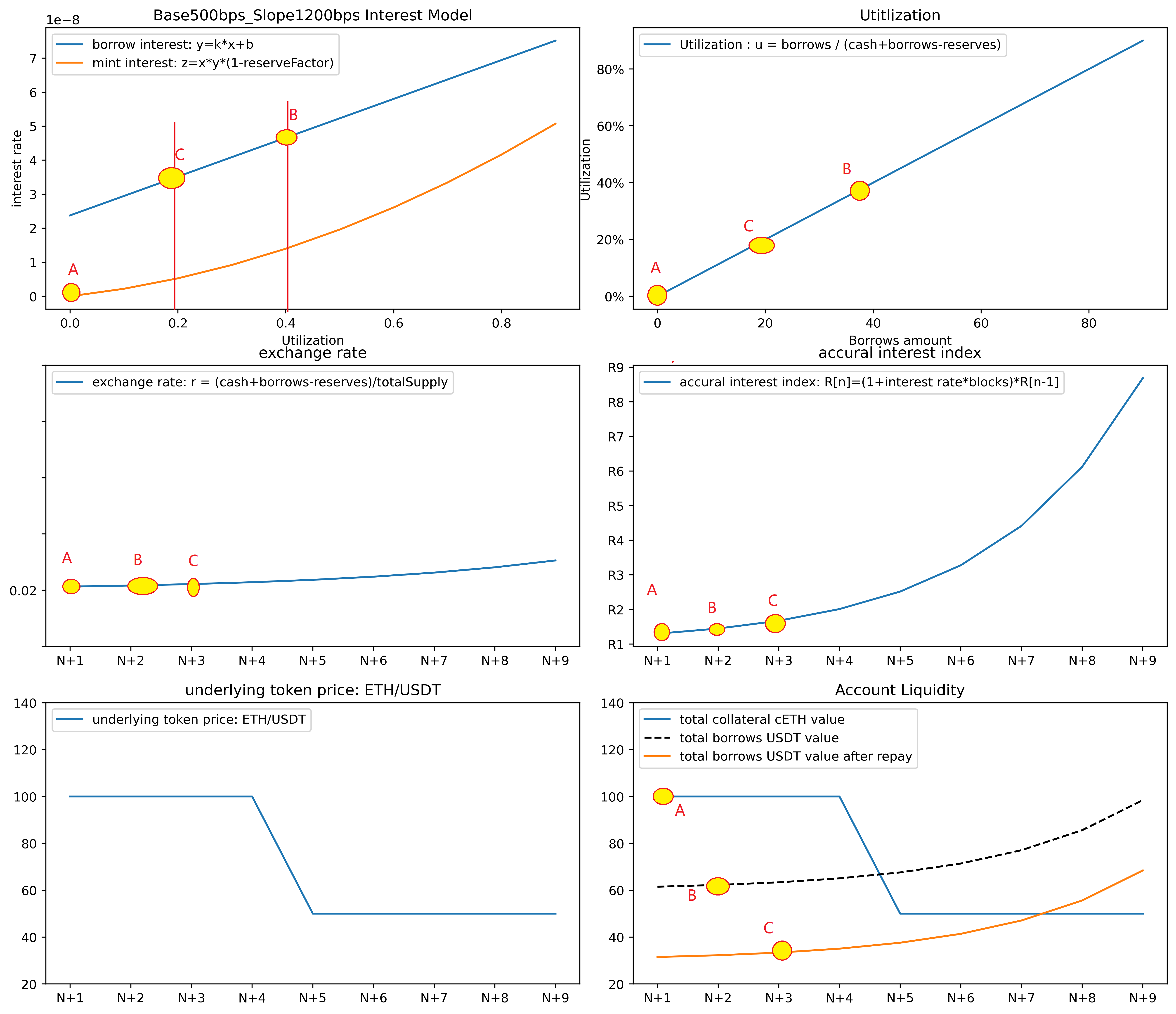
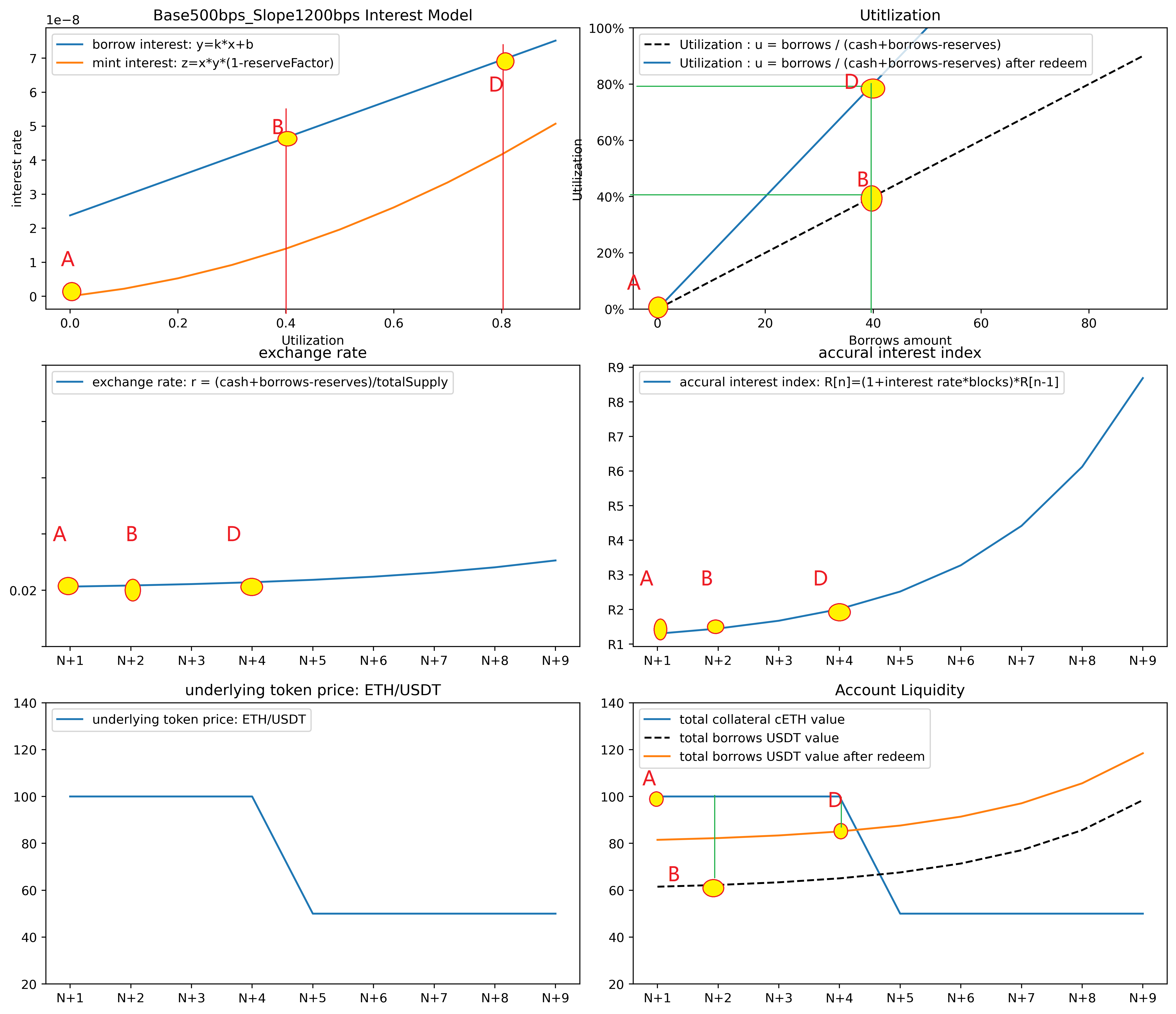
测试4:取 redeem
redeem是mint的逆运算,但在实际逻辑中,增加了一个检查账户虚拟流动性的一项。用户可以调用redeem来偿还给定数量的cToken,或者调用redeemUnderlying来偿还某数量的cToken得到给定数量的underlying Token. redeem操作的步骤是用户批准cUni合约使用用户的cUni代币,然后调用accuralInterest函数,来计算最新的利率指数Index,并对totalBorrows计息。再然后是调用comptroller.redeemAllowed函数,计算用户的虚拟流动性,看是否用户有足够的流动性来取走token。最后是redeemFresh函数根据要取走的数值,更新accountBorrow中的数值和totalBorrows。
redeemAllowed
在redeemAllowed,Comptroller除开验证cToken的合法性外,以及用户是否enterMarket,还会计算虚拟的账户流动性。与borrowAllowed的唯一区别是在计算underlying Token的价值时,borrowAllowed是
而redeemAllowed是
反映在图像6中,表现就是图六中的underlying token价值曲线上移,使得账户的流动性降低。当发生redeem之后,market的totalSupply降低,反映在资金利用率上就是资金利用率曲线上翘,相同的借贷金额会占据更大的资金利用率,从而导致借贷利率变化。
测试5:清算 liquidity
发生清算的一种典型情况是,用户enterMarkets了两个market,分别是cUni和cUSDT资金池。然后用户在cUni池中,存入Uni获得一定的cUni。用户凭借cUni在cUSDT资金池中借贷出USDT。然而,由于Uni的价格波动,导致Uni/USDT的价格突然下跌,此时用户放置在cUni池中的cUni的总价值小于了借出的USDT的价值,从而触发外部清算者进行清算。
//alice 有所有的Uni代币
uni.balanceOf(alice) = uint(-1)
//alice 调用unitroller的enterMarkets方法, 因为在mintAllowed函数中,存在一个检查:require(markets[cToken].isListed), 故即使在mint中也需要先调用enterMarkets
address[] memory addr = new address[](2);
addr[0] = cUni;
addr[1] = cUSDT;
ComptrollerG1(address(unitroller)).enterMarkets(addr);
//此时alice调用enterMarkets后,全局变量accountAssets[alice] = cToken[cUni], markets[cUni]={true, 60%,{alice:true},false}
//alice 调用cUni的mint方法
uni.approve(address(cUni),uint(-1));
cUni.mint(7584007913129639935);
cUSDT.borrow(1000000000);
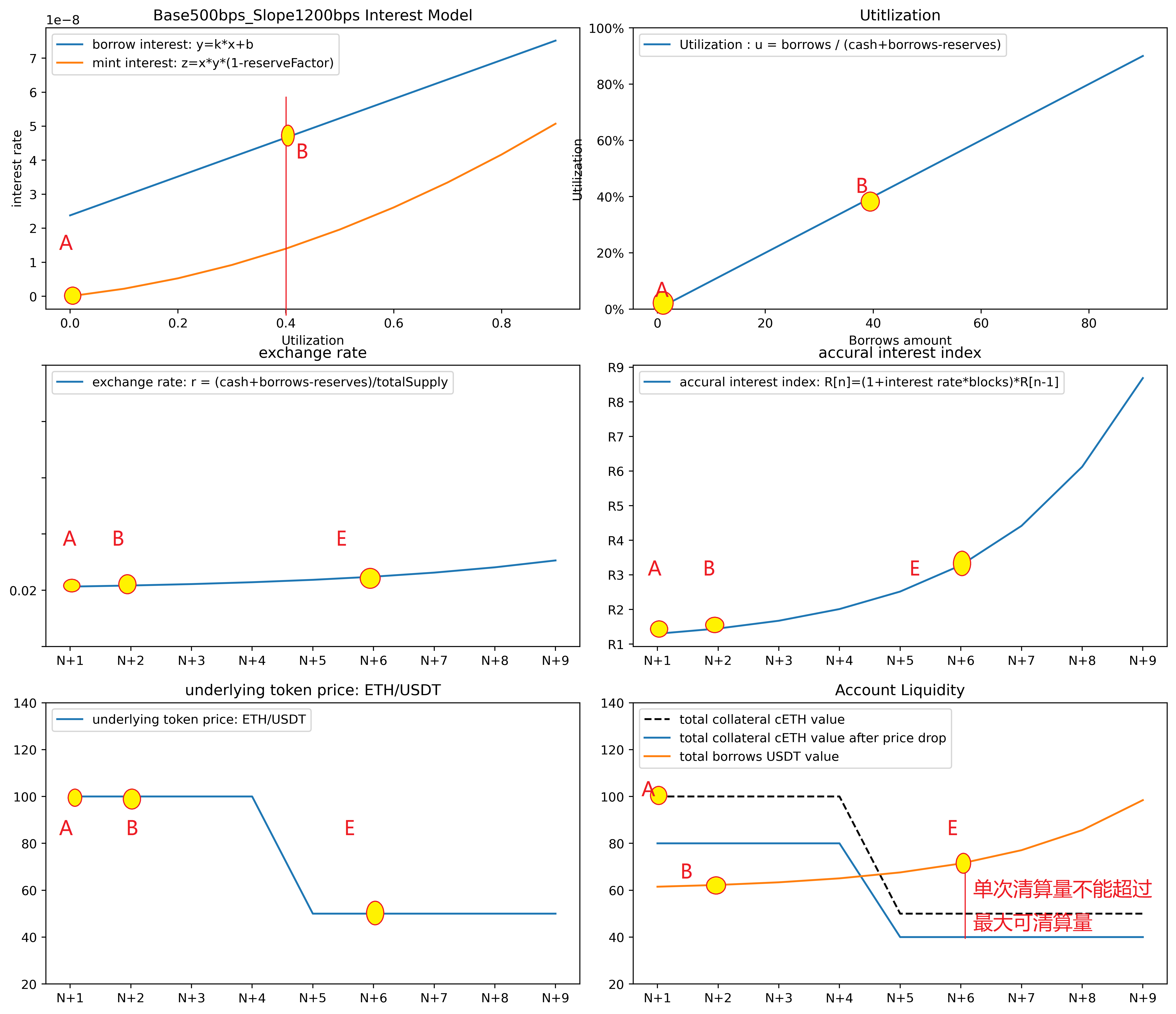
清算过程整体分为两部分:第一部分是repayBorrower部分,代为偿还underlying token,另一部分是seize部分,即将被清算者的cToken及奖励金一起奖励给清算者。由于清算涉及到两种cToken,故在清算的第一步是分别调用两种cToken的accural Interest函数,计算各自最新的利率指数Index,并计算含息债务总额。然后调用comptroller.liquidateBorrowAllowed函数,计算被清算账户的流动性,如果被清算账户的流动性为正,则不允许清算,如果被清算账户的流动性为负,并验算单笔交易的清算量不能超过被清算账户的最大可清算量,则允许清算。具体清算时,要求清算者不能是被清算者自己,然后计算转给被清算者的cToken数量, 如下公式所示:
在执行转账cToken到清算者之前,需调用comptroller.seizeAllowed函数,作用是验证调用seize函数的msg.sender和address(this)的comptroller保持一致。然后将清算者的账户余额加上seizeTokens,被清算者的余额减去seizeTokens。在完成seize部分后,函数跳转到repayBorrow部分,代为偿还underlying token。

Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK