Flink JobManager 详解
本篇文章是 Flink 系列 的第六篇,紧接着上篇文章,本篇主要讲述 Flink Master 中另一个组件 —— JobManager(在源码中对应的实现类是 JobMaster)。每个作业在启动后,Dispatcher 都会为这个作业创建一个 JobManager 对象,用来做这个作业相关的协调工作,比如:调度这个作业的 task、触发 Checkpoint 以及作业的容错恢复等。另外,本篇文章也将会看下一个作业在生成 ExecutionGraph 之后是如何在集群中调度起来的。
从之前文章的介绍中,我们已经知道 JobManager 其实就是一个作业的 master 服务,主要负责自己作业相关的协调工作,包括:向 ResourceManager 申请 Slot 资源来调度相应的 task 任务、定时触发作业的 checkpoint 和手动 savepoint 的触发、以及作业的容错恢复,这些流程将会在后面的系列文章中介绍(这些流程涉及到的组件比较多,需要等待后面把 TaskManager 及 Flink 的调度模型讲述完再回头来看),本文会从 JobManager 是如何初始化的、JobManager 有哪些组件以及分别提供了哪些功能这两块来讲述。
JobManager 简介
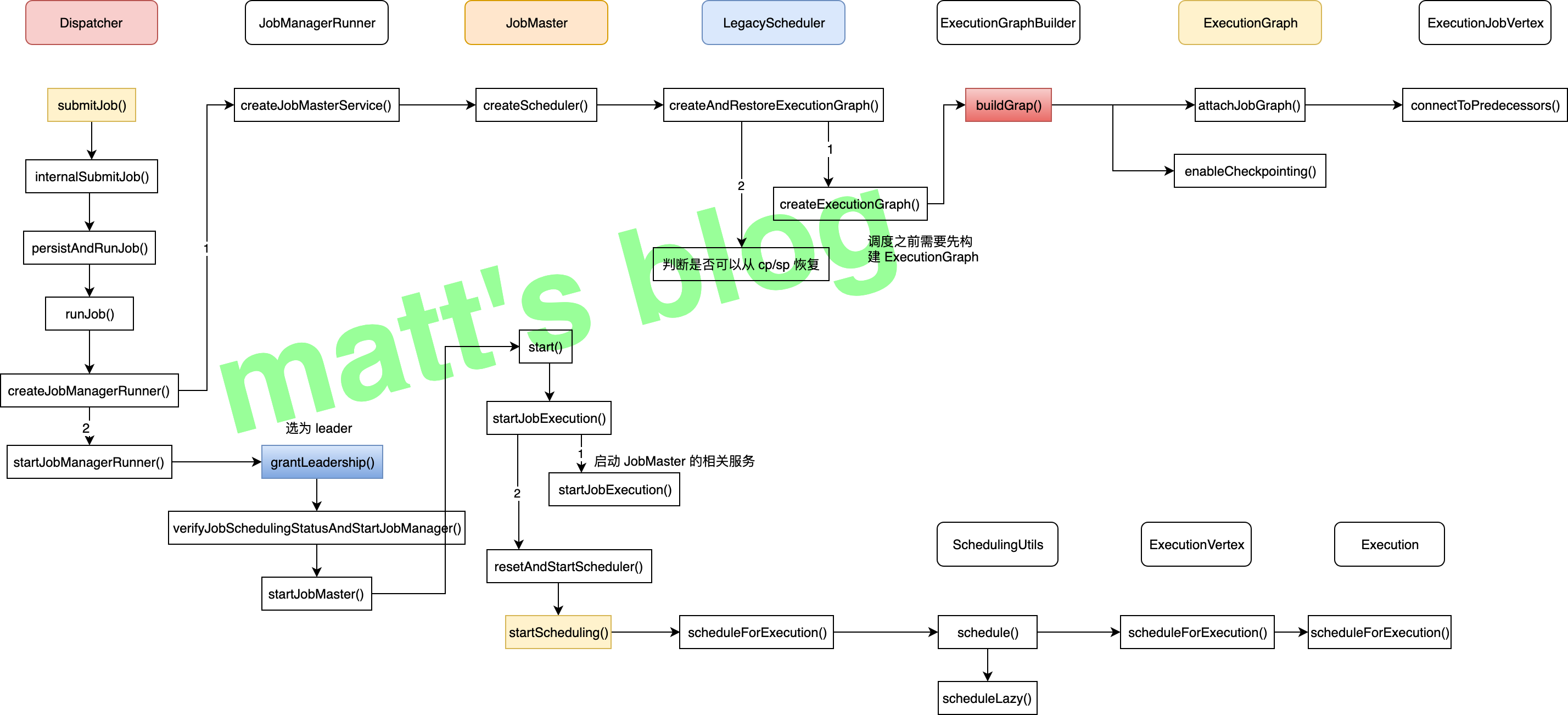
当用户向 Flink 集群提交一个作业后,Dispatcher 在收到 Client 端提交的 JobGraph 后,会为这个作业创建一个 JobManager 对象(对应的是 JobMaster 类),如下图所示:
一个新作业提交后的处理流程
JobManager 在初始化时,会创建 LegacyScheduler 对象,而 LegacyScheduler 在初始化时会将这个作业的 JobGraph 转化为 ExecutionGraph。在JobManager 启动后,就会开始给这个作业的 task 申请相应的资源、开始调度执行这个作业。
JobManager 详解
JobMaster 在实现中,也依赖了很多的服务,其中最重要的是 SchedulerNG 和 SlotPool,JobMaster 对外提供的接口实现中大都是使用前面这两个服务的方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| // JobMaster.java
public class JobMaster extends FencedRpcEndpoint<JobMasterId> implements JobMasterGateway, JobMasterService {
// LegacyScheduler: 用于调度作业的 ExecutionGraph
private SchedulerNG schedulerNG;
// SlotPoolImpl: 从名字也能看出它主要处理 slot 相关的内容,在 JM 这边的一个抽象
private final SlotPool slotPool;
// HA 服务,这里主要用于监控 RM leader,如果 RM Leader 有变化,这里会与新的 leader 建立连接
private final HighAvailabilityServices highAvailabilityServices;
/**
* 下面这些都是创建上面 SchedulerNG(即 LegacyScheduler)需要使用到的服务
*/
// 用于将数据上传到 BlobServer,这里上传的主要是 JobInformation 和 TaskInformation
private final BlobWriter blobWriter;
// 作业的 JobGraph 信息
private final JobGraph jobGraph;
// SchedulerImpl: 它也是一个调度器,将 slot 分配给对应的 task,它会调用 SlotPool 的相关接口(它里面有一个 slotSelectionStrategy 对象,用来决定一个 slot 分配的最佳算法)
private final Scheduler scheduler;
// 用于注册 Intermediate result partition,在作业调度的时候会用到
private final ShuffleMaster<?> shuffleMaster;
// 用于追踪 Intermediate result partition 的服务
private final PartitionTracker partitionTracker;
// --------- BackPressure --------
private final BackPressureStatsTracker backPressureStatsTracker;
}
|
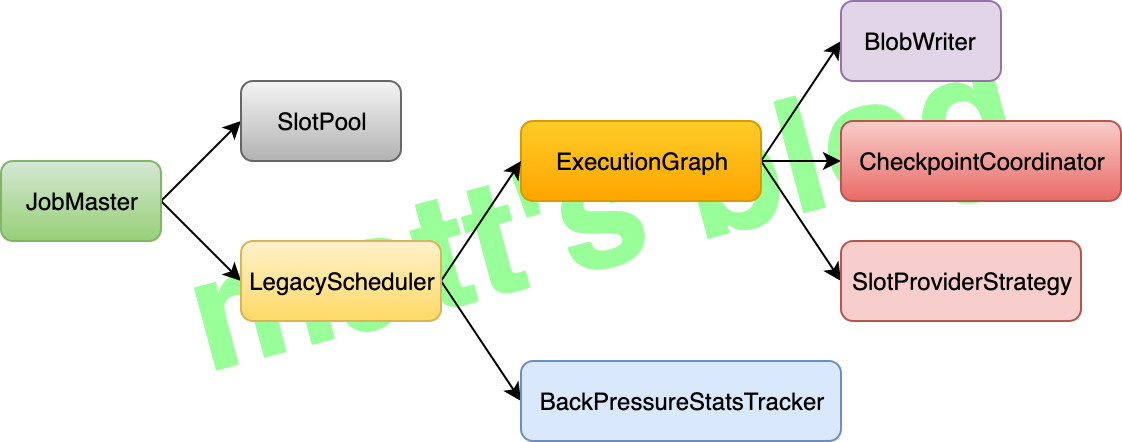
JobMaster 中涉及到重要组件如下图所示:
JobMaster 中的组件组成
JobMaster 主要有两个服务:
LegacyScheduler: ExecutionGraph 相关的调度都是在这里实现的,它类似更深层的抽象,封装了 ExecutionGraph 和 BackPressureStatsTracker,JobMaster 不直接去调用 ExecutionGraph 和 BackPressureStatsTracker 的相关方法,都是通过 LegacyScheduler 间接去调用;SlotPool: 它是 JobMaster 管理其 slot 的服务,它负责向 RM 申请/释放 slot 资源,并维护其相应的 slot 信息。
从前面的图中可以看出,如果 LegacyScheduler 想调用 CheckpointCoordinator 的方法,比如 LegacyScheduler 的 triggerSavepoint() 方法,它是需要先通过 executionGraph 的 getCheckpointCoordinator() 方法拿到 CheckpointCoordinator,然后再调用 CheckpointCoordinator 的 triggerSavepoint() 方法来触发这个作业的 savepoint。
JobMaster 的 API 概述
目前 JobMaster 对外提供的 API 列表如下(主要还是 JobMasterGateway 接口对应的实现):
cancel(): 取消当前正在执行的作业,如果作业还在调度,会执行停止,如果作业正在运行的话,它会向对应的 TM 发送取消 task 的请求(cancelTask() 请求);updateTaskExecutionState(): 更新某个 task 的状态信息,这个是 TM 主动向 JM 发送的更新请求;requestNextInputSplit(): Source ExecutionJobVertex 请求 next InputSlipt,这个一般是针对批处理读取而言,有兴趣的可以看下 FLIP-27: Refactor Source Interface,这里是社区计划对 Source 做的改进,未来会将批和流统一到一起;requestPartitionState(): 获取指定 Result Partition 对应生产者 JobVertex 的执行状态;scheduleOrUpdateConsumers(): TM 通知 JM 对应的 Result Partition 的数据已经可用,每个 ExecutionVertex 的每个 ResultPartition 都会调用一次这个方法(可能是在第一次生产数据时调用或者所有数据已经就绪时调用);disconnectTaskManager(): TM 心跳超时或者作业取消时,会调用这个方法,JM 会释放这个 TM 上的所有 slot 资源;acknowledgeCheckpoint(): 当一个 Task 做完 snapshot 后,通过这个接口通知 JM,JM 再做相应的处理,如果这个 checkpoint 所有的 task 都已经 ack 了,那就意味着这个 checkpoint 完成了;declineCheckpoint(): TM 向 JM 发送这个消息,告诉 JM 的 Checkpoint Coordinator 这个 checkpoint request 没有响应,比如:TM 触发 checkpoint 失败,然后 Checkpoint Coordinator 就会知道这个 checkpoint 处理失败了,再做相应的处理;requestKvStateLocation(): 请求某个注册过 registrationName 对应的 KvState 的位置信息;notifyKvStateRegistered(): 当注册一个 KvState 的时候,会调用这个方法,一些 operator 在初始化的时候会调用这个方法注册一个 KvState;notifyKvStateUnregistered(): 取消一个 KVState 的注册,这里是在 operator 关闭 state backend 时调用的(比如:operator 的生命周期结束了,就会调用这个方法);offerSlots(): TM 通知 JM 其上分配到的 slot 列表;failSlot(): 如果 TM 分配 slot 失败(情况可能很多,比如:slot 分配时状态转移失败等),将会通过这个接口告知 JM;registerTaskManager(): 向这个 JM 注册 TM,JM 会将 TM 注册到 SlotPool 中(只有注册过的 TM 的 Slot 才被认为是有效的,才可以做相应的分配),并且会通过心跳监控对应的 TM;disconnectResourceManager(): 与 ResourceManager 断开连接,这个是有三种情况会触发,JM 与 ResourceManager 心跳超时、作业取消、重连 RM 时会断开连接(比如:RM leader 切换、RM 的心跳超时);heartbeatFromTaskManager(): TM 向 JM 发送心跳信息;heartbeatFromResourceManager(): JM 向 ResourceManager 发送一个心跳信息,ResourceManager 只会监听 JM 是否超时;requestJobDetails(): 请求这个作业的 JobDetails(作业的概况信息,比如:作业执行了多长时间、作业状态等);requestJobStatus(): 请求这个作业的执行状态 JobStatus;requestJob(): 请求这个作业的 ArchivedExecutionGraph(它是 ExecutionGraph 序列化之后的结果);triggerSavepoint(): 对这个作业触发一次 savepoint;stopWithSavepoint(): 停止作业前触发一次 savepoint(触发情况是:用户手动停止作业时指定一个 savepoint 路径,这样的话,会在停止前做一次 savepoint);requestOperatorBackPressureStats(): 汇报某个 operator 反压的情况;notifyAllocationFailure(): 如果 RM 分配 slot 失败的话,将会通过这个接口通知 JM;
这里可以看到有部分接口的方法是在跟 RM 通信使用的,所以在 RM 的接口中也可以看到对应的方法。另外,JobMaster 上面这些方法在实现时基本都是在调用 LegacyScheduler 或 SlotPool 的具体实现方法来实现的。
SlotPool
SlotPool 是为当前作业的 slot 请求而服务的,它会向 ResourceManager 请求 slot 资源;SlotPool 会维护请求到的 slot 列表信息(即使 ResourceManager 挂掉了,SlotPool 也可以使用当前作业空闲的 slot 资源进行分配),而如果一个 slot 不再使用的话,即使作业在运行,也是可以释放掉的(所有的 slot 都是通过 AllocationID 来区分的)。
目前 SlotPool 提供的 API 列表如下:
connectToResourceManager(): SlotPool 与 ResourceManager 建立连接,之后 SlotPool 就可以向 ResourceManager 请求 slot 资源了;disconnectResourceManage(): SlotPool 与 ResourceManager 断开连接,这个方法被调用后,SlotPool 就不能从 ResourceManager 请求 slot 资源了,并且所有正在排队等待的 Slot Request 都被取消;allocateAvailableSlot(): 将指定的 Slot Request 分配到指定的 slot 上,这里只是记录其对应关系(哪个 slot 对应哪个 slot 请求);releaseSlot(): 释放一个 slot; requestNewAllocatedSlot(): 从 RM 请求一个新的 slot 资源分配,申请到的 slot 之后也会添加到 SlotPool 中;requestNewAllocatedBatchSlot(): 上面的方法是 Stream 类型,这里是 batch 类型,但向 RM 申请的时候,这里并没有区别,只是为了做相应的标识;getAvailableSlotsInformation(): 获取当前可用的 slot 列表;failAllocation(): 分配失败,并释放相应的 slot,可能是因为请求超时由 JM 触发或者 TM 分配失败;registerTaskManager(): 注册 TM,这里会记录一下注册过来的 TM,只能向注册过来的 TM 分配 slot;releaseTaskManager(): 注销 TM,这个 TM 相关的 slot 都会被释放,task 将会被取消,SlotPool 会通知相应的 TM 释放其 slot;createAllocatedSlotReport(): 汇报指定 TM 上的 slot 分配情况;
通过上面 SlotPool 对外提供的 API 列表,可以看到其相关方法都是跟 Slot 相关的,整体可以分为下面几部分:
- 与 ResourceManager 建立/取消 连接;
- 注册/注销 TM,这里只是记录注册过 TM 列表,只有是注册过的 TM 才允许使用其上面的 slot 资源;
- 向 ResourceManager 请求 slot 资源;
- 分配/释放 slot,这里只是更新其状态信息,并不做实质的操作。
SlotPool 这里,更多只是维护一个状态信息,以及与 ResourceManager(请求 slot 资源)和 TM(释放对应的 slot)做一些交互工作,它对这些功能做了相应的封装,方便 JobMaster 来调用。
LegacyScheduler
如前面所述,LegacyScheduler 其实是对 ExecutionGraph 和 BackPressureStatsTracker 方法的一个抽象,它还负责为作业创建对应的 ExecutionGraph 以及对这个作业进行调度。关于 LegacyScheduler 提供的 API 这里就不再展开,有兴趣的可以直接看下源码,它提供的大部分 API 都是在 JobMaster 的 API 列表中,因为 JobMaster 的很多方法实现本身就是调用 LegacyScheduler 对应的方法。
作业调度的详细流程
有了前面的讲述,这里看下一个新提交的作业,JobMaster 是如何调度起来的。当 JobMaster 调用 LegacyScheduler 的 startScheduling() 方法后,就会开始对这个作业进行相应的调度,申请对应的 slot,并部署 task,其实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| // LegacyScheduler.java
//note: ExecutionGraph 开始调度
@Override
public void startScheduling() {
//note: 启动这个线程
mainThreadExecutor.assertRunningInMainThread();
try {
//note: 调度这个 graph
executionGraph.scheduleForExecution();
}
catch (Throwable t) {
executionGraph.failGlobal(t);
}
}
|
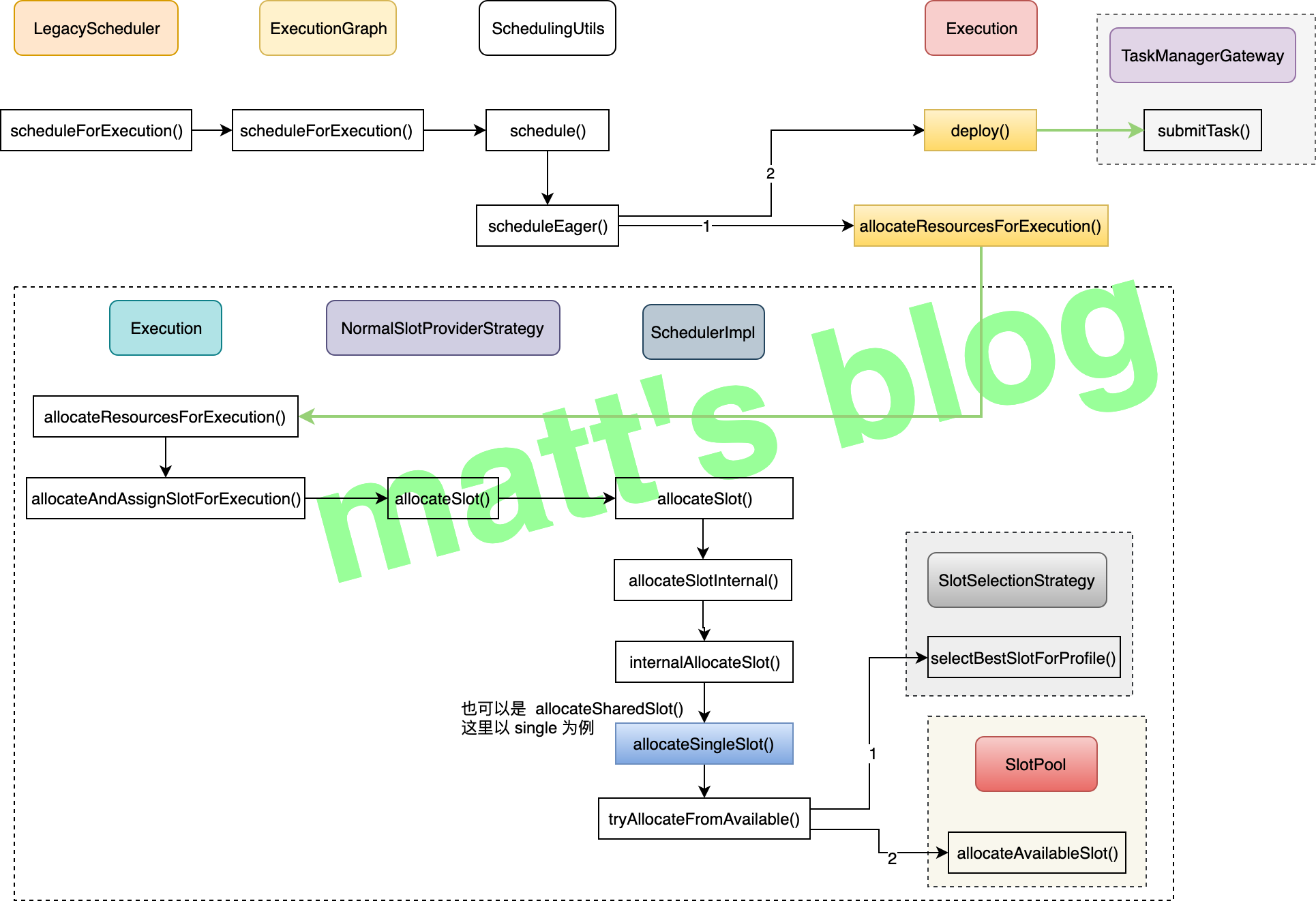
一个作业开始调度后详细流程如下图所示(其中比较核心方法已经标成黄颜色):
一个作业调度的详细流程
ExecutionGraph 通过 scheduleForExecution() 方法对这个作业调度执行,其方法实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| /note: 把 CREATED 状态转换为 RUNNING 状态,并做相应的调度,如果有异常这里会抛出
public void scheduleForExecution() throws JobException {
assertRunningInJobMasterMainThread();
final long currentGlobalModVersion = globalModVersion;
//note: 先将作业状态转移为 RUNNING
if (transitionState(JobStatus.CREATED, JobStatus.RUNNING)) {
//note: 这里会真正调度相应的 Execution Graph
final CompletableFuture<Void> newSchedulingFuture = SchedulingUtils.schedule(
scheduleMode,
getAllExecutionVertices(),
this);
if (state == JobStatus.RUNNING && currentGlobalModVersion == globalModVersion) {
schedulingFuture = newSchedulingFuture;
//note: 前面调度完成后,如果最后的结果有异常,这里会做相应的处理
newSchedulingFuture.whenComplete(
(Void ignored, Throwable throwable) -> {
if (throwable != null) {
final Throwable strippedThrowable = ExceptionUtils.stripCompletionException(throwable);
if (!(strippedThrowable instanceof CancellationException)) {
// only fail if the scheduling future was not canceled
failGlobal(strippedThrowable);
}
}
});
} else {
newSchedulingFuture.cancel(false);
}
}
else {
throw new IllegalStateException("Job may only be scheduled from state " + JobStatus.CREATED);
}
}
|
配合前面图中的流程,接下来,看下这个作业在 SchedulingUtils 中是如何调度的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
| // SchedulingUtils.java
public static CompletableFuture<Void> schedule(
ScheduleMode scheduleMode,
final Iterable<ExecutionVertex> vertices,
final ExecutionGraph executionGraph) {
switch (scheduleMode) {
// LAZY 的意思是:是有上游数据就绪后,下游的 task 才能调度,这个主要是批场景会用到,流不能走这个模式
case LAZY_FROM_SOURCES:
case LAZY_FROM_SOURCES_WITH_BATCH_SLOT_REQUEST:
return scheduleLazy(vertices, executionGraph);
// 流默认的是这个调度模式
case EAGER:
return scheduleEager(vertices, executionGraph);
default:
throw new IllegalStateException(String.format("Schedule mode %s is invalid.", scheduleMode));
}
}
/**
* Schedule vertices eagerly. That means all vertices will be scheduled at once.
* note: 所有的节点会被同时调度
*
* @param vertices Topologically sorted vertices to schedule.
* @param executionGraph The graph the given vertices belong to.
*/
public static CompletableFuture<Void> scheduleEager(
final Iterable<ExecutionVertex> vertices,
final ExecutionGraph executionGraph) {
executionGraph.assertRunningInJobMasterMainThread();
checkState(executionGraph.getState() == JobStatus.RUNNING, "job is not running currently");
// Important: reserve all the space we need up front.
// that way we do not have any operation that can fail between allocating the slots
// and adding them to the list. If we had a failure in between there, that would
// cause the slots to get lost
// collecting all the slots may resize and fail in that operation without slots getting lost
final ArrayList<CompletableFuture<Execution>> allAllocationFutures = new ArrayList<>();
final SlotProviderStrategy slotProviderStrategy = executionGraph.getSlotProviderStrategy();
final Set<AllocationID> allPreviousAllocationIds = Collections.unmodifiableSet(
computePriorAllocationIdsIfRequiredByScheduling(vertices, slotProviderStrategy.asSlotProvider()));
// allocate the slots (obtain all their futures)
for (ExecutionVertex ev : vertices) {
// these calls are not blocking, they only return futures
//note: 给每个 Execution 分配相应的资源
CompletableFuture<Execution> allocationFuture = ev.getCurrentExecutionAttempt().allocateResourcesForExecution(
slotProviderStrategy,
LocationPreferenceConstraint.ALL,
allPreviousAllocationIds);
allAllocationFutures.add(allocationFuture);
}
// this future is complete once all slot futures are complete.
// the future fails once one slot future fails.
final ConjunctFuture<Collection<Execution>> allAllocationsFuture = FutureUtils.combineAll(allAllocationFutures);
return allAllocationsFuture.thenAccept(
(Collection<Execution> executionsToDeploy) -> {
for (Execution execution : executionsToDeploy) {
try {
//note: 部署每个 Execution
execution.deploy();
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new CompletionException(
new FlinkException(
String.format("Could not deploy execution %s.", execution),
t));
}
}
})
// Generate a more specific failure message for the eager scheduling
.exceptionally(
//...
);
}
|
由于对于流作业来说,它默认的调度模式(ScheduleMode)是 ScheduleMode.EAGER,也就是说,所有 task 会同时调度起来,上面的代码里也可以看到调度的时候有两个主要方法:
allocateResourcesForExecution(): 它的作用是给这个 Execution 分配资源,获取要分配的 slot(它还会向 ShuffleMaster 注册 produced partition,这个 shuffle 部分内容后面文章再讲述,这里就不展开了);deploy(): 这个方法会直接向 TM 提交这个 task 任务;
这里,主要展开一下 allocateResourcesForExecution() 方法的实现,deploy() 的实现将会在后面 TaskManager 这篇文章中讲述。
如何给 ExecutionVertex 分配 slot
通过前面的代码,我们知道,allocateResourcesForExecution() 方法会给每一个 ExecutionVertex 分配一个 slot,而它具体是如何分配的,这个流程是在 Execution 的 allocateAndAssignSlotForExecution() 方法中实现的,代码如下如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
| /**
* Allocates and assigns a slot obtained from the slot provider to the execution.
* note: 从 slot provider 获取一个 slot,将任务分配到这个 slot 上
*
* @param slotProviderStrategy to obtain a new slot from
* @param locationPreferenceConstraint constraint for the location preferences
* @param allPreviousExecutionGraphAllocationIds set with all previous allocation ids in the job graph.
* Can be empty if the allocation ids are not required for scheduling.
* @return Future which is completed with the allocated slot once it has been assigned
* or with an exception if an error occurred.
*/
private CompletableFuture<LogicalSlot> allocateAndAssignSlotForExecution(
SlotProviderStrategy slotProviderStrategy,
LocationPreferenceConstraint locationPreferenceConstraint,
@Nonnull Set<AllocationID> allPreviousExecutionGraphAllocationIds) {
checkNotNull(slotProviderStrategy);
assertRunningInJobMasterMainThread();
//note: 获取这个 vertex 的相关信息
final SlotSharingGroup sharingGroup = vertex.getJobVertex().getSlotSharingGroup();
final CoLocationConstraint locationConstraint = vertex.getLocationConstraint();
// sanity check
//note: 做相应的检查
if (locationConstraint != null && sharingGroup == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Trying to schedule with co-location constraint but without slot sharing allowed.");
}
// this method only works if the execution is in the state 'CREATED'
//note: 这个只会在 CREATED 下工作
if (transitionState(CREATED, SCHEDULED)) {
final SlotSharingGroupId slotSharingGroupId = sharingGroup != null ? sharingGroup.getSlotSharingGroupId() : null;
//note: 创建一个 ScheduledUnit 对象(跟 sharingGroup/locationConstraint 都有关系)
ScheduledUnit toSchedule = locationConstraint == null ?
new ScheduledUnit(this, slotSharingGroupId) :
new ScheduledUnit(this, slotSharingGroupId, locationConstraint);
// try to extract previous allocation ids, if applicable, so that we can reschedule to the same slot
//note: 如果能找到之前调度的 AllocationID,会尽量先重新调度在同一个 slot 上
ExecutionVertex executionVertex = getVertex();
AllocationID lastAllocation = executionVertex.getLatestPriorAllocation();
Collection<AllocationID> previousAllocationIDs =
lastAllocation != null ? Collections.singletonList(lastAllocation) : Collections.emptyList();
// calculate the preferred locations
//note: 这里先根据 state 和上游数据的输入节点获取这个 Task Execution 的最佳 TM location
final CompletableFuture<Collection<TaskManagerLocation>> preferredLocationsFuture =
calculatePreferredLocations(locationPreferenceConstraint);
final SlotRequestId slotRequestId = new SlotRequestId();
//note: 根据指定的需求分配这个 slot
final CompletableFuture<LogicalSlot> logicalSlotFuture =
preferredLocationsFuture.thenCompose(
(Collection<TaskManagerLocation> preferredLocations) ->
slotProviderStrategy.allocateSlot(
slotRequestId,
toSchedule,
new SlotProfile(
vertex.getResourceProfile(),
preferredLocations,
previousAllocationIDs,
allPreviousExecutionGraphAllocationIds)));
// register call back to cancel slot request in case that the execution gets canceled
releaseFuture.whenComplete(
(Object ignored, Throwable throwable) -> {
if (logicalSlotFuture.cancel(false)) {
slotProviderStrategy.cancelSlotRequest(
slotRequestId,
slotSharingGroupId,
new FlinkException("Execution " + this + " was released."));
}
});
// This forces calls to the slot pool back into the main thread, for normal and exceptional completion
//note: 返回 LogicalSlot
return logicalSlotFuture.handle(
(LogicalSlot logicalSlot, Throwable failure) -> {
if (failure != null) {
throw new CompletionException(failure);
}
if (tryAssignResource(logicalSlot)) {
return logicalSlot;
} else {
// release the slot
logicalSlot.releaseSlot(new FlinkException("Could not assign logical slot to execution " + this + '.'));
throw new CompletionException(
new FlinkException(
"Could not assign slot " + logicalSlot + " to execution " + this + " because it has already been assigned "));
}
});
} else {
// call race, already deployed, or already done
throw new IllegalExecutionStateException(this, CREATED, state);
}
}
|
这里,简单总结一下上面这个方法的流程:
- 状态转换,将这个 Execution 的状态(
ExecutionState)从 CREATED 转为 SCHEDULED 状态;
- 根据是否是一个有状态的 operator 以及它上游输入节点位置,来计算一个最佳的 TM 位置列表(
TaskManagerLocation)列表;
- 如果这个 Execution 之前有调度记录,也就是说,这次由 failover 导致的重启,这里会拿到上次调度的 TM 位置信息;
- 根据 2、3 拿到 TM 位置信息,去调用 SlotProviderStrategy 的
allocateSlot() 获取要分配的 slot。
在 SchedulerImpl 去分配 slot 的时候,其实是会分两种情况的:
allocateSingleSlot(): 如果对应的 task 节点没有设置 SlotSharingGroup,会直接走这个方法,就不会考虑 share group 的情况,直接给这个 task 分配对应的 slot;allocateSharedSlot(): 如果对应的 task 节点有设置 SlotSharingGroup,就会走到这个方法,在分配 slot 的时候,考虑的因素就会多一些。
分配时如何选择最优的 TM 列表
这里,我们先来看下如何给这个 slot 选择一个最佳的 TM 列表,具体的方法实现是在 Execution 中的 calculatePreferredLocations() 方法中实现的,其具体的实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| // Execution.java
/**
* Calculates the preferred locations based on the location preference constraint.
* note: 根据 LocationPreferenceConstraint 策略计算前置输入节点的 TaskManagerLocation
*
* @param locationPreferenceConstraint constraint for the location preference
* @return Future containing the collection of preferred locations. This might not be completed if not all inputs
* have been a resource assigned.
*/
@VisibleForTesting
public CompletableFuture<Collection<TaskManagerLocation>> calculatePreferredLocations(LocationPreferenceConstraint locationPreferenceConstraint) {
//note: 获取一个最佳分配的 TM location 集合
final Collection<CompletableFuture<TaskManagerLocation>> preferredLocationFutures = getVertex().getPreferredLocations();
final CompletableFuture<Collection<TaskManagerLocation>> preferredLocationsFuture;
switch(locationPreferenceConstraint) {
case ALL:
//note: 默认是 ALL,就是前面拿到的列表,这里都可以使用
preferredLocationsFuture = FutureUtils.combineAll(preferredLocationFutures);
break;
case ANY:
//note: 遍历所有 input,先获取已经完成 assign 的 input 列表
final ArrayList<TaskManagerLocation> completedTaskManagerLocations = new ArrayList<>(preferredLocationFutures.size());
for (CompletableFuture<TaskManagerLocation> preferredLocationFuture : preferredLocationFutures) {
if (preferredLocationFuture.isDone() && !preferredLocationFuture.isCompletedExceptionally()) {
//note: 在这个 future 完成(没有异常的情况下),这里会使用这个 taskManagerLocation 对象
final TaskManagerLocation taskManagerLocation = preferredLocationFuture.getNow(null);
if (taskManagerLocation == null) {
throw new FlinkRuntimeException("TaskManagerLocationFuture was completed with null. This indicates a programming bug.");
}
completedTaskManagerLocations.add(taskManagerLocation);
}
}
preferredLocationsFuture = CompletableFuture.completedFuture(completedTaskManagerLocations);
break;
default:
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown LocationPreferenceConstraint " + locationPreferenceConstraint + '.');
}
return preferredLocationsFuture;
}
|
从上面的实现可以看出,这里是先通过 ExecutionVertex 的 getPreferredLocations() 方法获取一个 TaskManagerLocation 列表,然后再根据 LocationPreferenceConstraint 的模式做过滤,如果是 ALL,那么前面拿到的所有列表都会直接返回,而如果是 ANY,只会把那些已经分配好的 input 节点的 TaskManagerLocation 返回。
这里,看下 ExecutionVertex 的 getPreferredLocations() 方法的实现逻辑:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| // ExecutionVertex.java
/**
* Gets the overall preferred execution location for this vertex's current execution.
* The preference is determined as follows:
*
* <ol>
* <li>If the task execution has state to load (from a checkpoint), then the location preference
* is the location of the previous execution (if there is a previous execution attempt).
* <li>If the task execution has no state or no previous location, then the location preference
* is based on the task's inputs.
* </ol>
* note: 如果这个 task Execution 是从 checkpoint 加载的状态,那么这个 location preference 就是之前执行的状态;
* note: 如果这个 task Execution 没有状态信息或之前的 location 记录,这个 location preference 依赖于 task 的输入;
*
* <p>These rules should result in the following behavior:
*
* note: 1. 无状态 task 总是基于与输入共享的方式调度;
* note: 2. 有状态 task 基于与输入共享的方式来初始化他们最开始的调度;
* note: 3. 有状态 task 的重复执行会尽量与他们的 state 共享执行;
* <ul>
* <li>Stateless tasks are always scheduled based on co-location with inputs.
* <li>Stateful tasks are on their initial attempt executed based on co-location with inputs.
* <li>Repeated executions of stateful tasks try to co-locate the execution with its state.
* </ul>
*/
public Collection<CompletableFuture<TaskManagerLocation>> getPreferredLocations() {
Collection<CompletableFuture<TaskManagerLocation>> basedOnState = getPreferredLocationsBasedOnState();
return basedOnState != null ? basedOnState : getPreferredLocationsBasedOnInputs();
}
/**
* Gets the preferred location to execute the current task execution attempt, based on the state that the execution attempt will resume.
* note: 根据这个 Execution 试图恢复的状态来获取当前 task execution 的首选位置
*/
public Collection<CompletableFuture<TaskManagerLocation>> getPreferredLocationsBasedOnState() {
TaskManagerLocation priorLocation;
if (currentExecution.getTaskRestore() != null && (priorLocation = getLatestPriorLocation()) != null) {
return Collections.singleton(CompletableFuture.completedFuture(priorLocation));
}
else {
return null;
}
}
|
这里简单介绍一下其处理逻辑:
- 如果这个作业是从 Checkpoint 恢复的话,这里会根据它之前的状态信息获取上次的位置信息,直接返回这个位置信息;
- 另一种情况是,根据这个 ExecutionVertex 的
inputEdges,获取其上游 ExecutionVertex 的位置信息列表,但是如果这个列表的数目超过阈值(默认是 8),就会直接返回 null(上游过于分散,再根据 input 位置信息去分配就没有太大意义了)。
可以看出,在选取最优的 TaskManagerLocation 列表时,主要是根据 state 和 input 的位置信息来判断,会优先选择 state,也就是上次 checkpoint 中记录的位置。
最优的 slot 分配算法
在上面选择了最优的 TaskManagerLocation 列表后,这里来看下如何给 task 选择具体的 slot,这个是在 SlotSelectionStrategy 中的 selectBestSlotForProfile() 方法中做的,目前 SlotSelectionStrategy 有两个实现类:PreviousAllocationSlotSelectionStrategy 和 LocationPreferenceSlotSelectionStrategy,这个是在 state.backend.local-recovery 参数中配置的,默认是 false,选择的是 PreviousAllocationSlotSelectionStrategy,如果配置为 true,那么就会选择 PreviousAllocationSlotSelectionStrategy,这部分的逻辑如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| // DefaultSchedulerFactory.java
@Nonnull
private static SlotSelectionStrategy selectSlotSelectionStrategy(@Nonnull Configuration configuration) {
// 根据 state.backend.local-recover 配置选择
if (configuration.getBoolean(CheckpointingOptions.LOCAL_RECOVERY)) {
return PreviousAllocationSlotSelectionStrategy.INSTANCE;
} else {
return LocationPreferenceSlotSelectionStrategy.INSTANCE;
}
}
|
这里分别看下这两个实现类的 selectBestSlotForProfile() 的实现逻辑:
PreviousAllocationSlotSelectionStrategy: 它会根据上次的分配记录,如果这个位置刚好在 SlotPool 的可用列表里,这里就会直接选这个 slot,否则会走到 LocationPreferenceSlotSelectionStrategy 的处理逻辑;LocationPreferenceSlotSelectionStrategy: 这个是对可用的 slot 列表做打分,选择分数最高的(分数相同的话,会选择第一个),如果 slot 在前面得到的最优 TaskManagerLocation 列表中,分数就会比较高。
allocateSharedSlot VS allocateSingleSlot
在分配 slot 时,这里分为两种情况:
allocateSingleSlot(): 如果没有设置 SlotSharingGroup 将会走到这个方法,直接给这个 SlotRequestId 分配一个 slot,具体选择哪个 slot 就是上面的逻辑;allocateSharedSlot(): 而如果设置了 SlotSharingGroup 就会走到这里,先根据 SlotSharingGroupId 获取或创建对应的 SlotSharingManager,然后创建(或者根据 SlotSharingGroup 获取)一个的 MultiTaskSlot(每个 SlotSharingGroup 会对应一个 MultiTaskSlot 对象),这里再将这个 task 分配到这个 MultiTaskSlot 上(这个只是简单介绍,后面在调度模型文章中,将会详细讲述)。
到这里,Flink JobManager 的大部分内容已经讲述完了,还有一些小点会在后面的系列文章中再给大家讲述。这里总结一下,JobManager 主要是为一个具体的作业而服务的,它负责这个作业每个 task 的调度、checkpoint/savepoint(后面 checkpoint 的文章中会详述其流程)的触发以及容错恢复,它有两个非常重点的服务组件 —— LegacyScheduler 和 SlotPool,其中:
LegacyScheduler: 它封装了作业的 ExecutionGraph 以及 BackPressureStatsTracker 中的接口,它会负责这个作业具体调度、savepoint 触发等工作;SlotPool: 它主要负责这个作业 slot 相关的内容,像与 ResourceManager 通信、分配或释放 slot 资源等工作。
文章的后半部分,又总结了一个作业是如何调度起来的,首先是分配 slot,最后是通过 deploy() 接口向 TM 提交这个 task,本文着重关注了 slot 的分配,task 的部署将会在下节的 TaskManager 详解中给大家介绍。