LeetCode: 590. N-ary Tree Postorder Traversal
source link: https://mozillazg.com/2020/12/leetcode-987-vertical-order-traversal-of-a-binary-tree.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
题目¶
原题地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/vertical-order-traversal-of-a-binary-tree/
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
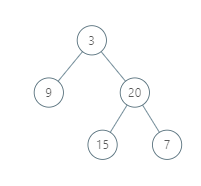
Example 1:
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]] Explanation: Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0): Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1); The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2); The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1); The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2:
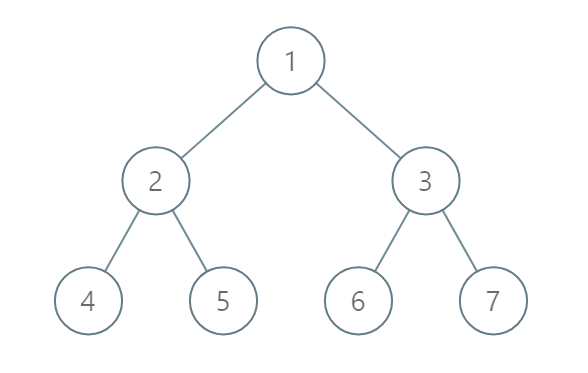
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]] Explanation: The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme. However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note:
- The tree will have between 1 and 1000 nodes.
- Each node's value will be between 0 and 1000.
解法¶
计算每个节点的 (x, y) 坐标,然后按 x 轴的值排序, 遍历排序后的结果,x 轴值相等的节点在同一条垂直线上可以归为一组。
这个方法的 Python 代码类似下面这样:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def verticalTraversal(self, root):
self._positions = []
self._collect_positions(root, 0, 0)
vals = []
last_x = -1001
for x, y, val in sorted(self._positions):
# x 轴值相同的归为一组
if x != last_x:
vals.append([])
last_x = x
vals[-1].append(val)
return vals
def _collect_positions(self, root, x, y):
if root is None:
return
self._positions.append((x, y, root.val))
# 之所以是 y + 1 而不是 y - 1 是为了实现排序后低层级的在前面
self._collect_positions(root.left, x - 1, y + 1)
self._collect_positions(root.right, x + 1, y + 1)
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK