

那些有趣的代码(三)--勤俭持家的 ArrayList | 犀利豆的博客
source link: https://xilidou.com/2019/12/05/arraylist-serializable/?
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

上周在群里有小盆友问 transient 关键字是干什么的。这篇文章就以此为契机介绍一下 transient 的作用,以及在 ArrayList 里面的应用。
要了解 transient 我们先聊聊 Java 的序列化。
复习序列化
所谓序列化是指,把对象转化为字节流的一种机制。同理,反序列化指的就是把字节流转化为对象。
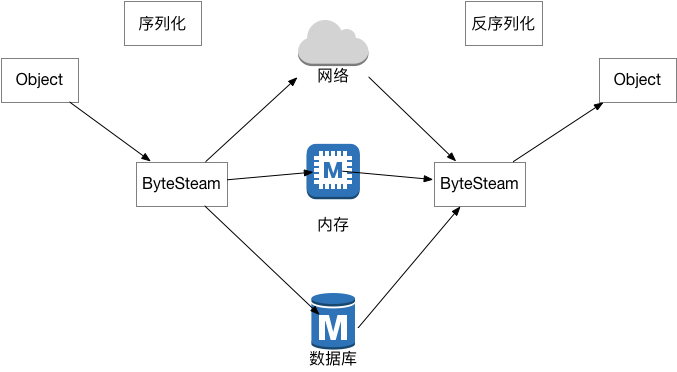
- 对于 Java 对象来说,如果使用 JDK 的序列化实现。对象需要实现
java.io.Serializable接口。 - 可以使用
ObjectOutputStream()和ObjectInputStream()对对象进行序列化和反序列化。 - 序列化的时候会调用
writeObject()方法,把对象转换为字节流。 - 反序列化的时候会调用
readObject()方法,把字节流转换为对象。 - Java 在反序列化的时候会校验字节流中的
serialVersionUID与对象的serialVersionUID时候一致。如果不一致就会抛出InvalidClassException异常。官方强烈推荐为序列化的对象指定一个固定的serialVersionUID。否则虚拟机会根据类的相关信息通过一个摘要算法生成,所以当我们改变类的参数的时候虚拟机生成的serialVersionUID是会变化的。 transient关键字修饰的变量 不会 被序列化为字节流
复习ArrayList
1、ArrayList 是基于数组实现的,是一个动态数组,容量支持自动自动增长
2、ArrayList 线程不安全
3、ArrayList 实现了 Serializable,支持序列化
上文我们说到 ArrayList 是基于数组实现,我们看看源码:
1 | /** |
有几个重要的信息:
- ArraryList 是动态数组,这个 elementData 就是存储对象的数据。
- 这个数组居然使用了 transient 来修饰。
- 数组的长度等于 ArrayList 的容量。而不是 ArrayList 的元素数量。
- size 是指的 ArrayList 中元素的数量,不是动态数组的长度。
- size 没有被 transient 修饰,是可以被序列化的。
这,怎么回事。ArrayList 存储数据的数组,居然不需要序列化?
莫慌,我们继续往下看代码。上文我们说过,对象的序列化和反序列化是通过调用方法 writeObject() 和 readObject() 完成了,我们发现,ArrayList 自己实现这两个方法看代码:
1 | /** |
注意,在 writeObject() 方法中,
1 | // Write out all elements in the proper order. |
按需序列化,用了几个下标序列化几个对象。
读取的时候也是:
1 | for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { |
有几个读几个。
总结一下:
- 被
transient修饰的变量不会被序列化。 - ArrayList 的底层数组
elementData被transient修饰,不会直接被序列化。 - 为了实现 ArrayList 元素的序列化,ArrayList 重写了
writeObject()和readObject()方法。 - 按需序列化数组,只序列化存在的数据,而不是序列化整个
elementData数组。
用多少,序列化多少,真是勤俭持家的 ArrayList。
有趣的代码系列
那些有趣的代码(一)–有点萌的 Tomcat 的线程池
那些有趣的代码(二)–偏不听父母话的 Tomcat 类加载器
欢迎关注我的微信公众号
Recommend
-
 145
145
ArrayList部分一共五篇文章了,并且引入了时间复杂度来分析,强烈建议大家一定要按顺序阅读,本文是第1篇。前些天的文章,反复的画图,不停的重复,就是想让大家理解,对象在内存中是什么样的。也是为今天的及以后的讲解打下基础。如果要说大家在写Java代码的时候...
-
 78
78
原文地址:https://www.xilidou.com/2018/02/01/java-cas/ CAS 是现代操作系统,解决并发问题的一个重要手段,最近在看 eureka 的源码的时候。遇到了很多 CAS 的操作。今天就系统的回顾一下 Java 中的CAS。 阅读这篇文章你将会了解到: 什么是 CAS CAS 实现原理是...
-
 28
28
-
 93
93
最近抓紧时间看看了看tomcat 和 jetty 的源代码。发现了一些有趣的代码,这里和大家分享一下。 Tomcat 作为一个老牌的 servlet 容器,处理多线程肯定得心应手,为了能保证多线程环境下的高效,必然使用了线程池。 但是...
-
 33
33
那些有趣的代码(一)--有点萌的 Tomcat 的线程池 2019-10-15
-
 32
32
看 Tomcat 的源码越看越有趣。Tomcat 的代码总有一种处处都有那么一点调皮的感觉。今天就聊一聊 Tomcat 的类加载机制。 了解过 JVM 的类加载一定知道,JVM 类加载的双亲委派机制。但是 Tomcat 却打破了 JVM 固有的双亲委派加载机...
-
 32
32
看 Tomcat 的源码越看越有趣。Tomcat 的代码总有一种处处都有那么一点调皮的感觉。今天就聊一聊 Tomcat 的类加载机制。 了解过 JVM 的类加载一定知道,JVM 类加载的双亲委派机制。但是 Tomcat 却打破了 JVM 固有的双亲...
-
 21
21
上周在群里有小盆友问 transient 关键字是干什么的。这篇文章就以此为契机介绍一下 transient 的作用,以及在 ArrayList 里面的应用。 要了解 transient 我们先聊聊 Java 的序列化。 复习...
-
 18
18
是的,最近我又换工作了,在看新团队的代码的时候发现,同事们为了追求服务的响应时间,在项目中大量的使用了很多高级的数据结构。 作为传统 Curd 程序员,对算法和数据结构已经比较生疏了。如今看到这些”高级的代码“...
-
 3
3
预算不足,小红书营销做爆品从0到1【勤俭持家版】...
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK