

Difference Between insert(), insertOne(), and insertMany() in Pymongo
source link: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-insert-insertone-and-insertmany-in-pymongo/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

- Last Updated : 26 May, 2020
MongoDB is a NoSql Database that can be used to store data required by different applications. Python can be used to access MongoDB databases. Python requires a driver to access the databases. PyMongo enables interacting with MongoDB database from Python applications. The pymongo package acts as a native Python driver for MongoDB. Pymongo provides commands that can be used in Python applications to perform required action on the MongoDB. MongoDB offers three methods to insert records or documents into the database which are as follows:
-
insert() : Used to insert a document or documents into a collection. If the collection does not exist, then insert() will create the collection and then insert the specified documents.
Syntax
db.collection.insert(<document or array of documents>,
{
writeConcern: <document>,
ordered: <boolean>
}
)Parameter
- <document>: The document or record that is to be stored in the database
- writeConcern: Optional.
- ordered: Optional. Can be set to true or false.
Return Value: A WriteResult object or BulkWriteResult object for single or bulk inserts respectively.
Example:
filter_none
edit
closeplay_arrow
link
brightness_4
code# importing Mongoclient from pymongofrompymongoimportMongoClient# databasedb=myclient["GFG"]# Created or Switched to collection# names: Collegecollection=db["College"]mylist=[{"_id":1,"name":"Vishwash","Roll No":"1001","Branch":"CSE"},{"_id":2,"name":"Vishesh","Roll No":"1002","Branch":"IT"},{"_id":3,"name":"Shivam","Roll No":"1003","Branch":"ME"},{"_id":4,"name":"Yash","Roll No":"1004","Branch":"ECE"},]# Inseting the entire list in the collectioncollection.insert(mylist)Output:

-
insertOne() : Used to insert a single document or record into the database. If the collection does not exist, then insertOne() method creates the collection first and then inserts the specified document.
Syntax
db.collection.insertOne(<document>,
{
writeConcern: <document>
}
)Parameter
- <document> The document or record that is to be stored in the database
- writeConcern: Optional.
Return Value: It returns the _id of the document inserted into the database.
Note: The Pymongo command for insertOne() is insert_one()
Example:filter_none
edit
closeplay_arrow
link
brightness_4
code# importing Mongoclient from pymongofrompymongoimportMongoClient# Making Connection# databasedb=myclient["GFG"]# Created or Switched to collection# names: GeeksForGeekscollection=db["Student"]# Creating Dictionary of records to be# insertedrecord={"_id":5,"name":"Raju","Roll No":"1005","Branch":"CSE"}# Inserting the record1 in the collection# by using collection.insert_one()rec_id1=collection.insert_one(record)Output:
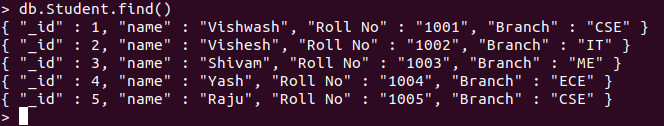
-
insertMany()
Syntax
db.collection.insertMany([ <document 1>, <document 2>, … ],
{
writeConcern: <document>,
ordered: <boolean>
}
)Parameter
- <documents> The document or record that is to be stored in the database
- writeConcern: Optional.
- ordered: Optional. Can be set to true or false.
Return Value: It returns the _ids of the documents inserted into the database.
Note: The Pymongo command for insertMany() is insert_many()
Example:filter_none
edit
closeplay_arrow
link
brightness_4
code# importing Mongoclient from pymongofrompymongoimportMongoClient# databasedb=myclient["GFG"]# Created or Switched to collection# names: GeeksForGeekscollection=db["College"]mylist=[{"_id":6,"name":"Deepanshu","Roll No":"1006","Branch":"CSE"},{"_id":7,"name":"Anshul","Roll No":"1007","Branch":"IT"}]# Inseting the entire list in the collectioncollection.insert_many(mylist)Output:

Attention geek! Strengthen your foundations with the Python Programming Foundation Course and learn the basics.
To begin with, your interview preparations Enhance your Data Structures concepts with the Python DS Course.
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK