

Design and implementation of the Sun network filesystem
source link: https://xuanwo.io/2020/18-nfs-v2/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Design and implementation of the Sun network filesystem
今天要介绍的论文是 Design and implementation of the Sun network filesystem。
- 发表于 USENIX Summer 1985
- 历史悠久的会议,多年之前是每年夏冬各一次,1995 年改名为
USENIX Technical Conference,次年更名为USENIX Annual Technical Conference(缩写USENIX ATC,也常进一步省略为USENIX)并一直延续至今。
- 历史悠久的会议,多年之前是每年夏冬各一次,1995 年改名为
NFS 尝试解决文件系统资源共享中遇到的这些问题:
- 架构/设备强绑定,现有的实现很难在不同的架构中迁移
- 挂了之后很难自动恢复
为此,它提出了如下的设计目标:
- 设备和操作系统独立
- 支持灾难恢复
- 支持 UNIX 语义
- 合理的性能
NFS Protocol
NFS 使用的协议有如下几个特点:
- 基于 Sun RPC 机制,使用了
Sun External Data Representation(缩写为 XDR,看起来是 80/90 年代的 protobuf 类似物)。 - 无状态:客户端维护自己请求的所有信息,服务器端不会维护过去的请求的任何信息,这主要是为了方便实现灾难恢复。
- 基于 UDP:因为 NFS 协议无状态,所以就算 UDP 包丢了也没关系,只要重发即可。原因没有详细展开,猜测可能是比较方便实现。
- 同步:同样因为 NFS 协议是无状态的,所以服务器端需要同步处理所有的请求,返回结果之前就要把数据都 commit 到磁盘。
NFS 协议的细节就不展开,主要分享两个我比较感兴趣的点:
首先是 NFS 绝大多数操作都基于 File Handle,查找/创建文件的操作会返回一个 fh,然后客户端每次请求的时候把这个 fh 作为参数之一以标记想操作的这个文件。比如:
lookup(dirfh, name) returns (fh, attr)
Returns a new fhandle and attributes for the named file in a directory.
create(dirfh, name, attr) returns (newfh, attr)
Creates a new file and returns its fhandle and attributes.
write(fh, offset, count, data) returns (attr)
Writes count bytes of data to a file beginning offset bytes from the beginning of the file.
Returns the attributes of the file after the write takes place.
其次是 NFS 的 readdir 操作引入了 cookie 概念:
readdir(dirfh, cookie, count) returns(entries)
Returns up to count bytes of directory entries from the directory dirfh.
Each entry contains a filename, file id, and an opaque pointer to the next directory entry called a cookie.
The cookie is usedin subsequent readdir calls to start reading at a specific entry in the directory.
A readdir call with the cookie of zero returns entries starting with the first entry in the directory.
在返回的每个 Entry 中都会带上叫 cookie 的值,cookie 用在后续的 readdir 调用中用于开始读取目录中的特定条目,这实际上就是后来对象存储 next_marker / continuation_token 的雏形。
为了实现真正的透明访问,而不是诸如 host:path 或 /../host/path 这样的区分本地/远端文件的形式,NFS 引入了一层新的抽象:VFS, the Virtual Filesystem。
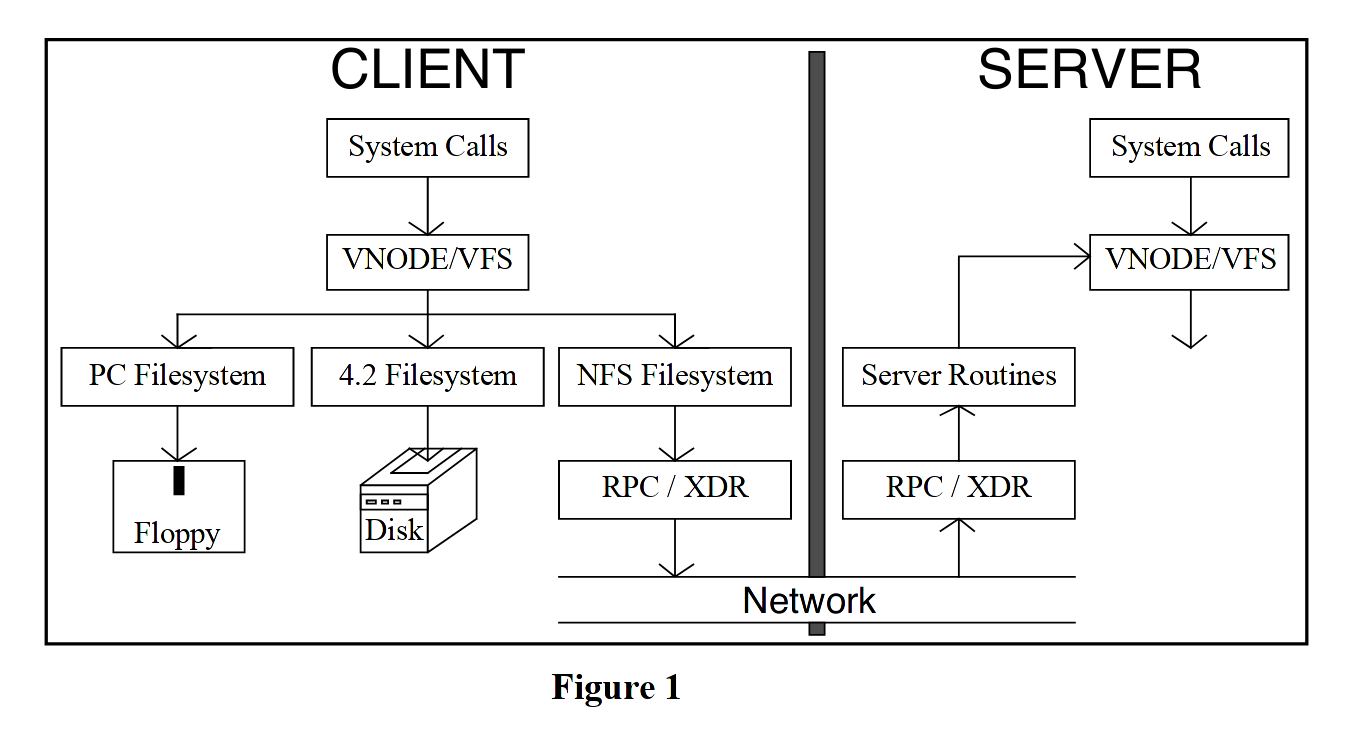
VFS 要求文件系统实现两组 API:
- VFS 实现文件系统相关的操作,比如
umount,rootstatfs等 - Vnode 实现文件相关的操作,比如
open,close,read,write等
通过这一层抽象,在内核层面抹平了本地与远端文件系统的差异。设计者花了大概三个月的时间在内核中加入了这一抽象,benchmark 的结果表明这一抽象没有带来太多的开销(在最坏情况下也只有 2% 的性能降低)。主要的工作是去除内核中对 inode 的直接调用和各种依赖于 inode 以及磁盘格式假设的代码。当然相关的工具要做的事情也不是少,比如加入 getdirentries syscall 来读取目录中的文件,并修改 readdir 来调用 getdirentries 而不是重写整个库。
NFS 的设计目标提出要跟本地的小磁盘性能差不多,为此设计者们花了很多时间来做优化,这些优化包括:
- 服务器端和客户端的
read-ahead/write-behindbuffer cache - 在客户端缓存文件属性和目录名
- 将 UDP 的最大包大小从 2048B 调整为 9000B
- 增加一种新的 XDR 类型,使得它可以在 kernel 中直接进行转换,避免 copy 的开销
在这些优化之后,论文表示一个无盘工作站可以比有本地磁盘的跑的更快。
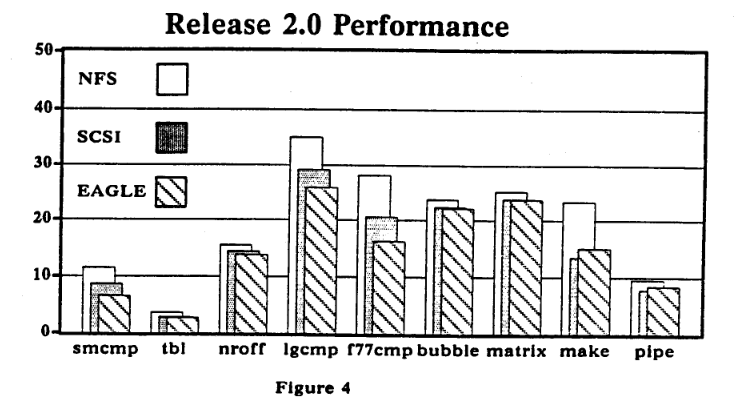
(这个图来自更早期的工作,Release 3.0 中应当实现了某些测试用例的反超,但是附图已经损坏,所以我们不得而知了)
NFS 如何处理并发的文件访问?
来自评论区 noirgif
首先要说明的是,NFS 本身并不支持文件锁,设计者引入了一个叫做 status monitor 的外部服务实现了基于 RPC 的文件锁机制。所以设计者在论文中指出 NFS 是不支持多客户端并发访问文件:NFS 不会去维护锁,而一次 write 又有可能有多次 RPC 请求,所以不同的客户端在并发写的时候可能会写坏掉。不过在客户端内可以自行维护锁,所以同一个客户端不同的进程/线程访问 NFS 是不会出现这样的问题的(合理推测)。
在我看来 NFSv2 对后世最大的共享就是提出并实现了 VFS,这一设计被后来出现的 Linux 内核采纳,并进一步发扬广大:The “Virtual File System” in Linux。另外值得一提的是,Sun 公司为了鼓励大家使用 NFS,它开源了整个 NFS 的协议和用户侧 RPC / XDR 的实现源码,并将 NFS / VFS port 到了不同的操作系统上(这里面有 MS/DOS,为了能够 port NFS 还顺手实现了 UDP/IP 的协议栈)。
Sun 被 Oracle 收购真的是一生之恨,永远怀念 Sun Microsystems: Java, Solaris, ZFS, NFS, SPARC, …
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK